mirror of https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff
Update Integrations page to cover `ruff server`
This commit is contained in:
parent
55f4812051
commit
800ff0a693
|
|
@ -1,11 +1,288 @@
|
|||
# Integrations
|
||||
# Editor Integrations
|
||||
|
||||
## Ruff Language Server (`ruff server`)
|
||||
|
||||
The Ruff language server, also known as `ruff server`, is what powers the diagnostic and formatting capabilities of Ruff's VS Code extension and other editors. It is a single, common backend for editor integrations built directly into Ruff, and a direct replacement for `ruff-lsp`, our previous language server. You can read more about `ruff server` in the [`v0.4.5` blog post](https://astral.sh/blog/ruff-v0.4.5).
|
||||
|
||||
`ruff server` uses the LSP (Language Server Protocol), and as such works with any editor that supports this protocol. VS Code, Neovim, Helix, and Kate all have official, documented support for `ruff server`. Other editors may support the older `ruff-lsp` server - see the [Setup](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp#setup) guide in `ruff-lsp` for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
## VS Code (Official)
|
||||
|
||||
Download the [Ruff VS Code extension](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=charliermarsh.ruff),
|
||||
which supports fix actions, import sorting, and more.
|
||||
Download the [Ruff VS Code extension](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=charliermarsh.ruff), which supports fix actions, import sorting, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
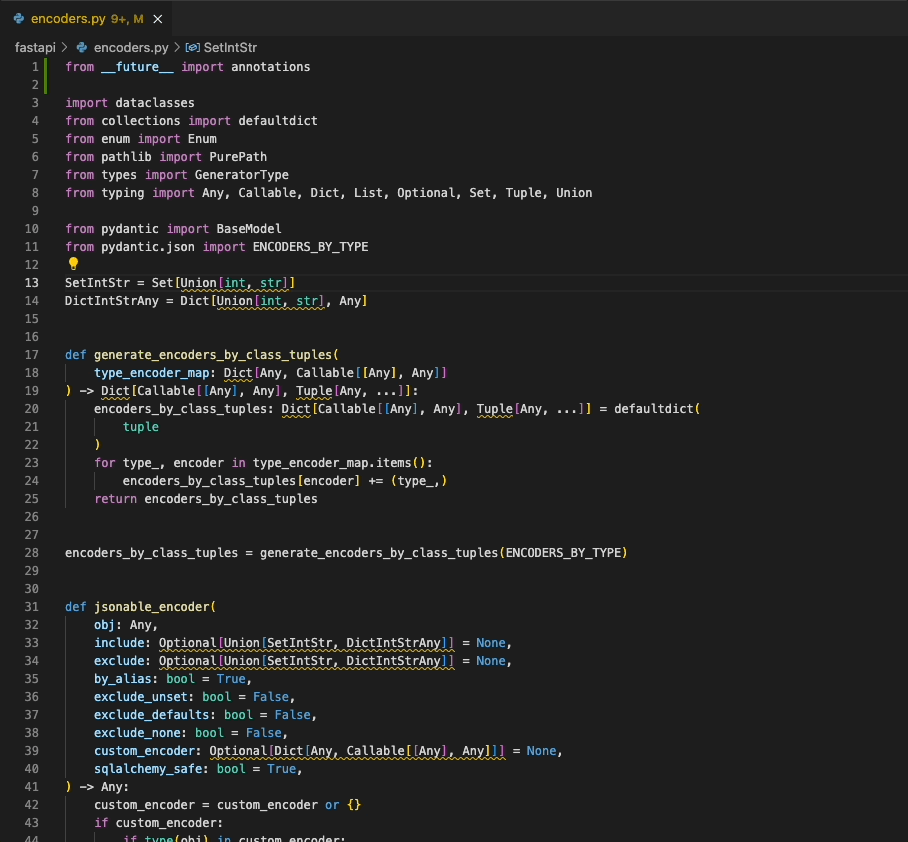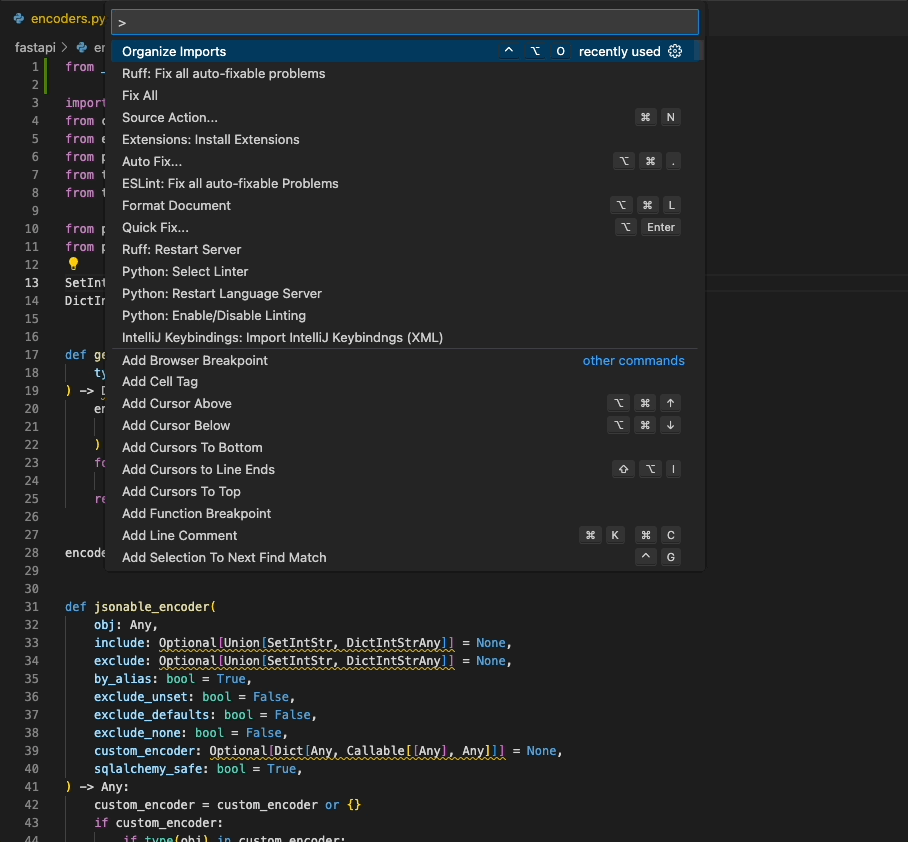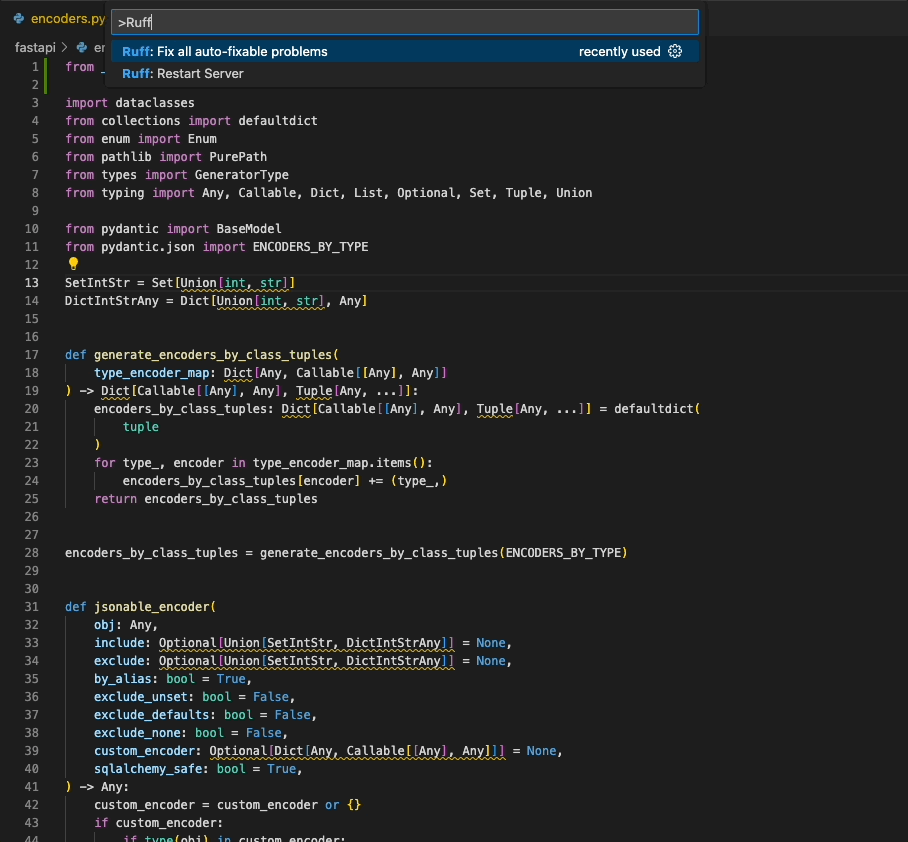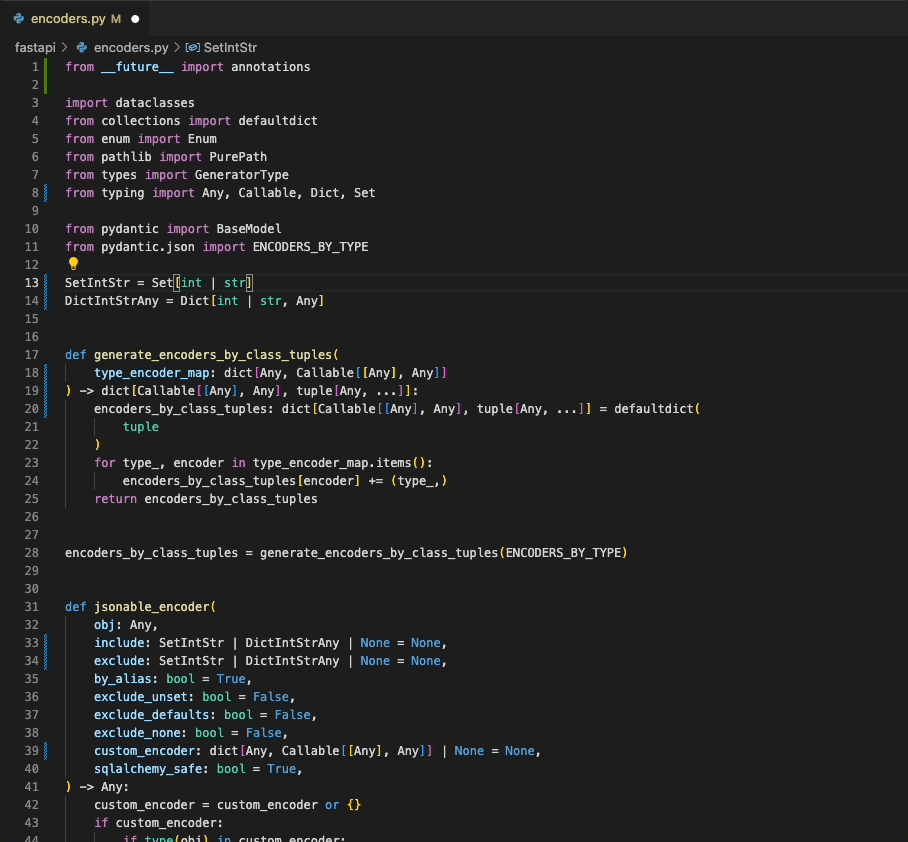
|
||||
By default, the extension will attempt to use the `ruff` executable installed on your local system, and will use a bundled executable if that's not available. If `ruff` is `v0.4.5` or later, the extension will automatically use `ruff server` - otherwise, it will use `ruff-lsp`. To configure this behavior, refer to the `languageServer` setting (add link here).
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about configuring the extension, and the settings available for the extension, refer to [Configuring Ruff](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/?tab=readme-ov-file#configuring-ruff) in the `ruff-vscode` documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Vim & Neovim (Official)
|
||||
|
||||
### Using `nvim-lspconfig`
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install [`nvim-lspconfig`](https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig).
|
||||
1. Setup `nvim-lspconfig` with the [suggested configuration](https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/tree/master#suggested-configuration).
|
||||
1. Finally, add this to your `init.lua`:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup {}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See [`nvim-lspconfig`'s server configuration guide](https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/blob/master/doc/server_configurations.md#ruff) for more details
|
||||
on how to configure the server from there.
|
||||
|
||||
> \[!IMPORTANT\]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If you have the older language server (`ruff-lsp`) configured in Neovim, make sure to disable it to prevent any conflicts.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tips
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using Ruff alongside another LSP (like Pyright), you may want to defer to that LSP for certain capabilities,
|
||||
like `textDocument/hover`:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
local on_attach = function(client, bufnr)
|
||||
if client.name == 'ruff' then
|
||||
-- Disable hover in favor of Pyright
|
||||
client.server_capabilities.hoverProvider = false
|
||||
end
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup {
|
||||
on_attach = on_attach,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you'd like to use Ruff exclusively for linting, formatting, and import organization, you can disable those
|
||||
capabilities for Pyright:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
require('lspconfig').pyright.setup {
|
||||
settings = {
|
||||
pyright = {
|
||||
-- Using Ruff's import organizer
|
||||
disableOrganizeImports = true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
python = {
|
||||
analysis = {
|
||||
-- Ignore all files for analysis to exclusively use Ruff for linting
|
||||
ignore = { '*' },
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Ruff will not show any logs. To enable logging in Neovim, you'll need to set the `RUFF_TRACE` environment variable
|
||||
to either `messages` or `verbose`:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup {
|
||||
cmd_env = { RUFF_TRACE = "messages" }
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can set the log level in `settings`:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup {
|
||||
cmd_env = { RUFF_TRACE = "messages" },
|
||||
init_options = {
|
||||
settings = {
|
||||
logLevel = "debug",
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It's also possible to divert Ruff's logs to a separate file with the `logFile` setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup {
|
||||
cmd_env = { RUFF_TRACE = "messages" },
|
||||
init_options = {
|
||||
settings = {
|
||||
logLevel = "debug",
|
||||
logFile = "~/.local/state/nvim/ruff.log"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `logFile` path supports tildes and environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
## Helix (Official)
|
||||
|
||||
First, open the language configuration file for Helix. On Linux and macOS, this will be at `~/.config/helix/languages.toml`,
|
||||
and on Windows this will be at `%AppData%\helix\languages.toml`.
|
||||
|
||||
Add the language server by adding:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[language-server.ruff]
|
||||
command = "ruff"
|
||||
args = ["server", "--preview"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, you'll register the language server as the one to use with Python.
|
||||
If you don't already have a language server registered to use with Python, add this to `languages.toml`:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[[language]]
|
||||
name = "python"
|
||||
language-servers = ["ruff"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Otherwise, if you already have `language-servers` defined, you can simply add `"ruff"` to the list. For example,
|
||||
if you already have `pylsp` as a language server, you can modify the language entry as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[[language]]
|
||||
name = "python"
|
||||
language-servers = ["ruff", "pylsp"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> \[!NOTE\]
|
||||
> Multiple language servers for a single language are only supported in Helix version [`23.10`](https://github.com/helix-editor/helix/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md#2310-2023-10-24) and later.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you've set up the server, you should see diagnostics in your Python files. Code actions and other LSP features should also be available.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*This screenshot is using `select=["ALL]"` for demonstration purposes.*
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to, as an example, turn on auto-formatting, add `auto-format = true`:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[[language]]
|
||||
name = "python"
|
||||
language-servers = ["ruff", "pylsp"]
|
||||
auto-format = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See the [Helix documentation](https://docs.helix-editor.com/languages.html) for more settings you can use here.
|
||||
|
||||
You can pass settings into `ruff server` using `[language-server.ruff.config.settings]`. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[language-server.ruff.config.settings]
|
||||
lineLength = 80
|
||||
[language-server.ruff.config.settings.lint]
|
||||
select = ["E4", "E7"]
|
||||
preview = false
|
||||
[language-server.ruff.config.settings.format]
|
||||
preview = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Ruff does not log anything to Helix. To enable logging, set the `RUFF_TRACE` environment variable
|
||||
to either `messages` or `verbose`.
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[language-server.ruff]
|
||||
command = "ruff"
|
||||
args = ["server", "--preview"]
|
||||
environment = { "RUFF_TRACE" = "messages" }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> \[!NOTE\]
|
||||
> `RUFF_TRACE=verbose` does not enable Helix's verbose mode by itself. You'll need to run Helix with `-v` for verbose logging.
|
||||
|
||||
To change the log level for Ruff (which is `info` by default), use the `logLevel` setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[language-server.ruff]
|
||||
command = "ruff"
|
||||
args = ["server", "--preview"]
|
||||
environment = { "RUFF_TRACE" = "messages" }
|
||||
|
||||
[language-server.ruff.config.settings]
|
||||
logLevel = "debug"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also divert Ruff's logs to a separate file with the `logFile` setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[language-server.ruff]
|
||||
command = "ruff"
|
||||
args = ["server", "--preview"]
|
||||
environment = { "RUFF_TRACE" = "messages" }
|
||||
|
||||
[language-server.ruff.config.settings]
|
||||
logLevel = "debug"
|
||||
logFile = "~/.cache/helix/ruff.log"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `logFile` path supports tildes and environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
## Kate (Official)
|
||||
|
||||
1. Activate the [LSP Client plugin](https://docs.kde.org/stable5/en/kate/kate/plugins.html#kate-application-plugins).
|
||||
1. Setup LSP Client [as desired](https://docs.kde.org/stable5/en/kate/kate/kate-application-plugin-lspclient.html).
|
||||
1. Finally, add this to `Settings` -> `Configure Kate` -> `LSP Client` -> `User Server Settings`:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"servers": {
|
||||
"python": {
|
||||
"command": ["ruff", "server", "--preview"],
|
||||
"url": "https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff",
|
||||
"highlightingModeRegex": "^Python$",
|
||||
"settings": {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See [LSP Client documentation](https://docs.kde.org/stable5/en/kate/kate/kate-application-plugin-lspclient.html) for more details
|
||||
on how to configure the server from there.
|
||||
|
||||
> \[!IMPORTANT\]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Kate's LSP Client plugin does not support multiple servers for the same language.
|
||||
|
||||
## PyCharm (External Tool)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff can be installed as an [External Tool](https://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/configuring-third-party-tools.html)
|
||||
in PyCharm. Open the Preferences pane, then navigate to "Tools", then "External Tools". From there,
|
||||
add a new tool with the following configuration:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ruff should then appear as a runnable action:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## PyCharm (Unofficial)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is also available as the [Ruff](https://plugins.jetbrains.com/plugin/20574-ruff) plugin on the
|
||||
IntelliJ Marketplace (maintained by @koxudaxi).
|
||||
|
||||
## Emacs (Unofficial)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is available as [`flymake-ruff`](https://melpa.org/#/flymake-ruff) on MELPA:
|
||||
|
||||
```elisp
|
||||
(require 'flymake-ruff)
|
||||
(add-hook 'python-mode-hook #'flymake-ruff-load)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is also available as [`emacs-ruff-format`](https://github.com/scop/emacs-ruff-format):
|
||||
|
||||
```elisp
|
||||
(require 'ruff-format)
|
||||
(add-hook 'python-mode-hook 'ruff-format-on-save-mode)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, it can be used via the [Apheleia](https://github.com/radian-software/apheleia) formatter library, by setting this configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```emacs-lisp
|
||||
(add-to-list 'apheleia-mode-alist '(python-mode . ruff))
|
||||
(add-to-list 'apheleia-mode-alist '(python-ts-mode . ruff))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TextMate (Unofficial)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is also available via the [`textmate2-ruff-linter`](https://github.com/vigo/textmate2-ruff-linter)
|
||||
bundle for TextMate.
|
||||
|
||||
# Other Integrations
|
||||
|
||||
## pre-commit
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -62,257 +339,6 @@ When running without `--fix`, Ruff's formatter hook can be placed before or afte
|
|||
`ruff format` should never introduce new lint errors, so it's safe to run Ruff's format hook _after_
|
||||
`ruff check --fix`.)
|
||||
|
||||
## Language Server Protocol (Official)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff supports the [Language Server Protocol](https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/)
|
||||
via the [`ruff-lsp`](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp) Python package, available on
|
||||
[PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/ruff-lsp/).
|
||||
|
||||
[`ruff-lsp`](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp) enables Ruff to be used with any editor that
|
||||
supports the Language Server Protocol, including [Neovim](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp#example-neovim),
|
||||
[Sublime Text](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp#example-sublime-text), Emacs, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to use `ruff-lsp` with Neovim, install `ruff-lsp` from PyPI along with
|
||||
[`nvim-lspconfig`](https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig). Then, set up the Neovim LSP client
|
||||
using the [suggested configuration](https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/tree/master#configuration)
|
||||
(`:h lspconfig-keybindings`). Finally, configure `ruff-lsp` in your `init.lua`:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
-- Configure `ruff-lsp`.
|
||||
-- See: https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/blob/master/doc/server_configurations.md#ruff_lsp
|
||||
-- For the default config, along with instructions on how to customize the settings
|
||||
require('lspconfig').ruff_lsp.setup {
|
||||
init_options = {
|
||||
settings = {
|
||||
-- Any extra CLI arguments for `ruff` go here.
|
||||
args = {},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Upon successful installation, you should see Ruff's diagnostics surfaced directly in your editor:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To use `ruff-lsp` with other editors, including Sublime Text and Helix, see the [`ruff-lsp` documentation](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp#installation-and-usage).
|
||||
|
||||
## Language Server Protocol (Unofficial)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is also available as the [`python-lsp-ruff`](https://github.com/python-lsp/python-lsp-ruff)
|
||||
plugin for [`python-lsp-server`](https://github.com/python-lsp/python-lsp-server), both of which are
|
||||
installable from PyPI:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install python-lsp-server python-lsp-ruff
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The LSP server can then be used with any editor that supports the Language Server Protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to use `python-lsp-ruff` with Neovim, add something like the following to your
|
||||
`init.lua`:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
require'lspconfig'.pylsp.setup {
|
||||
settings = {
|
||||
pylsp = {
|
||||
plugins = {
|
||||
ruff = {
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
},
|
||||
pycodestyle = {
|
||||
enabled = false
|
||||
},
|
||||
pyflakes = {
|
||||
enabled = false
|
||||
},
|
||||
mccabe = {
|
||||
enabled = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Vim & Neovim
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff can be integrated into any editor that supports the Language Server Protocol via [`ruff-lsp`](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp)
|
||||
(see: [Language Server Protocol](#language-server-protocol-official)), including Vim and Neovim.
|
||||
|
||||
It's recommended that you use [`ruff-lsp`](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp), the
|
||||
officially supported LSP server for Ruff. To use `ruff-lsp` with Neovim, install `ruff-lsp` from
|
||||
PyPI along with [`nvim-lspconfig`](https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig). Then, add something
|
||||
like the following to your `init.lua`:
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
-- See: https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/tree/54eb2a070a4f389b1be0f98070f81d23e2b1a715#suggested-configuration
|
||||
local opts = { noremap=true, silent=true }
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>e', vim.diagnostic.open_float, opts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '[d', vim.diagnostic.goto_prev, opts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', ']d', vim.diagnostic.goto_next, opts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>q', vim.diagnostic.setloclist, opts)
|
||||
|
||||
-- Use an on_attach function to only map the following keys
|
||||
-- after the language server attaches to the current buffer
|
||||
local on_attach = function(client, bufnr)
|
||||
-- Enable completion triggered by <c-x><c-o>
|
||||
vim.api.nvim_buf_set_option(bufnr, 'omnifunc', 'v:lua.vim.lsp.omnifunc')
|
||||
|
||||
-- Mappings.
|
||||
-- See `:help vim.lsp.*` for documentation on any of the below functions
|
||||
local bufopts = { noremap=true, silent=true, buffer=bufnr }
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', 'gD', vim.lsp.buf.declaration, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', 'gd', vim.lsp.buf.definition, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', 'K', vim.lsp.buf.hover, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', 'gi', vim.lsp.buf.implementation, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-k>', vim.lsp.buf.signature_help, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>wa', vim.lsp.buf.add_workspace_folder, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>wr', vim.lsp.buf.remove_workspace_folder, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>wl', function()
|
||||
print(vim.inspect(vim.lsp.buf.list_workspace_folders()))
|
||||
end, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>D', vim.lsp.buf.type_definition, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>rn', vim.lsp.buf.rename, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>ca', vim.lsp.buf.code_action, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', 'gr', vim.lsp.buf.references, bufopts)
|
||||
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>f', function() vim.lsp.buf.format { async = true } end, bufopts)
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
-- Configure `ruff-lsp`.
|
||||
-- See: https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/blob/master/doc/server_configurations.md#ruff_lsp
|
||||
-- For the default config, along with instructions on how to customize the settings
|
||||
require('lspconfig').ruff_lsp.setup {
|
||||
on_attach = on_attach,
|
||||
init_options = {
|
||||
settings = {
|
||||
-- Any extra CLI arguments for `ruff` go here.
|
||||
args = {},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is also available as part of the [coc-pyright](https://github.com/fannheyward/coc-pyright)
|
||||
extension for `coc.nvim`.
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>With the <a href="https://github.com/dense-analysis/ale">ALE</a> plugin for (Neo)Vim.</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```vim
|
||||
let g:ale_linters = { "python": ["ruff"] }
|
||||
let g:ale_fixers = {
|
||||
\ "python": ["black", "ruff"],
|
||||
\}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
Ruff can also be integrated via
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/blob/master/doc/server_configurations.md#efm">
|
||||
<code>efm</code>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
in just a
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/JafarAbdi/myconfigs/blob/6f0b6b2450e92ec8fc50422928cd22005b919110/efm-langserver/config.yaml#L14-L20">
|
||||
few lines.
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
tools:
|
||||
python-ruff: &python-ruff
|
||||
lint-command: "ruff check --config ~/myconfigs/linters/ruff.toml --quiet ${INPUT}"
|
||||
lint-stdin: true
|
||||
lint-formats:
|
||||
- "%f:%l:%c: %m"
|
||||
format-command: "ruff check --stdin-filename ${INPUT} --config ~/myconfigs/linters/ruff.toml --fix --exit-zero --quiet -"
|
||||
format-stdin: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
With the <a href="https://github.com/stevearc/conform.nvim"><code>conform.nvim</code></a> plugin for Neovim.
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
require("conform").setup({
|
||||
formatters_by_ft = {
|
||||
python = {
|
||||
-- To fix lint errors.
|
||||
"ruff_fix",
|
||||
-- To run the Ruff formatter.
|
||||
"ruff_format",
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
With the <a href="https://github.com/mfussenegger/nvim-lint"><code>nvim-lint</code></a> plugin for Neovim.
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```lua
|
||||
require("lint").linters_by_ft = {
|
||||
python = { "ruff" },
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
## PyCharm (External Tool)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff can be installed as an [External Tool](https://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/configuring-third-party-tools.html)
|
||||
in PyCharm. Open the Preferences pane, then navigate to "Tools", then "External Tools". From there,
|
||||
add a new tool with the following configuration:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ruff should then appear as a runnable action:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## PyCharm (Unofficial)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is also available as the [Ruff](https://plugins.jetbrains.com/plugin/20574-ruff) plugin on the
|
||||
IntelliJ Marketplace (maintained by @koxudaxi).
|
||||
|
||||
## Emacs (Unofficial)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is available as [`flymake-ruff`](https://melpa.org/#/flymake-ruff) on MELPA:
|
||||
|
||||
```elisp
|
||||
(require 'flymake-ruff)
|
||||
(add-hook 'python-mode-hook #'flymake-ruff-load)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is also available as [`emacs-ruff-format`](https://github.com/scop/emacs-ruff-format):
|
||||
|
||||
```elisp
|
||||
(require 'ruff-format)
|
||||
(add-hook 'python-mode-hook 'ruff-format-on-save-mode)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, it can be used via the [Apheleia](https://github.com/radian-software/apheleia) formatter library, by setting this configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```emacs-lisp
|
||||
(add-to-list 'apheleia-mode-alist '(python-mode . ruff))
|
||||
(add-to-list 'apheleia-mode-alist '(python-ts-mode . ruff))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TextMate (Unofficial)
|
||||
|
||||
Ruff is also available via the [`textmate2-ruff-linter`](https://github.com/vigo/textmate2-ruff-linter)
|
||||
bundle for TextMate.
|
||||
|
||||
## mdformat (Unofficial)
|
||||
|
||||
[mdformat](https://mdformat.readthedocs.io/en/stable/users/plugins.html#code-formatter-plugins) is
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue