## Summary
Running a resolution that required forking was failing due to breaking
an invariant in PubGrub. It looks like we were adding the same
incompatibility multiple times, or something like that. The issue
appears to be that when forking, we modify the current state, then clone
it as the "next state", then push to the "forked states" -- but that
means we're cloning the _modified_ state.
This PR changes the order of operations such that we clone, then modify.
It shouldn't introduce any additional clones though.
## Summary
This PR ensures that if a lockfile already contains a resolved reference
(e.g., you locked with `main` previously, and it locked to a specific
commit), and you run `uv lock`, we use the same SHA, even if it's not
the latest SHA for that tag. This avoids upgrading Git dependencies
without `--upgrade`.
Closes#3920.
## Summary
This PR removes the static resolver map:
```rust
static RESOLVED_GIT_REFS: Lazy<Mutex<FxHashMap<RepositoryReference, GitSha>>> =
Lazy::new(Mutex::default);
```
With a `GitResolver` struct that we now pass around on the
`BuildContext`. There should be no behavior changes here; it's purely an
internal refactor with an eye towards making it cleaner for us to
"pre-populate" the list of resolved SHAs.
With the change, we remove the special casing of workspace dependencies
and resolve `tool.uv` for all git and directory distributions. This
gives us support for non-editable workspace dependencies and path
dependencies in other workspaces. It removes a lot of special casing
around workspaces. These changes are the groundwork for supporting
`tool.uv` with dynamic metadata.
The basis for this change is moving `Requirement` from
`distribution-types` to `pypi-types` and the lowering logic from
`uv-requirements` to `uv-distribution`. This changes should be split out
in separate PRs.
I've included an example workspace `albatross-root-workspace2` where
`bird-feeder` depends on `a` from another workspace `ab`. There's a
bunch of failing tests and regressed error messages that still need
fixing. It does fix the audited package count for the workspace tests.
## Summary
This PR changes the lock-file format to use inline tables for wheels and
source distributions, which currently use separate tables that make the
file harder to follow.
```diff
[[distribution]]
name = "typing-extensions"
version = "4.10.0"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
- [distribution.sdist]
- url = "0d26ce356c7c323176620b7b483e44/typing_extensions-4.10.0.tar.gz"
- hash = "sha256:b0abd7c89e8fb96f98db18d86106ff1d90ab692004eb746cf6eda2682f91b3cb"
- size = 77558
-
- [[distribution.wheel]]
- url = "dc04a3ea60b9bc8074b5d6b7ab90bb/typing_extensions-4.10.0-py3-none-any.whl"
- hash = "sha256:69b1a937c3a517342112fb4c6df7e72fc39a38e7891a5730ed4985b5214b5475"
- size = 33926
+ sdist = { url = "0d26ce356c7c323176620b7b483e44/typing_extensions-4.10.0.tar.gz", hash = "sha256:b0abd7c89e8fb96f98db18d86106ff1d90ab692004eb746cf6eda2682f91b3cb", size = 77558 }
+ wheel = [{ url = "dc04a3ea60b9bc8074b5d6b7ab90bb/typing_extensions-4.10.0-py3-none-any.whl", hash = "sha256:69b1a937c3a517342112fb4c6df7e72fc39a38e7891a5730ed4985b5214b5475", size = 33926 }]
```
The downside is that the inline-tables end up quite long and TOML
doesn't support line breaks in inline tables, yet.
Part of https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3611.
We significantly regressed performance in some cases because we were
cloning the resolver state one more time than we needed to. That doesn't
sound like a lot, but in the case where there are no forks, it implies
we were cloning the state for every `get_dependencies` called when we
shouldn't have been cloning it at all.
Avoiding the clone results in somewhat tortured code. This can probably
be refactored by moving bits out to a helper routine, but that also
seemed non-trivial. So we let this suffice for now.
This addresses the lack of marker support in prior commits.
Specifically, we add them as a new field to `AnnotatedDist`, and from
there, they get added to a `Distribution` in a `Lock`.
This commit is a pretty invasive change that implements the merging
of resolutions created by each fork of the resolver.
The main idea here is that each `SolveState` is converted into a
`Resolution` (a new type) and stored on the heap after its fork
completes. When all forks complete, they are all merged into a single
`Resolution`. This `Resolution` is then used to build a `ResolutionGraph`.
Construction of `ResolutionGraph` mostly stays the same (despite the
gnarly diff due to an indent change) with one exception: the code to
extract dependency edges out of PubGrub's state has been moved to
`SolveState::into_resolution`. The idea here is that once a fork
completes, we extract what we need from the PubGrub state and then
throw it away. We store these edges in our own intermediate type which
is then converted into petgraph edges in the `ResolutionGraph`
constructor.
One interesting change we make here is that our edge
data is now a `Version` instead of a `Range<Version>`. I don't think
`Range<Version>` was actually being used anywhere, so this seems okay?
In any case, I think `Version` here is correct because a resolution
corresponds to specific dependencies of each package. Moreover, I didn't
see an easy way to make things work with `Range<Version>`. Notably,
since we no longer have the guarantee that there is only one version of
each package, we need to use `(PackageName, Version)` instead of just
`PackageName` for inverted lookups in `ResolutionGraph::from_state`.
Finally, the main resolver loop itself is changed a bit to track all
forked resolutions and then merge them at the end.
Note that we don't really have any dealings with markers in this commit.
We'll get to that in a subsequent commit.
This changes the constructor to just take an `InMemoryIndex`
directly instead of the constituent parts. No real reason other
than it seems a little simpler.
There are still some TODOs/FIXMEs here, but this makes represents a
chunk of the resolver refactoring to enable forking. We don't do any
merging of resolutions yet, so crucially, this code is broken when no
marker environment is provided. But when a marker environment is
provided, this should behave the same as a non-forking resolver. In
particular, `get_dependencies_forking` is just `get_dependencies`
whenever there's a marker environment.
## Summary
Ensures that we avoid upgrading packages unless `--upgrade` or similar
is passed.
For now, the resolver only respects these for registry distributions.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3918.
## Summary
This PR adds extras to the lockfile, and enables users to selectively
sync extras in `uv sync` and `uv run`. The end result here was fairly
simple, though it required a few refactors to get here. The basic idea
is that `DistributionId` now includes `extra: Option<ExtraName>`, so we
effectively treat extras as separate packages. Generating the lockfile,
and generating the resolution from the lockfile, fall out of this
naturally with no special-casing or additional changes.
The main downside here is that it bloats the lockfile significantly.
Specifically:
- We include _all_ distribution URLs and hashes for _every_ extra
variant.
- We include all dependencies for the extra variant, even though that
are dependencies of the base package.
We could normalize this representation by changing each distribution
have an `optional-dependencies` hash map that keys on extras, but we
actually don't have the information we need to create that right now
(specifically, we can't differentiate between dependencies that
_require_ the extra and dependencies on the base package).
Closes#3700.
## Summary
This PR just ensures that when running `uv lock` (or `uv run`), we lock
with all extras. When we later install, we'll also _install_ with all
extras, but that will be changed in a future PR.
## Summary
Today, we represent each package as a single node in the graph, and
combine all the extras. This is helpful for the `requirements.txt`-style
resolution, in which we want to show each a single line for each package
with the extras combined into a single array.
This PR modifies the representation to instead use a separate node for
each (package, extra) pair. We then reduce into the previous format when
printing in the `requirements.txt`-style format, so there shouldn't be
any user-facing changes here.
## Summary
There are a few behavior changes in here:
- We now enforce `--require-hashes` for editables, like pip. So if you
use `--require-hashes` with an editable requirement, we'll reject it. I
could change this if it seems off.
- We now treat source tree requirements, editable or not (e.g., both `-e
./black` and `./black`) as if `--refresh` is always enabled. This
doesn't mean that we _always_ rebuild them; but if you pass
`--reinstall`, then yes, we always rebuild them. I think this is an
improvement and is close to how editables work today.
Closes#3844.
Closes#2695.
## Summary
This PR makes a variety of invalid states unrepresentable by changing
`Preference` to require a `PackageName` and `Version`, rather than
accepting a generic `Requirement`. There should be no meaningful
behavior changes.
## Summary
We actually _already_ ignore these (preferences only apply to versions,
not URLs), it just happens later on. This PR thus just avoids crashing.
The behavior is unchanged.
Closes#3822.
## Summary
Related to https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3818. We should
_always_ include the package name if we know it's not a file path, even
if it starts with an environment variable.
## Summary
It turns out that in the
[spec](https://packaging.python.org/en/latest/specifications/binary-distribution-format/#file-name-convention),
if a wheel filename includes a build tag, then we need to use it to
break ties. This PR implements that behavior. (Previously, we dropped
the build tag entirely.)
Closes#3779.
## Test Plan
Run: `cargo run pip install -i https://pypi.anaconda.org/intel/simple
mkl_fft==1.3.8 --python-platform linux --python-version 3.10`. This now
resolves without error. Previously, we selected build tag 63 of
`mkl_fft==1.3.8`, which led to an incompatibility with NumPy. Now, we
select build tag 70.
When parsing requirements from any source, directly parse the url parts
(and reject unsupported urls) instead of parsing url parts at a later
stage. This removes a bunch of error branches and concludes the work
parsing url parts once and passing them around everywhere.
Many usages of the assembled `VerbatimUrl` remain, but these can be
removed incrementally.
Please review commit-by-commit.
## Summary
We now show yanks as part of the resolution diagnostics, so they now
appear for `sync`, `install`, `compile`, and any other operations.
Further, they'll also appear for cached packages (but not packages that
are _already_ installed).
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3768.
Closes#3766.
## Summary
This PR takes the functions used in `pip install`, moves them into a
common module, and then replaces all the `pip sync` logic with calls
into those functions. The net effect is that `pip install` and `pip
sync` share far more code and demonstrate much more consistent behavior.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3555.
## Summary
This PR adds editables using a new source type (`editable+...`), and
then extracts the editables from the lockfile in `uv sync`.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3695.
Updates our Python interpreter discovery to conform to the rules
described in #2386, please see that issue for a full description of the
behavior. Briefly, we now will search for interpreters that satisfy a
requested version without stopping at the first Python executable.
Additionally, if retrieving information about an interpreter fails we
will continue to search for a working interpreter. We also add the
plumbing necessary to request Python implementations other than CPython,
though we do not add support for other implementations at this time.
A major internal goal of this work is to prepare for user-facing managed
toolchains i.e. fetching a requested version during `uv run`. These APIs
are not introduced, but there is some managed toolchain handling as
required for our test suite.
Some noteworthy implementation changes:
- The `uv_interpreter::find_python` module has been removed in favor of
a `uv_interpreter::discovery` module.
- There are new types to help structure interpreter requests and track
sources
- Executable discovery is implemented as a big lazy iterator and is a
central authority for source precedence
- `uv_interpreter::Error` variants were split into scoped types in each
module
- There's much more unit test coverage, but not for Windows yet
Remaining work:
- [x] Write new test cases
- [x] Determine correct behavior around executables in the current
directory
- _Future_: Combine `PythonVersion` and `VersionRequest`
- _Future_: Consider splitting `ManagedToolchain` into local and remote
variants
- _Future_: Add Windows unit test coverage
- _Future_: Explore behavior around implementation precedence (i.e.
CPython over PyPy)
Refactors split into:
- #3329
- #3330
- #3331
- #3332Closes#2386
Instead of saying
> we can conclude that you require==0a0.dev0 and
pandas-stubs==2.0.3.230814 are incompatible.
we'll say
> we can conclude that your requirements and pandas-stubs==2.0.3.230814
are incompatible.
Closes#3710
I'm not sure how to get unit test coverage for this, might look into
that. Ideally we'd skip this branch entirely?
Pubgrub stores incompatibilities as (package name, version range)
tuples, meaning it needs to clone the package name for each
incompatibility, and each non-borrowed operation on incompatibilities.
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/3673 made me realize that
`PubGrubPackage` has gotten large (expensive to copy), so like `Version`
and other structs, i've added an `Arc` wrapper around it.
It's a pity clippy forbids `.deref()`, it's less opaque than `&**` and
has IDE support (clicking on `.deref()` jumps to the right impl).
## Benchmarks
It looks like this matters most for complex resolutions which, i assume
because they carry larger `PubGrubPackageInner::Package` and
`PubGrubPackageInner::Extra` types.
```bash
hyperfine --warmup 5 "./uv-main pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/jupyter.in" "./uv-branch pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/jupyter.in"
hyperfine --warmup 5 "./uv-main pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/airflow.in" "./uv-branch pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/airflow.in"
hyperfine --warmup 5 "./uv-main pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/boto3.in" "./uv-branch pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/boto3.in"
```
```
Benchmark 1: ./uv-main pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/jupyter.in
Time (mean ± σ): 18.2 ms ± 1.6 ms [User: 14.4 ms, System: 26.0 ms]
Range (min … max): 15.8 ms … 22.5 ms 181 runs
Benchmark 2: ./uv-branch pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/jupyter.in
Time (mean ± σ): 17.8 ms ± 1.4 ms [User: 14.4 ms, System: 25.3 ms]
Range (min … max): 15.4 ms … 23.1 ms 159 runs
Summary
./uv-branch pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/jupyter.in ran
1.02 ± 0.12 times faster than ./uv-main pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/jupyter.in
```
```
Benchmark 1: ./uv-main pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/airflow.in
Time (mean ± σ): 153.7 ms ± 3.5 ms [User: 165.2 ms, System: 157.6 ms]
Range (min … max): 150.4 ms … 163.0 ms 19 runs
Benchmark 2: ./uv-branch pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/airflow.in
Time (mean ± σ): 123.9 ms ± 4.6 ms [User: 152.4 ms, System: 133.8 ms]
Range (min … max): 118.4 ms … 138.1 ms 24 runs
Summary
./uv-branch pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/airflow.in ran
1.24 ± 0.05 times faster than ./uv-main pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/airflow.in
```
```
Benchmark 1: ./uv-main pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/boto3.in
Time (mean ± σ): 327.0 ms ± 3.8 ms [User: 344.5 ms, System: 71.6 ms]
Range (min … max): 322.7 ms … 334.6 ms 10 runs
Benchmark 2: ./uv-branch pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/boto3.in
Time (mean ± σ): 311.2 ms ± 3.1 ms [User: 339.3 ms, System: 63.1 ms]
Range (min … max): 307.8 ms … 317.0 ms 10 runs
Summary
./uv-branch pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/boto3.in ran
1.05 ± 0.02 times faster than ./uv-main pip compile -q ./scripts/requirements/boto3.in
```
<!--
Thank you for contributing to uv! To help us out with reviewing, please
consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
This PR falls back to writing an unnamed requirement if it appears to be
a relative URL. pip is way more flexible when providing an unnamed
requirement than when providing a PEP 508 requirement. For example,
_only_ this works:
```
black @ file:///Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/scripts/packages/black_editable
```
Any other form will fail.
Meanwhile, _all_ of these work:
```
file:///Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/scripts/packages/black_editable
scripts/packages/black_editable
./scripts/packages/black_editable
file:./scripts/packages/black_editable
file:scripts/packages/black_editable
```
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3180.
This makes use of the newly added `Ord` impl on `PubGrubPackage` to make
the output of `format_terms` independent of hashmap iteration order.
This was already collecting the terms into an intermediate `Vec`, so
sorting probably isn't going to add any significant overhead here.
(Plus, this is only running when formatting an error message after a
solution could not be found, so an extra sort doesn't seem like a big
deal here.)
Note that some tests are updated in this commit as a result of this
change. As far as I can tell, the semantic meaning of the output remains
the same. But the order of the listed packages does not.
Specific thing motivating this change is, in a subsequent, I added
`Option<MarkerTree>` to `PubGrubPackage::Package`, and this caused
similar changes in test output. So I backtracked and isolated this
change from the addition of `Option<MarkerTree>`.
It turns out that we use PubGrubPackage as the key in hashmaps in a fair
few places. And when we iterate over hashmaps, the order is unspecified.
This can in turn result in changes in output as a result of changes in
the PubGrubPackage definition, purely as a function of its changing
hash. This is confusing as there should be no semantic difference.
Thus, this is a precursor to introducing some more determinism to places
I found in the error reporting whose output depending on hashmap
iteration order.
It looks like the last vestiges of `Derivative` were removed in commit
7eaed07f6c, but the then rendered
superfluous `derive(Derivative)` wasn't removed.
This is split out from workspaces support, which needs editables in the
bluejay commands. It consists mainly of refactorings:
* Move the `editable` module one level up.
* Introduce a `BuiltEditableMetadata` type for `(LocalEditable,
Metadata23, Requirements)`.
* Add editables to `InstalledPackagesProvider` so we can use
`EmptyInstalledPackages` for them.
## Summary
The main motivation here is that the `.filename()` method that we
implement on `Url` will do URL decoding for the last segment, which we
were missing here.
The errors are a bit awkward, because in
`crates/uv-resolver/src/lock.rs`, we wrap in `failed to extract filename
from URL: {url}`, so in theory we want the underlying errors to _omit_
the URL? But sometimes they use `#[error(transparent)]`?
## Summary
Uncertain about this, but we don't actually need the full
`SourceDistFilename`, only the name and version -- and we often have
that information already (as in the lockfile routines). So by flattening
the fields onto `RegistrySourceDist`, we can avoid re-parsing for
information we already have.
## Summary
This PR adds lossless deserialization for `GitSourceDist` distributions
in the lockfile. Specifically, we now properly preserve the requested
revision, the subdirectory, and the precise Git commit SHA.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
This PR introduces parallelism to the resolver. Specifically, we can
perform PubGrub resolution on a separate thread, while keeping all I/O
on the tokio thread. We already have the infrastructure set up for this
with the channel and `OnceMap`, which makes this change relatively
simple. The big change needed to make this possible is removing the
lifetimes on some of the types that need to be shared between the
resolver and pubgrub thread.
A related PR, https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/1163, found that
adding `yield_now` calls improved throughput. With optimal scheduling we
might be able to get away with everything on the same thread here.
However, in the ideal pipeline with perfect prefetching, the resolution
and prefetching can run completely in parallel without depending on one
another. While this would be very difficult to achieve, even with our
current prefetching pattern we see a consistent performance improvement
from parallelism.
This does also require reverting a few of the changes from
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/3413, but not all of them. The
sharing is isolated to the resolver task.
## Test Plan
On smaller tasks performance is mixed with ~2% improvements/regressions
on both sides. However, on medium-large resolution tasks we see the
benefits of parallelism, with improvements anywhere from 10-50%.
```
./scripts/requirements/jupyter.in
Benchmark 1: ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 29.2 ms ± 1.8 ms [User: 20.3 ms, System: 29.8 ms]
Range (min … max): 26.4 ms … 36.0 ms 91 runs
Benchmark 2: ./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 25.5 ms ± 1.0 ms [User: 19.5 ms, System: 25.5 ms]
Range (min … max): 23.6 ms … 27.8 ms 99 runs
Summary
./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm) ran
1.15 ± 0.08 times faster than ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
```
```
./scripts/requirements/boto3.in
Benchmark 1: ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 487.1 ms ± 6.2 ms [User: 464.6 ms, System: 61.6 ms]
Range (min … max): 480.0 ms … 497.3 ms 10 runs
Benchmark 2: ./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 430.8 ms ± 9.3 ms [User: 529.0 ms, System: 77.2 ms]
Range (min … max): 417.1 ms … 442.5 ms 10 runs
Summary
./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm) ran
1.13 ± 0.03 times faster than ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
```
```
./scripts/requirements/airflow.in
Benchmark 1: ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 478.1 ms ± 18.8 ms [User: 482.6 ms, System: 205.0 ms]
Range (min … max): 454.7 ms … 508.9 ms 10 runs
Benchmark 2: ./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 308.7 ms ± 11.7 ms [User: 428.5 ms, System: 209.5 ms]
Range (min … max): 287.8 ms … 323.1 ms 10 runs
Summary
./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm) ran
1.55 ± 0.08 times faster than ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
```
## Summary
Fixes a small discrepancy between the pip compile outputs for
`annotation-style=split` and `annotation-style=line` commands.
### Problem
Consider the following `pyproject.toml` file.
```sh
$ cat pyproject.toml
[project]
name = "uv_test"
dynamic = ["version"]
dependencies = ["click"]
```
Running uv pip compile with annotation-style=split on uv 0.1.44 version
yields the following:
```sh
❯ uv pip compile pyproject.toml --annotation-style=split
Resolved 1 package in 2ms
# This file was autogenerated by uv via the following command:
# uv pip compile pyproject.toml --annotation-style=split
click==8.1.7
# via uv-test (pyproject.toml)
```
However, running uv pip compile with annotation-style=line doesn't
include source info for root level dependencies.
```sh
❯ uv pip compile pyproject.toml --annotation-style=line
Resolved 1 package in 1ms
# This file was autogenerated by uv via the following command:
# uv pip compile pyproject.toml --annotation-style=line
click==8.1.7
```
With this PR:
```sh
❯ ../target/debug/uv pip compile --annotation-style=line pyproject.toml
Resolved 1 package in 6ms
# This file was autogenerated by uv via the following command:
# uv pip compile --annotation-style=line pyproject.toml
click==8.1.7 # via uv-test (pyproject.toml)
```
This also now matches `pip-tools` output:
```sh
❯ pip-compile --annotation-style=line pyproject.toml
#
# This file is autogenerated by pip-compile with Python 3.12
# by the following command:
#
# pip-compile --annotation-style=line pyproject.toml
#
click==8.1.7 # via uv_test (pyproject.toml)
```
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
Following from #3595, we'd like wheels to make their way into the lock
file even if the current environment selects an sdist. With #3595, this
didn't happen:
$ cargo run -p uv -- pip compile -p3.10 <(echo psycopg2)
--unstable-uv-lock-file
$ cat uv.lock
version = 1
[[distribution]]
name = "psycopg2"
version = "2.9.9"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[distribution.sdist]
url =
"dc6acaf46d76fce95daac5e0f0301b/psycopg2-2.9.9.tar.gz"
hash =
"sha256:d1454bde93fb1e224166811694d600e746430c006fbb031ea06ecc2ea41bf156"
The above example uses `psycopg2`, which has an sdist and wheels only on
Windows. Since I ran the above on Linux, an sdist was selected. But no
wheels appeared in the lock file.
With this PR, wheels are now correctly plumbed through:
$ cargo run -p uv -- pip compile -p3.10 <(echo psycopg2)
--unstable-uv-lock-file
$ cat uv.lock
version = 1
[[distribution]]
name = "psycopg2"
version = "2.9.9"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[distribution.sdist]
url =
"dc6acaf46d76fce95daac5e0f0301b/psycopg2-2.9.9.tar.gz"
hash =
"sha256:d1454bde93fb1e224166811694d600e746430c006fbb031ea06ecc2ea41bf156"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"2767d96391f5cde90b82cb3e8c2a12/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp310-cp310-win32.whl"
hash =
"sha256:38a8dcc6856f569068b47de286b472b7c473ac7977243593a288ebce0dc89516"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"6572dec6831f85491a5e4dda606a98/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp310-cp310-win_amd64.whl"
hash =
"sha256:426f9f29bde126913a20a96ff8ce7d73fd8a216cfb323b1f04da402d452853c3"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"1fc5b9d33c858a602868a592cdc1b0/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp311-cp311-win32.whl"
hash =
"sha256:ade01303ccf7ae12c356a5e10911c9e1c51136003a9a1d92f7aa9d010fb98372"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"5133dd3183e671b278ce248810b7f7/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp311-cp311-win_amd64.whl"
hash =
"sha256:121081ea2e76729acfb0673ff33755e8703d45e926e416cb59bae3a86c6a4981"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"f74ffe6b6fe119ccb8a6546c3fb893/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp312-cp312-win32.whl"
hash =
"sha256:d735786acc7dd25815e89cc4ad529a43af779db2e25aa7c626de864127e5a024"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"c4a26e1918ab7ee854fb5247f16c40/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp312-cp312-win_amd64.whl"
hash =
"sha256:a7653d00b732afb6fc597e29c50ad28087dcb4fbfb28e86092277a559ae4e693"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"ffeb9ac356ce0d6c4f2f34e396dbc0/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp37-cp37m-win32.whl"
hash =
"sha256:5e0d98cade4f0e0304d7d6f25bbfbc5bd186e07b38eac65379309c4ca3193efa"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"0a39176d36fd7105774e57996f63cd/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp37-cp37m-win_amd64.whl"
hash =
"sha256:7e2dacf8b009a1c1e843b5213a87f7c544b2b042476ed7755be813eaf4e8347a"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"86b90d30c4420cc3c0f6da2b8f3a9a/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp38-cp38-win32.whl"
hash =
"sha256:ff432630e510709564c01dafdbe996cb552e0b9f3f065eb89bdce5bd31fabf4c"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"c439b378ef79997a935f10374f3c0d/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp38-cp38-win_amd64.whl"
hash =
"sha256:bac58c024c9922c23550af2a581998624d6e02350f4ae9c5f0bc642c633a2d5e"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"5080c0e61ad5f08b9503e508aac116/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp39-cp39-win32.whl"
hash =
"sha256:c92811b2d4c9b6ea0285942b2e7cac98a59e166d59c588fe5cfe1eda58e72d59"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url =
"ec73fe66d4d65f5bbe54efb191d9e6/psycopg2-2.9.9-cp39-cp39-win_amd64.whl"
hash =
"sha256:de80739447af31525feddeb8effd640782cf5998e1a4e9192ebdf829717e3913"
Ref #3351
Our current flow of data from "simple registry package" to "final
resolved distribution" goes through a number of types:
* `SimpleMetadata` is the API response from a registry that includes all
published versions for a package. Each version has an assortment of
metadata
associated with it.
* `VersionFiles` is the aforementioned metadata. It is split in two: a
group of files for source distributions and a group of files for wheels.
* `PrioritizedDist` collects a subset of the files from `VersionFiles`
to form a selection of the "best" sdist and the "best" wheel for the
current environment.
* `CompatibleDist` is created from a borrowed `PrioritizedDist` that,
perhaps among other things, encapsulates the decision of whether to pick
an sdist or a wheel. (This decision depends both on compatibility and
the action being performed. e.g., When doing installation, a
`CompatibleDist` will sometimes select an sdist over a wheel.)
* `ResolvedDistRef` is like a `ResolvedDist`, but borrows a `Dist`.
* `ResolvedDist` is the almost-final-form of a distribution in a
resolution and is created from a `ResolvedDistRef`.
* `AnnotatedResolvedDist` is a new data type that is the actual final
form of a distribution that a universal lock file cares about. It
bundles a `ResolvedDist` with some metadata needed to generate a lock
file.
One of the requirements of a universal lock file is that we include all
wheels (and maybe all source distributions? but at least one if it's
present) associated with a distribution. But the above flow of data (in
the step from `VersionFiles` to `PrioritizedDist`) drops all wheels
except for the best one.
To remedy this, in this PR, we rejigger `PrioritizedDist`,
`CompatibleDist` and `ResolvedDistRef` so that all wheel data is
preserved. And when a `ResolvedDistRef` is finally turned into a
`ResolvedDist`, we copy all of the wheel data. And finally, we adjust
the `Lock` constructor to read this new data and include it in the lock
file. To make this work, we also modify `RegistryBuiltDist` so that it
can contain one or more wheels instead of just one.
One shortcoming here (called out in the code as a FIXME) is that if a
source distribution is selected as the "best" thing to use (perhaps
there are no compatible wheels), then the wheels won't end up in the
lock file. I plan to fix this in a follow-up PR.
We also aren't totally consistent on source distribution naming.
Sometimes we use `sdist`. Sometimes `source`. Sometimes `source_dist`.
I think it'd be nice to just use `sdist` everywhere, but I do prefer
the type names to be `SourceDist`. And sometimes you want function
names to match the type names (i.e., `from_source_dist`), which in turn
leads to an appearance of inconsistency. I'm open to ideas.
Closes#3351
## Summary
In `ResolutionGraph::from_state`, we have mechanisms to grab the hashes
and metadata for all distributions -- but we then throw that information
away. This PR preserves it on a new `AnnotatedDist` (yikes, open to
suggestions) that wraps `ResolvedDist` and includes (1) the hashes
(computed or from the registry) and (2) the `Metadata23`, which lets us
extract the version.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3356.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3357.
## Summary
Splits this into two loops that each handle independent cases, to make
the code a little easier to reason about. No behavioral or logic changes
-- just splitting the `match` across two loops.
## Summary
It's confusing that we use `constraints` here because constraints mean
something else for us (e.g., `--constraint constraints.txt`). These are
really the dependencies of a given `PubGrubPackage` -- the type is even
called `PubGrubDependencies`.
## Summary
I think this is overall good change because it explicitly encodes (in
the type system) something that was previously implicit. I'm not a huge
fan of the names here, open to input.
It covers some of https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3506 but I
don't think it _closes_ it.
<!--
Thank you for contributing to uv! To help us out with reviewing, please
consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Just fix typos.
While `alpha-numeric` is not really a misspelling:
- it is missing from mainstream curated dictionaries, all of them
suggest `alphanumeric`;
- it is less used than `alphanumeric` (more than ⨉10 less) according to
the Google [Ngram
Viewer](https://books.google.com/ngrams/graph?content=alpha-numeric%2Calphanumeric&year_start=1900&year_end=2019&corpus=en-2019);
- it is [missing from
SCOWL](http://app.aspell.net/lookup?dict=en_US-large;words=alpha-numeric).
## Test Plan
CI jobs.
## Summary
This PR consolidates the concurrency limits used throughout `uv` and
exposes two limits, `UV_CONCURRENT_DOWNLOADS` and
`UV_CONCURRENT_BUILDS`, as environment variables.
Currently, `uv` has a number of concurrent streams that it buffers using
relatively arbitrary limits for backpressure. However, many of these
limits are conflated. We run a relatively small number of tasks overall
and should start most things as soon as possible. What we really want to
limit are three separate operations:
- File I/O. This is managed by tokio's blocking pool and we should not
really have to worry about it.
- Network I/O.
- Python build processes.
Because the current limits span a broad range of tasks, it's possible
that a limit meant for network I/O is occupied by tasks performing
builds, reading from the file system, or even waiting on a `OnceMap`. We
also don't limit build processes that end up being required to perform a
download. While this may not pose a performance problem because our
limits are relatively high, it does mean that the limits do not do what
we want, making it tricky to expose them to users
(https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1205,
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3311).
After this change, the limits on network I/O and build processes are
centralized and managed by semaphores. All other tasks are unbuffered
(note that these tasks are still bounded, so backpressure should not be
a problem).
This only makes hashes optional for wheels/sdists that come from
registires or direct URLs. For wheels/sdists that come from other
sources, a hash should not be present.
For path dependencies, a hash should not be present because the state of
the path dependency is not intended to be tracked in the lock file. This
is consistent with how other tools deal with path dependencies, and if
it were otherwise, the hash would I believe need to be updated for every
change to the path dependency.
For git dependencies (source dists only), a hash should not be present
because the lock will contain the specific commit revision hash. This is
functionally equivalent to a hash, and so a hash is redundant.
As part of this change, we validate the presence or absence of a hash
based on the dependency source. We also add our first regression tests.
This still keeps the resolver state on the stack, but it organizes it
into a more structured representation. This is a precursor to
implementing resolver forking, where we will ultimately put this state
on the heap. The idea is that this will let us maintain multiple
independent resolver states that will all produce their own resolution
(and potentially other forked states).
Closes#3354
We now use the getters and setters everywhere.
There were some places where we wanted to build a `MarkerEnvironment`
out of whole cloth, usually in tests. To facilitate those use cases, we
add a `MarkerEnvironmentBuilder` that provides a convenient constructor.
It's basically like a `MarkerEnvironment::new`, but with named
parameters. That's useful here because there are so many fields (and
they many have the same type).
This commit touches a lot of code, but the conceptual change here is
pretty simple: make it so we can run the resolver without providing a
`MarkerEnvironment`. This also indicates that the resolver should run in
universal mode. That is, the effect of a missing marker environment is
that all marker expressions that reference the marker environment are
evaluated to `true`. That is, they are ignored. (The only markers we
evaluate in that context are extras, which are the only markers that
aren't dependent on the environment.)
One interesting change here is that a `Resolver` no longer needs an
`Interpreter`. Previously, it had only been using it to construct a
`PythonRequirement`, by filling in the installed version from the
`Interpreter` state. But we now construct a `PythonRequirement`
explicitly since its `target` Python version should no longer be tied to
the `MarkerEnvironment`. (Currently, the marker environment is mutated
such that its `python_full_version` is derived from multiple sources,
including the CLI, which I found a touch confusing.)
The change in behavior can now be observed through the
`--unstable-uv-lock-file` flag. First, without it:
```
$ cat requirements.in
anyio>=4.3.0 ; sys_platform == "linux"
anyio<4 ; sys_platform == "darwin"
$ cargo run -qp uv -- pip compile -p3.10 requirements.in
anyio==4.3.0
exceptiongroup==1.2.1
# via anyio
idna==3.7
# via anyio
sniffio==1.3.1
# via anyio
typing-extensions==4.11.0
# via anyio
```
And now with it:
```
$ cargo run -qp uv -- pip compile -p3.10 requirements.in --unstable-uv-lock-file
x No solution found when resolving dependencies:
`-> Because you require anyio>=4.3.0 and anyio<4, we can conclude that the requirements are unsatisfiable.
```
This is expected at this point because the marker expressions are being
explicitly ignored, *and* there is no forking done yet to account for
the conflict.
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1343. This is kinda a first
draft at the moment, but does at least mostly work locally (barring some
bits of the test suite that seem to not work for me in general).
## Test Plan
Mostly running the existing tests and checking the revised output is
sane
## Outstanding issues
Most of these come down to "AFAIK, the existing tools don't support
these patterns, but `uv` does" and so I'm not sure there's an existing
good answer here! Most of the answers so far are "whatever was easiest
to build"
- [x] ~~Is "-r pyproject.toml" correct? Should it show something else or
get skipped entirely~~ No it wasn't. Fixed in
3044fa8b86
- [ ] If the requirements file is stdin, that just gets skipped. Should
it be recorded?
- [ ] Overrides get shown as "--override<override.txt>". Correct?
- [x] ~~Some of the tests (e.g.
`dependency_excludes_non_contiguous_range_of_compatible_versions`) make
assumptions about the order of package versions being outputted, which
this PR breaks. I'm not sure if the text is fairly arbitrary and can be
replaced or whether the behaviour needs fixing?~~ - fixed by removing
the custom pubgrub PartialEq/Hash
- [ ] Are all the `TrackedFromStr` et al changes needed, or is there an
easier way? I don't think so, I think it's necessary to track these sort
of things fairly comprehensively to make this feature work, and this
sort of invasive change feels necessary, but happy to be proved wrong
there :)
- [x] ~~If you have a requirement coming in from two or more different
requirements files only one turns up. I've got a closed-source example
for this (can go into more detail if needed), mostly consisting of a
complicated set of common deps creating a larger set. It's a rarer case,
but worth considering.~~ 042432b200
- [ ] Doesn't add annotations for `setup.py` yet
- This is pretty hard, as the correct location to insert the path is
`crates/pypi-types/src/metadata.rs`'s `parse_pkg_info`, which as it's
based off a source distribution has entirely thrown away such matters as
"where did this package requirement get built from". Could add "`built
package name`" as a dep, but that's a little odd.
Pubgrub got a new feature where all unavailability is a custom, instead
of the reasonless `UnavailableDependencies` and our custom `String` type
previously (https://github.com/pubgrub-rs/pubgrub/pull/208). This PR
introduces a `UnavailableReason` that tracks either an entire version
being unusable, or a specific version. The error messages now also track
this difference properly.
The pubgrub commit is our main rebased onto the merged
https://github.com/pubgrub-rs/pubgrub/pull/208, i'll push
`konsti/main-rebase-generic-reason` to `main` after checking for rebase
problems.
## Summary
All of the resolver code is run on the main thread, so a lot of the
`Send` bounds and uses of `DashMap` and `Arc` are unnecessary. We could
also switch to using single-threaded versions of `Mutex` and `Notify` in
some places, but there isn't really a crate that provides those I would
be comfortable with using.
The `Arc` in `OnceMap` can't easily be removed because of the uv-auth
code which uses the
[reqwest-middleware](https://docs.rs/reqwest-middleware/latest/reqwest_middleware/trait.Middleware.html)
crate, that seems to adds unnecessary `Send` bounds because of
`async-trait`. We could duplicate the code and create a `OnceMapLocal`
variant, but I don't feel that's worth it.
## Introduction
PEP 621 is limited. Specifically, it lacks
* Relative path support
* Editable support
* Workspace support
* Index pinning or any sort of index specification
The semantics of urls are a custom extension, PEP 440 does not specify
how to use git references or subdirectories, instead pip has a custom
stringly format. We need to somehow support these while still stying
compatible with PEP 621.
## `tool.uv.source`
Drawing inspiration from cargo, poetry and rye, we add `tool.uv.sources`
or (for now stub only) `tool.uv.workspace`:
```toml
[project]
name = "albatross"
version = "0.1.0"
dependencies = [
"tqdm >=4.66.2,<5",
"torch ==2.2.2",
"transformers[torch] >=4.39.3,<5",
"importlib_metadata >=7.1.0,<8; python_version < '3.10'",
"mollymawk ==0.1.0"
]
[tool.uv.sources]
tqdm = { git = "https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm", rev = "cc372d09dcd5a5eabdc6ed4cf365bdb0be004d44" }
importlib_metadata = { url = "https://github.com/python/importlib_metadata/archive/refs/tags/v7.1.0.zip" }
torch = { index = "torch-cu118" }
mollymawk = { workspace = true }
[tool.uv.workspace]
include = [
"packages/mollymawk"
]
[tool.uv.indexes]
torch-cu118 = "https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118"
```
See `docs/specifying_dependencies.md` for a detailed explanation of the
format. The basic gist is that `project.dependencies` is what ends up on
pypi, while `tool.uv.sources` are your non-published additions. We do
support the full range or PEP 508, we just hide it in the docs and
prefer the exploded table for easier readability and less confusing with
actual url parts.
This format should eventually be able to subsume requirements.txt's
current use cases. While we will continue to support the legacy `uv pip`
interface, this is a piece of the uv's own top level interface. Together
with `uv run` and a lockfile format, you should only need to write
`pyproject.toml` and do `uv run`, which generates/uses/updates your
lockfile behind the scenes, no more pip-style requirements involved. It
also lays the groundwork for implementing index pinning.
## Changes
This PR implements:
* Reading and lowering `project.dependencies`,
`project.optional-dependencies` and `tool.uv.sources` into a new
requirements format, including:
* Git dependencies
* Url dependencies
* Path dependencies, including relative and editable
* `pip install` integration
* Error reporting for invalid `tool.uv.sources`
* Json schema integration (works in pycharm, see below)
* Draft user-level docs (see `docs/specifying_dependencies.md`)
It does not implement:
* No `pip compile` testing, deprioritizing towards our own lockfile
* Index pinning (stub definitions only)
* Development dependencies
* Workspace support (stub definitions only)
* Overrides in pyproject.toml
* Patching/replacing dependencies
One technically breaking change is that we now require user provided
pyproject.toml to be valid wrt to PEP 621. Included files still fall
back to PEP 517. That means `pip install -r requirements.txt` requires
it to be valid while `pip install -r requirements.txt` with `-e .` as
content falls back to PEP 517 as before.
## Implementation
The `pep508` requirement is replaced by a new `UvRequirement` (name up
for bikeshedding, not particularly attached to the uv prefix). The still
existing `pep508_rs::Requirement` type is a url format copied from pip's
requirements.txt and doesn't appropriately capture all features we
want/need to support. The bulk of the diff is changing the requirement
type throughout the codebase.
We still use `VerbatimUrl` in many places, where we would expect a
parsed/decomposed url type, specifically:
* Reading core metadata except top level pyproject.toml files, we fail a
step later instead if the url isn't supported.
* Allowed `Urls`.
* `PackageId` with a custom `CanonicalUrl` comparison, instead of
canonicalizing urls eagerly.
* `PubGrubPackage`: We eventually convert the `VerbatimUrl` back to a
`Dist` (`Dist::from_url`), instead of remembering the url.
* Source dist types: We use verbatim url even though we know and require
that these are supported urls we can and have parsed.
I tried to make improve the situation be replacing `VerbatimUrl`, but
these changes would require massive invasive changes (see e.g.
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/3253). A main problem is the ref
`VersionOrUrl` and applying overrides, which assume the same
requirement/url type everywhere. In its current form, this PR increases
this tech debt.
I've tried to split off PRs and commits, but the main refactoring is
still a single monolith commit to make it compile and the tests pass.
## Demo
Adding
d1ae3b85d5/pyproject.json
as json schema (v7) to pycharm for `pyproject.toml`, you can try the IDE
support already:
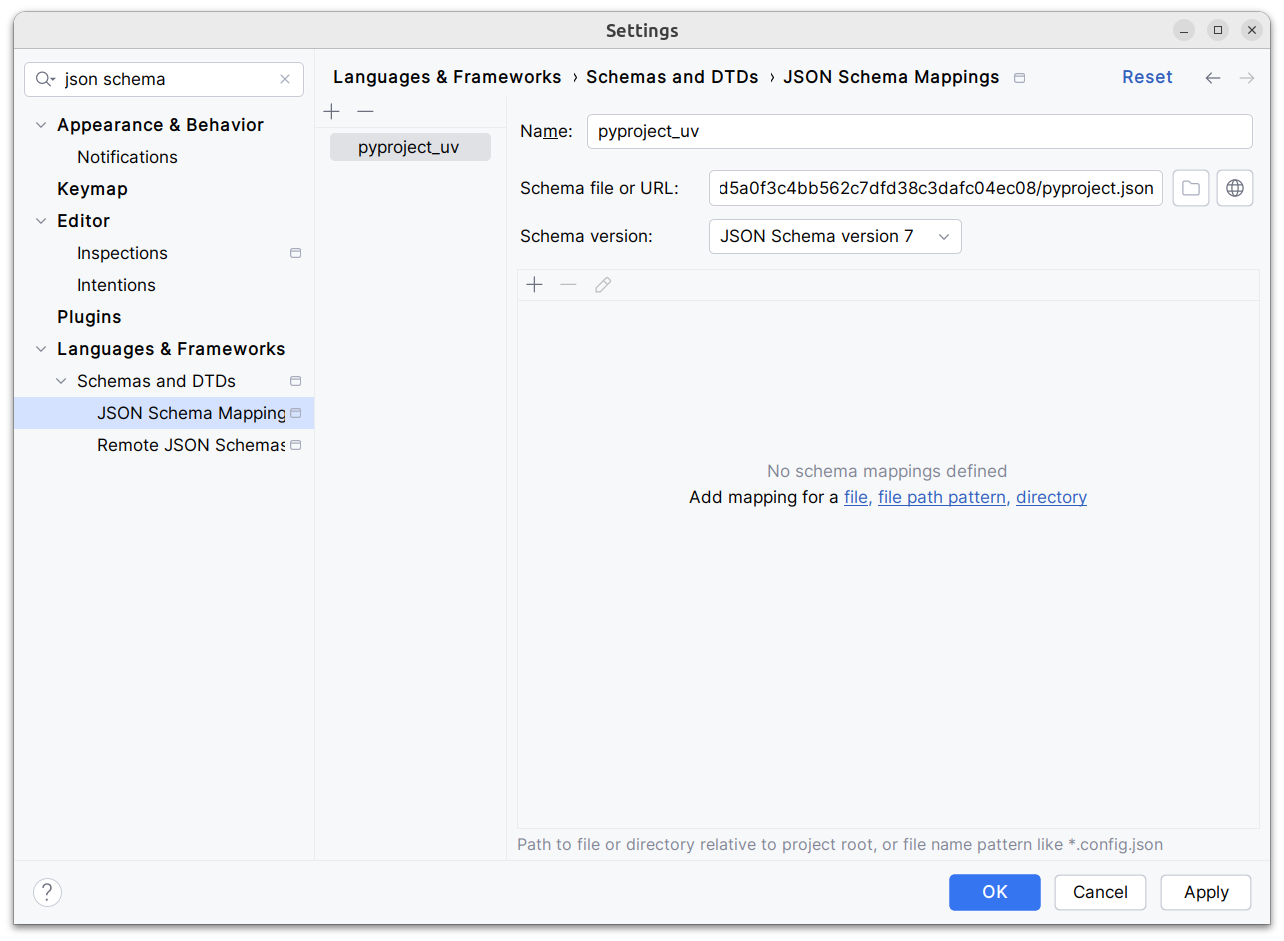
[dove.webm](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/assets/6826232/c293c272-c80b-459d-8c95-8c46a8d198a1)
In *some* places in our crates, `serde` (and `rkyv`) are optional
dependencies. I believe this was done out of reasons of "good sense,"
that is, it follows a Rust ecosystem pattern where serde integration
tends to be an opt-in crate feature. (And similarly for `rkyv`.)
However, ultimately, `uv` itself requires `serde` and `rkyv` to
function. Since our crates are strictly internal, there are limited
consumers for our crates without `serde` (and `rkyv`) enabled. I think
one possibility is that optional `serde` (and `rkyv`) integration means
that someone can do this:
cargo test -p pep440_rs
And this will run tests _without_ `serde` or `rkyv` enabled. That in
turn could lead to faster iteration time by reducing compile times. But,
I'm not sure this is worth supporting. The iterative compilation times
of
individual crates are probably fast enough in debug mode, even with
`serde` and `rkyv` enabled. Namely, `serde` and `rkyv` themselves
shouldn't need to be re-compiled in most cases. On `main`:
```
from-scratch: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --lib` 0.685
incremental: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --lib` 0.278s
from-scratch: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --features serde,rkyv --lib` 3.948s
incremental: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --features serde,rkyv --lib` 0.321s
```
So while a from-scratch build does take significantly longer, an
incremental build is about the same.
The benefit of doing this change is two-fold:
1. It brings out crates into alignment with "reality." In particular,
some crates were _implicitly_ relying on `serde` being enabled
without explicitly declaring it. This technically means that our
`Cargo.toml`s were wrong in some cases, but it is hard to observe it
because of feature unification in a Cargo workspace.
2. We no longer need to deal with the cognitive burden of writing
`#[cfg_attr(feature = "serde", ...)]` everywhere.
This PR principally adds a routine for converting a `Lock` to a
`Resolution`, where a `Resolution` is a map of package names pinned to
a specific version.
I'm not sure that a `Resolution` is ultimately what we want here (we
might need more stuff), but this was the quickest route I could find to
plug a `Lock` into our existing `uv pip install` infrastructure.
This commit also does a little refactoring of the `Lock` types. The
main thing is to permit extra state on some of the types (like a
`by_id` map on `Lock` for quick lookups of distributions) that aren't
included in the serialization format of a `Lock`. We achieve this
by defining separate `Wire` types that are automatically converted
to-and-from via `serde`.
Note that like with the lock file format types themselves, we leave a
few `todo!()` expressions around. The main idea is to get something
minimally working without spending too much effort here. (A fair bit
of refactoring will be required to generate a lock file, and it's
not clear how much this code will wind up needing to change anyway.)
In particular, we only handle the case of installing wheels from a
registry.
A demonstration of the full flow:
```
$ requirements.in
anyio
$ cargo run -p uv -- pip compile -p3.10 requirements.in --unstable-uv-lock-file
$ uv venv
$ cargo run -p uv -- pip install --unstable-uv-lock-file anyio -r requirements.in
Installed 5 packages in 7ms
+ anyio==4.3.0
+ exceptiongroup==1.2.1
+ idna==3.7
+ sniffio==1.3.1
+ typing-extensions==4.11.0
```
In order to install from a lock file, we start from the root and do a
breadth first traversal over its dependencies. We aren't yet filtering
on marker expressions (since they aren't in the lock file yet), but we
should be able to add that in the future. In so doing, the traversal
should select only the subset of distributions relevant for the current
platform.
This is meant to be a base on which to build. There are some parts
which are implicitly incomplete and others which are explicitly
incomplete. The latter are indicated by TODO comments.
Here is a non-exhaustive list of incomplete things. In many cases, these
are incomplete simply because the data isn't present in a
`ResolutionGraph`. Future work will need to refactor our resolver so
that this data is correctly passed down.
* Not all wheels are included. Only the "selected" wheel for the current
distribution is included.
* Marker expressions are always absent.
* We don't emit hashes for certainly kinds of distributions (direct
URLs, git, and path).
* We don't capture git information from a dependency specification.
Right now, we just always emit "default branch."
There are perhaps also other changes we might want to make to the format
of a more cosmetic nature. Right now, all arrays are encoded using
whatever the `toml` crate decides to do. But we might want to exert more
control over this. For example, by using inline tables or squashing more
things into strings (like I did for `Source` and `Hash`). I think the
main trade-off here is that table arrays are somewhat difficult to read
(especially without indentation), where as squashing things down into a
more condensed format potentially makes future compatible additions
harder.
I also went pretty light on the documentation here than what I would
normally do. That's primarily because I think this code is going to
go through some evolution and I didn't want to spend too much time
documenting something that is likely to change.
Finally, here's an example of the lock file format in TOML for the
`anyio` dependency. I generated it with the following command:
```
cargo run -p uv -- pip compile -p3.10 ~/astral/tmp/reqs/anyio.in --unstable-uv-lock-file
```
And that writes out a `uv.lock` file:
```toml
version = 1
[[distribution]]
name = "anyio"
version = "4.3.0"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "2f20c40b45242c0b33774da0e2e34f/anyio-4.3.0-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:048e05d0f6caeed70d731f3db756d35dcc1f35747c8c403364a8332c630441b8"
[[distribution.dependencies]]
name = "exceptiongroup"
version = "1.2.1"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.dependencies]]
name = "idna"
version = "3.7"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.dependencies]]
name = "sniffio"
version = "1.3.1"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.dependencies]]
name = "typing-extensions"
version = "4.11.0"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution]]
name = "exceptiongroup"
version = "1.2.1"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "79fe92dd414cadab75055b0ae00b33/exceptiongroup-1.2.1-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:5258b9ed329c5bbdd31a309f53cbfb0b155341807f6ff7606a1e801a891b29ad"
[[distribution]]
name = "idna"
version = "3.7"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "741d8c8280948df2ea0eda2c8b79e8/idna-3.7-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:82fee1fc78add43492d3a1898bfa6d8a904cc97d8427f683ed8e798d07761aa0"
[[distribution]]
name = "sniffio"
version = "1.3.1"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "75a9c94214239abab1ea2cc8f38b40/sniffio-1.3.1-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:2f6da418d1f1e0fddd844478f41680e794e6051915791a034ff65e5f100525a2"
[[distribution]]
name = "typing-extensions"
version = "4.11.0"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "936e2092671b43269810cd589ceaf5/typing_extensions-4.11.0-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:c1f94d72897edaf4ce775bb7558d5b79d8126906a14ea5ed1635921406c0387a"
```
## Summary
This index strategy resolves every package to the latest possible
version across indexes. If a version is in multiple indexes, the first
available index is selected.
Implements #3137
This closely matches pip.
## Test Plan
Good question. I'm hesitant to use my certifi example here, since that
would inevitably break when torch removes this package. Please comment!
## Summary
Simplifies dependency errors of the form `you require package-a and you
require package-b` to `you require package-a and package-b`. Resolves
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1009.
The only thing a `OnceMap` really needs to be able to do with the value
is to clone it. All extant uses benefited from having this done for them
by automatically wrapping values in an `Arc`. But this isn't necessarily
true for all things. For example, a value might have an `Arc` internally
to making cloning cheap in other contexts, and it doesn't make sense to
re-wrap it in an `Arc` just to use it with a `OnceMap`. Or
alternatively, cloning might just be cheap enough on its own that an
`Arc` isn't worth it.
## Summary
We now recursively expand any self-dependencies via extras, which lets
us detect conflicts sooner and avoid building unnecessary versions of
packages that are excluded via the extra.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3135.
Previously, uv-auth would fail to compile due to a missing process
feature. I chose to make all tokio features we use top level features,
so we can share the tokio cache between all test invocations.
## Summary
See the diff in the tests. If you have a constraint with an extra, we
should respect it, but we shouldn't _add_ the extra to the requirements.
## Summary
I found some of these too bare (e.g., when they _just_ show a package
name with no other information). For me, this makes it easier to
differentiate error message copy from data. But open to other opinions.
Take a look at the fixture changes and LMK!
## Summary
This PR avoids: (1) using the lookahead resolver when `--no-deps` is
specified (we'll never use those requirements), and (2) including any
transitive requirements when searching for allowed URLs, etc., when
`--no-deps` is specified.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3183.
## Summary
pip prefers somewhat-constrained over unconstrained packages... but only
if they're at equal depths in the tree. We don't have a way to track the
latter property yet (I've added a TODO), so for now, we should remove
this constraint -- it seems to be counter-productive.
I've filed https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3149 as a follow-up.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3143
## Test Plan
- `git clone https://github.com/drivendataorg/zamba.git`
- `cat "-e .[tests]" > req.in`
- `cargo run venv && cargo run pip compile req.in --refresh -n
--python-platform linux --python-version 3.8`
## Summary
We weren't setting a priority for editables, so they were being visited
last.
I think there's still a problem whereby we're not aggressive enough in
visiting recursive extras (and, in fact, that's making it really hard to
write a test -- I wrote a test, but the most-reduced case still fails,
and I'd need to add a layer of indirection to make it
fail-on-main-but-pass-on-this-branch), but that problem likely already
existed on main prior to #3087, so I just want to get this quick fix out
now.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3127.
## Test Plan
- `git clone https://github.com/cda-tum/mqt-core.git`
- `cargo run venv`
- `cargo run pip install 'scikit-build-core[pyproject]>=0.8.1'
'setuptools_scm>=7' 'pybind11>=2.12' --resolution=lowest-direct`
- `cargo run pip install --no-build-isolation
'-ve.[test,qiskit,evaluation,coverage]' --resolution=lowest-direct`
Given requirements like:
```
black==23.1.0
black[colorama]
```
The resolver will (on `main`) add a dependency on Black, and then try to
use the most recent version of Black to satisfy `black[colorama]`. For
sake of example, assume `black==24.0.0` is the most recent version. Once
the selects this most recent version, it'll fetch the metadata, then
return the dependencies for `black==24.0.0` with the `colorama` extra
enabled. Finally, it will tack on `black==24.0.0` (a dependency on the
base package). The resolver will then detect a conflict between
`black==23.1.0` and `black==24.0.0`, and throw out
`black[colorama]==24.0.0`, trying to next most-recent version.
This is both wasteful and can cause problems, since we're fetching
metadata for versions that will _never_ satisfy the resolver. In the
`apache-airflow[all]` case, I also ran into an issue whereby we were
attempting to build very old versions of `apache-airflow` due to
`apache-airflow[pandas]`, which in turn led to resolution failures.
The solution proposed here is that we create a new proxy package with
exactly two dependencies: one on `black` and one of `black[colorama]`.
Both of these packages must be at the same version as the proxy package,
so the resolver knows much _earlier_ that (in the above example) the
extra variant _must_ match `23.1.0`.
## Summary
resolves https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3106
## Test Plan
added a simple test where the password provided in `UV_INDEX_URL` is
hidden in the output as expected.
## Summary
This PR adds basic struct definitions along with a "workspace" concept
for discovering settings. (The "workspace" terminology is used to match
Ruff; I did not invent it.)
A few notes:
- We discover any `pyproject.toml` or `uv.toml` file in any parent
directory of the current working directory. (We could adjust this to
look at the directories of the input files.)
- We don't actually do anything with the configuration yet; but those
PRs are large and I want this to be reviewed in isolation.
## Summary
This makes it easier to add (e.g.) JSON Schema derivations to the type.
If we have support for other dates in the future, we can generalize it
to a `UserDate` or similar.
freethreaded python reintroduces abiflags since it is incompatible with
regular native modules and abi3.
Tests: None yet! We're lacking cpython 3.13 no-gil builds we can use in
ci.
My test setup:
```
PYTHON_CONFIGURE_OPTS="--enable-shared --disable-gil" pyenv install 3.13.0a5
cargo run -q -- venv -q -p python3.13 .venv3.13 --no-cache-dir && cargo run -q -- pip install -v psutil --no-cache-dir && .venv3.13/bin/python -c "import psutil"
```
Fixes#2429
## Summary
This PR enables `--require-hashes` with unnamed requirements. The key
change is that `PackageId` becomes `VersionId` (since it refers to a
package at a specific version), and the new `PackageId` consists of
_either_ a package name _or_ a URL. The hashes are keyed by `PackageId`,
so we can generate the `RequiredHashes` before we have names for all
packages, and enforce them throughout.
Closes#2979.
## Summary
This PR enables hash generation for URL requirements when the user
provides `--generate-hashes` to `pip compile`. While we include the
hashes from the registry already, today, we omit hashes for URLs.
To power hash generation, we introduce a `HashPolicy` abstraction:
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum HashPolicy<'a> {
/// No hash policy is specified.
None,
/// Hashes should be generated (specifically, a SHA-256 hash), but not validated.
Generate,
/// Hashes should be validated against a pre-defined list of hashes. If necessary, hashes should
/// be generated so as to ensure that the archive is valid.
Validate(&'a [HashDigest]),
}
```
All of the methods on the distribution database now accept this policy,
instead of accepting `&'a [HashDigest]`.
Closes#2378.
## Summary
This PR modifies the distribution database to return both the
`Metadata23` and the computed hashes when clients request metadata.
No behavior changes, but this will be necessary to power
`--generate-hashes`.
## Summary
This represents a change to `--require-hashes` in the event that we
don't find a matching hash from the registry. The behavior in this PR is
closer to pip's.
Prior to this PR, if a distribution had no reported hash, or only
mismatched hashes, we would mark it as incompatible. Now, we mark it as
compatible, but we use the hash-agreement as part of the ordering, such
that we prefer any distribution with a matching hash, then any
distribution with no hash, then any distribution with a mismatched hash.
As a result, if an index reports incorrect hashes, but the user provides
the correct one, resolution now succeeds, where it would've failed.
Similarly, if an index omits hashes altogether, but the user provides
the correct one, resolution now succeeds, where it would've failed.
If we end up picking a distribution whose hash ultimately doesn't match,
we'll reject it later, after resolution.
## Summary
This PR adds support for hash-checking mode in `pip install` and `pip
sync`. It's a large change, both in terms of the size of the diff and
the modifications in behavior, but it's also one that's hard to merge in
pieces (at least, with any test coverage) since it needs to work
end-to-end to be useful and testable.
Here are some of the most important highlights:
- We store hashes in the cache. Where we previously stored pointers to
unzipped wheels in the `archives` directory, we now store pointers with
a set of known hashes. So every pointer to an unzipped wheel also
includes its known hashes.
- By default, we don't compute any hashes. If the user runs with
`--require-hashes`, and the cache doesn't contain those hashes, we
invalidate the cache, redownload the wheel, and compute the hashes as we
go. For users that don't run with `--require-hashes`, there will be no
change in performance. For users that _do_, the only change will be if
they don't run with `--generate-hashes` -- then they may see some
repeated work between resolution and installation, if they use `pip
compile` then `pip sync`.
- Many of the distribution types now include a `hashes` field, like
`CachedDist` and `LocalWheel`.
- Our behavior is similar to pip, in that we enforce hashes when pulling
any remote distributions, and when pulling from our own cache. Like pip,
though, we _don't_ enforce hashes if a distribution is _already_
installed.
- Hash validity is enforced in a few different places:
1. During resolution, we enforce hash validity based on the hashes
reported by the registry. If we need to access a source distribution,
though, we then enforce hash validity at that point too, prior to
running any untrusted code. (This is enforced in the distribution
database.)
2. In the install plan, we _only_ add cached distributions that have
matching hashes. If a cached distribution is missing any hashes, or the
hashes don't match, we don't return them from the install plan.
3. In the downloader, we _only_ return distributions with matching
hashes.
4. The final combination of "things we install" are: (1) the wheels from
the cache, and (2) the downloaded wheels. So this ensures that we never
install any mismatching distributions.
- Like pip, if `--require-hashes` is provided, we require that _all_
distributions are pinned with either `==` or a direct URL. We also
require that _all_ distributions have hashes.
There are a few notable TODOs:
- We don't support hash-checking mode for unnamed requirements. These
should be _somewhat_ rare, though? Since `pip compile` never outputs
unnamed requirements. I can fix this, it's just some additional work.
- We don't automatically enable `--require-hashes` with a hash exists in
the requirements file. We require `--require-hashes`.
Closes#474.
## Test Plan
I'd like to add some tests for registries that report incorrect hashes,
but otherwise: `cargo test`
## Summary
This lets us remove circular dependencies (in the future, e.g., #2945)
that arise from `FlatIndex` needing a bunch of resolver-specific
abstractions (like incompatibilities, required hashes, etc.) that aren't
necessary to _fetch_ the flat index entries.
## Summary
If the user runs with `--generate-hashes`, and the lockfile doesn't
contain _any_ hashes for a package (despite being pinned), we should add
new hashes. This mirrors running `uv pip compile --generate-hashes` for
the first time with an existing lockfile.
Closes#2962.
## Summary
If we build a source distribution from the registry, and the version
doesn't match that of the filename, we should error, just as we do for
mismatched package names. However, we should also backtrack here, which
we didn't previously.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2953.
## Test Plan
Verified that `cargo run pip install docutils --verbose --no-cache
--reinstall` installs `docutils==0.21` instead of the invalid
`docutils==0.21.post1`.
In the logs, I see:
```
WARN Unable to extract metadata for docutils: Package metadata version `0.21` does not match given version `0.21.post1`
```
## Summary
The prefetcher tallies the number of times we tried a given package, and
then once we hit a threshold, grabs the version map, assuming it's
already been fetched. For direct URL distributions, though, we don't
have a version map! And there's no need to prefetch.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2941.
## Summary
Right now, we have a `Hashes` representation that looks like:
```rust
/// A dictionary mapping a hash name to a hex encoded digest of the file.
///
/// PEP 691 says multiple hashes can be included and the interpretation is left to the client.
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Eq, PartialEq, Default, Deserialize)]
pub struct Hashes {
pub md5: Option<Box<str>>,
pub sha256: Option<Box<str>>,
pub sha384: Option<Box<str>>,
pub sha512: Option<Box<str>>,
}
```
It stems from the PyPI API, which returns a dictionary of hashes.
We tend to pass these around as a vector of `Vec<Hashes>`. But it's a
bit strange because each entry in that vector could contain multiple
hashes. And it makes it difficult to ask questions like "Is
`sha256:ab21378ca980a8` in the set of hashes"?
This PR instead treats `Hashes` as the PyPI-internal type, and uses a
new `Vec<HashDigest>` everywhere in our own APIs.
Needed to prevent circular dependencies in my toolchain work (#2931). I
think this is probably a reasonable change as we move towards persistent
configuration too?
Unfortunately `BuildIsolation` needs to be in `uv-types` to avoid
circular dependencies still. We might be able to resolve that in the
future.
With pubgrub being fast for complex ranges, we can now compute the next
n candidates without taking a performance hit. This speeds up cold cache
`urllib3<1.25.4` `boto3` from maybe 40s - 50s to ~2s. See docstrings for
details on the heuristics.
**Before**

**After**

---
We need two parts of the prefetching, first looking for compatible
version and then falling back to flat next versions. After we selected a
boto3 version, there is only one compatible botocore version remaining,
so when won't find other compatible candidates for prefetching. We see
this as a pattern where we only prefetch boto3 (stack bars), but not
botocore (sequential requests between the stacked bars).

The risk is that we're completely wrong with the guess and cause a lot
of useless network requests. I think this is acceptable since this
mechanism only triggers when we're already on the bad path and we should
simply have fetched all versions after some seconds (assuming a fast
index like pypi).
---
It would be even better if the pubgrub state was copy-on-write so we
could simulate more progress than we actually have; currently we're
guessing what the next version is which could be completely wrong, but i
think this is still a valuable heuristic.
Fixes#170.
## Summary
Is this, perhaps, not totally necessary? It doesn't show up in any
fixtures beyond those that I added recently.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2846.
Batch prefetching needs more information from the candidate selector, so
i've split `select` into methods. Split out from #2452. No functional
changes.
## Summary
This partially revives https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/2135 (with
some modifications) to enable users to opt-in to looking for packages
across multiple indexes.
The behavior is such that, in version selection, we take _any_
compatible version from a "higher-priority" index over the compatible
versions of a "lower-priority" index, even if that means we might accept
an "older" version.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2775.
## Summary
Rather than storing the `redirects` on the resolver, this PR just
re-uses the "convert this URL to precise" logic when we convert to a
`Resolution` after-the-fact. I think this is a lot simpler: it removes
state from the resolver, and simplifies a lot of the hooks around
distribution fetching (e.g., `get_or_build_wheel_metadata` no longer
returns `(Metadata23, Option<Url>)`).
## Summary
This PR leverages our lookahead direct URL resolution to significantly
improve the range of Git URLs that we can accept (e.g., if a user
provides the same requirement, once as a direct dependency, and once as
a tag). We did some of this in #2285, but the solution here is more
general and works for arbitrary transitive URLs.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2614.
Originally a regression test for #2779 but we found out that there's
some weird behavior where different `anyio` versions were preferred
based on the platform.
Addresses panic introduced in #2596 and reported in
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2763#issuecomment-2030674936
When there are multiple versions of a package available, we remove the
existing packages before installing the resolved version to "fix" the
environment. We must remove all of the package versions and reinstall
because removing _any_ of the package versions could break the others.
Since reinstalls require a pull from the remote, this broke a contract
between the resolver and the planner which must always agree on which
packages should come from the remote. This further demonstrates that we
should be constructing the install plan with more concrete knowledge
from the resolver (i.e. `ResolvedDist` instead of `Requirement`) to
avoid having to manually ensure logic matches.
## Test plan
Fails on `main` with panic succeeds on branch
```
uv venv --seed
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install anyio==3.7.0 --ignore-installed
pip install anyio==4.0.0 --ignore-installed
cargo run -- pip install anyio black -v
```
## Summary
This fixes a potential bug that revealed itself in
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/2761. We don't run into this now
because we always use "allowed URLs", stores the "last" compatible URL
in the map. But the use of the "raw" URL (rather than the "canonical"
URL) means that other writers have to follow that same assumption and
iterate over dependencies in-order.
## Summary
This PR would enable us to support transitive URL requirements. The key
idea is to leverage the fact that...
- URL requirements can only come from URL requirements.
- URL requirements identify a _specific_ version, and so don't require
backtracking.
Prior to running the "real" resolver, we recursively resolve any URL
requirements, and collect all the known URLs upfront, then pass those to
the resolver as "lookahead" requirements. This means the resolver knows
upfront that if a given package is included, it _must_ use the provided
URL.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1808.
## Summary
We can access cache from `BuildContext`. This mirrors
`SourceDistCachedBuilder`, which doesn't accept `Cache` as an argument
and always accesses it through `BuildContext`.
## Summary
We iterate over the project "requirements" directly in a variety of
places. However, it's not always the case that an input "requirement" on
its own will _actually_ be part of the resolution, since we support
"overrides".
Historically, then, overrides haven't worked as expected for _direct_
dependencies (and we have some tests that demonstrate the current,
"wrong" behavior). This is just a bug, but it's not really one that
comes up in practice, since it's rare to apply an override to your _own_
dependency.
However, we're now considering expanding the lookahead concept to
include local transitive dependencies. In this case, it's more and more
important that overrides and constraints are handled consistently.
This PR modifies all the locations in which we iterate over requirements
directly, and modifies them to respect overrides (and constraints, where
necessary).
Previously, we did not consider installed distributions as candidates
while performing resolution. Here, we update the resolver to use
installed distributions that satisfy requirements instead of pulling new
distributions from the registry.
The implementation details are as follows:
- We now provide `SitePackages` to the `CandidateSelector`
- If an installed distribution satisfies the requirement, we prefer it
over remote distributions
- We do not want to allow installed distributions in some cases, i.e.,
upgrade and reinstall
- We address this by introducing an `Exclusions` type which tracks
installed packages to ignore during selection
- There's a new `ResolvedDist` wrapper with `Installed(InstalledDist)`
and `Installable(Dist)` variants
- This lets us pass already installed distributions throughout the
resolver
The user-facing behavior is thoroughly covered in the tests, but
briefly:
- Installing a package that depends on an already-installed package
prefers the local version over the index
- Installing a package with a name that matches an already-installed URL
package does not reinstall from the index
- Reinstalling (--reinstall) a package by name _will_ pull from the
index even if an already-installed URL package is present
- To reinstall the URL package, you must specify the URL in the request
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1661
Addresses:
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1476
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1856
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2093
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2282
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2383
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2560
## Test plan
- [x] Reproduction at `charlesnicholson/uv-pep420-bug` passes
- [x] Unit test for editable package
([#1476](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1476))
- [x] Unit test for previously installed package with empty registry
- [x] Unit test for local non-editable package
- [x] Unit test for new version available locally but not in registry
([#2093](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2093))
- ~[ ] Unit test for wheel not available in registry but already
installed locally
([#2282](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2282))~ (seems
complicated and not worthwhile)
- [x] Unit test for install from URL dependency then with matching
version ([#2383](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2383))
- [x] Unit test for install of new package that depends on installed
package does not change version
([#2560](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2560))
- [x] Unit test that `pip compile` does _not_ consider installed
packages
## Summary
This looks like a big change but it really isn't. Rather, I just split
`get_or_build_wheel` into separate `get_wheel` and `build_wheel` methods
internally, which made `get_or_build_wheel_metadata` capable of _not_
relying on `Tags`, which in turn makes it easier for us to use the
`DistributionDatabase` in various places without having it coupled to an
interpreter or environment (something we already did for
`SourceDistributionBuilder`).
## Summary
This PR enables the resolver to "accept" URLs, prereleases, and local
version specifiers for direct dependencies of path dependencies. As a
result, `uv pip install .` and `uv pip install -e .` now behave
identically, in that neither has a restriction on URL dependencies and
the like.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2643.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1853.
## Summary
This PR removes the custom `DistFinder` that we use in `pip sync`. This
originally existed because `VersionMap` wasn't lazy, and so we saved a
lot of time in `DistFinder` by reading distribution data lazily. But
now, AFAICT, there's really no benefit. Maintaining `DistFinder` means
we effectively have to maintain two resolvers, and end up fixing bugs in
`DistFinder` that don't exist in the `Resolver` (like #2688.
Closes#2694.
Closes#2443.
## Test Plan
I ran this benchmark a bunch. It's basically a wash. Sometimes one is
faster than the other.
```
❯ python -m scripts.bench \
--uv-path ./target/release/main \
--uv-path ./target/release/uv \
scripts/requirements/compiled/trio.txt --min-runs 50 --benchmark install-warm --warmup 25
Benchmark 1: ./target/release/main (install-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 54.0 ms ± 10.6 ms [User: 8.7 ms, System: 98.1 ms]
Range (min … max): 45.5 ms … 94.3 ms 50 runs
Warning: Statistical outliers were detected. Consider re-running this benchmark on a quiet PC without any interferences from other programs. It might help to use the '--warmup' or '--prepare' options.
Benchmark 2: ./target/release/uv (install-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 50.7 ms ± 9.2 ms [User: 8.7 ms, System: 98.6 ms]
Range (min … max): 44.0 ms … 98.6 ms 50 runs
Warning: The first benchmarking run for this command was significantly slower than the rest (77.6 ms). This could be caused by (filesystem) caches that were not filled until after the first run. You should consider using the '--warmup' option to fill those caches before the actual benchmark. Alternatively, use the '--prepare' option to clear the caches before each timing run.
Summary
'./target/release/uv (install-warm)' ran
1.06 ± 0.29 times faster than './target/release/main (install-warm)'
```
## Summary
In `pip sync`, we weren't properly handling cases in which a package
_only_ existed in `--find-links` (e.g., the user passed `--offline` or
`--no-index`).
I plan to explore removing `Finder` entirely to avoid these mismatch
bugs between `pip sync` and other commands, but this is fine for now.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2688.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
For $reasons, we'll want to be able to clone a `Manifest` so
that it can be re-used to generate a marker expression.
There is likely a refactoring that could be done to avoid the
cloning, but a `Manifest` is likely to be small in practice, and
we'll only need to clone it once.
This is driving me a little crazy and is becoming a larger problem in
#2596 where I need to move more types (like `Upgrade` and `Reinstall`)
into this crate. Anything that's shared across our core resolver,
install, and build crates needs to be defined in this crate to avoid
cyclic dependencies. We've outgrown it being a single file with some
shared traits.
There are no behavioral changes here.
With https://github.com/pubgrub-rs/pubgrub/pull/190, pubgrub attaches
all types to a dependency provider to reduce the number of generics. We
need a dummy dependency provider now to emulate this. On the plus side,
pep440_rs drops its pubgrub dependency.
## Summary
This PR enables the source distribution database to be used with unnamed
requirements (i.e., URLs without a package name). The (significant)
upside here is that we can now use PEP 517 hooks to resolve unnamed
requirement metadata _and_ reuse any computation in the cache.
The changes to `crates/uv-distribution/src/source/mod.rs` are quite
extensive, but mostly mechanical. The core idea is that we introduce a
new `BuildableSource` abstraction, which can either be a distribution,
or an unnamed URL:
```rust
/// A reference to a source that can be built into a built distribution.
///
/// This can either be a distribution (e.g., a package on a registry) or a direct URL.
///
/// Distributions can _also_ point to URLs in lieu of a registry; however, the primary distinction
/// here is that a distribution will always include a package name, while a URL will not.
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy)]
pub enum BuildableSource<'a> {
Dist(&'a SourceDist),
Url(SourceUrl<'a>),
}
```
All the methods on the source distribution database now accept
`BuildableSource`. `BuildableSource` has a `name()` method, but it
returns `Option<&PackageName>`, and everything is required to work with
and without a package name.
The main drawback of this approach (which isn't a terrible one) is that
we can no longer include the package name in the cache. (We do continue
to use the package name for registry-based distributions, since those
always have a name.). The package name was included in the cache route
for two reasons: (1) it's nice for debugging; and (2) we use it to power
`uv cache clean flask`, to identify the entries that are relevant for
Flask.
To solve this, I changed the `uv cache clean` code to look one level
deeper. So, when we want to determine whether to remove the cache entry
for a given URL, we now look into the directory to see if there are any
wheels that match the package name. This isn't as nice, but it does work
(and we have test coverage for it -- all passing).
I also considered removing the package name from the cache routes for
non-registry _wheels_, for consistency... But, it would require a cache
bump, and it didn't feel important enough to merit that.
## Summary
First piece of https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/313. In order to
support unnamed requirements, we need to be able to parse them in
`requirements-txt`, which in turn means that we need to introduce a new
type that's distinct from `pep508::Requirement`, given that these
_aren't_ PEP 508-compatible requirements.
Part of: https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/313.
Scott schafer got me the idea: We can avoid repeating the path for
workspaces dependencies everywhere if we declare them in the virtual
package once and treat them as workspace dependencies from there on.
## Summary
We strip extras by default, but there are some valid use-cases in which
they're required (see the linked issue). This PR doesn't change our
default, but it does add `--no-strip-extras`, which lets users preserve
extras in the output requirements.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1595.
## Summary
I tried out `cargo shear` to see if there are any unused dependencies
that `cargo udeps` isn't reporting. It turned out, there are a few. This
PR removes those dependencies.
## Test Plan
`cargo build`
## Summary
When a user runs with `--output-file` and `--generate-hashes`, we should
_only_ update the hashes if the pinned version itself changes.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1530.
## Summary
This PR adds limited support for PEP 440-compatible local version
testing. Our behavior is _not_ comprehensively in-line with the spec.
However, it does fix by _far_ the biggest practical limitation, and
resolves all the issues that've been raised on uv related to local
versions without introducing much complexity into the resolver, so it
feels like a good tradeoff for me.
I'll summarize the change here, but for more context, see [Andrew's
write-up](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1855#issuecomment-1967024866)
in the linked issue.
Local version identifiers are really tricky because of asymmetry.
`==1.2.3` should allow `1.2.3+foo`, but `==1.2.3+foo` should not allow
`1.2.3`. It's very hard to map them to PubGrub, because PubGrub doesn't
think of things in terms of individual specifiers (unlike the PEP 440
spec) -- it only thinks in terms of ranges.
Right now, resolving PyTorch and friends fails, because...
- The user provides requirements like `torch==2.0.0+cu118` and
`torchvision==0.15.1+cu118`.
- We then match those exact versions.
- We then look at the requirements of `torchvision==0.15.1+cu118`, which
includes `torch==2.0.0`.
- Under PEP 440, this is fine, because `torch @ 2.0.0+cu118` should be
compatible with `torch==2.0.0`.
- In our model, though, it's not, because these are different versions.
If we change our comparison logic in various places to allow this, we
risk breaking some fundamental assumptions of PubGrub around version
continuity.
- Thus, we fail to resolve, because we can't accept both `torch @ 2.0.0`
and `torch @ 2.0.0+cu118`.
As compared to the solutions we explored in
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1855#issuecomment-1967024866, at
a high level, this approach differs in that we lie about the
_dependencies_ of packages that rely on our local-version-using package,
rather than lying about the versions that exist, or the version we're
returning, etc.
In short:
- When users specify local versions upfront, we keep track of them. So,
above, we'd take note of `torch` and `torchvision`.
- When we convert the dependencies of a package to PubGrub ranges, we
check if the requirement matches `torch` or `torchvision`. If it's
an`==`, we check if it matches (in the above example) for
`torch==2.0.0`. If so, we _change_ the requirement to
`torch==2.0.0+cu118`. (If it's `==` some other version, we return an
incompatibility.)
In other words, we selectively override the declared dependencies by
making them _more specific_ if a compatible local version was specified
upfront.
The net effect here is that the motivating PyTorch resolutions all work.
And, in general, transitive local versions work as expected.
The thing that still _doesn't_ work is: imagine if there were _only_
local versions of `torch` available. Like, `torch @ 2.0.0` didn't exist,
but `torch @ 2.0.0+cpu` did, and `torch @ 2.0.0+gpu` did, and so on.
`pip install torch==2.0.0` would arbitrarily choose one one `2.0.0+cpu`
or `2.0.0+gpu`, and that's correct as per PEP 440 (local version
segments should be completely ignored on `torch==2.0.0`). However, uv
would fail to identify a compatible version. I'd _probably_ prefer to
fix this, although candidly I think our behavior is _ok_ in practice,
and it's never been reported as an issue.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1855.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2080.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2328.
## Summary
This PR attempts to use a similar trick to that we added in
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/1878, but for post-releases.
In https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/1878, we added a fake "minimum"
version to enable us to treat `< 1.0.0` as _excluding_ pre-releases of
1.0.0.
Today, on `main`, we accept post-releases and local versions in `>
1.0.0`. But per PEP 440, that should _exclude_ post-releases and local
versions, unless the specifier is itself a pre-release, in which case,
pre-releases are allowed (e.g., `> 1.0.0.post0` should allow `>
1.0.0.post1`).
To support this, we add a fake "maximum" version that's greater than all
the post and local releases for a given version. This leverages our last
remaining free bit in the compact representation.
The architecture of uv does not necessarily match that of the python
interpreter (#2326). In cross compiling/testing scenarios the operating
system can also mismatch. To solve this, we move arch and os detection
to python, vendoring the relevant pypa/packaging code, preventing
mismatches between what the python interpreter was compiled for and what
uv was compiled for.
To make the scripts more manageable, they are now a directory in a
tempdir and we run them with `python -m` . I've simplified the
pypa/packaging code since we're still building the tags in rust. A
`Platform` is now instantiated by querying the python interpreter for
its platform. The pypa/packaging files are copied verbatim for easier
updates except a `lru_cache()` python 3.7 backport.
Error handling is done by a `"result": "success|error"` field that allow
passing error details to rust:
```console
$ uv venv --no-cache
× Can't use Python at `/home/konsti/projects/uv/.venv/bin/python3`
╰─▶ Unknown operation system `linux`
```
I've used the [maturin sysconfig
collection](855f6d2cb1/sysconfig)
as reference. I'm unsure how to test these changes across the wide
variety of platforms.
Fixes#2326
## Summary
Per [PEP 508](https://peps.python.org/pep-0508/), `python_version` is
just major and minor:

Right now, we're using the provided version directly, so if it's, e.g.,
`-p 3.11.8`, we'll inject the wrong marker. This was causing `pandas` to
omit `numpy` when `-p 3.11.8` was provided, since its markers look like:
```
Requires-Dist: numpy<2,>=1.22.4; python_version < "3.11"
Requires-Dist: numpy<2,>=1.23.2; python_version == "3.11"
Requires-Dist: numpy<2,>=1.26.0; python_version >= "3.12"
```
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2392.
## Summary
This PR ensures that we expand environment variables _before_ sniffing
for the URL scheme (e.g., `file://` vs. `https://` vs. something else).
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2375.
## Summary
This is a more robust fix for
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2300.
The basic issue is:
- When we resolve, we attempt to pre-fetch the distribution metadata for
candidate packages.
- It's possible that the resolution completes _without_ those pre-fetch
responses. (In the linked issue, this was mainly because we were running
with `--no-deps`, but the pre-fetch was causing us to attempt to build a
package to get its dependencies. The resolution would then finish before
the build completed.)
- In that case, the `Index` will be marked as "waiting" for that
response -- but it'll never come through.
- If there's a subsequent call to the `Index`, to see if we should fetch
or are waiting for that response, we'll end up waiting for it forever,
since it _looks_ like it's in-flight (but isn't). (In the linked issue,
we had to build the source distribution for the install phase of `pip
install`, but `setuptools` was in this bad state from the _resolve_
phase.)
This PR modifies the resolver to ensure that we flush the stream of
requests before returning. Specifically, we now `join` rather than
`select` between the resolution and request-handling futures.
This _could_ be wasteful, since we don't _need_ those requests, but it
at least ensures that every `.wait` is followed by ` .done`. In
practice, I expect this not to have any significant effect on
performance, since we end up using the pre-fetched distributions almost
every time.
## Test Plan
I ran through the test plan from
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/2373, but ran the build 10 times
and ensured it never crashed. (I reverted
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/2373, since that _also_ fixes the
issue in the proximate case, by never fetching `setuptools` during the
resolve phase.)
I also added logging to verify that requests are being handled _after_
the resolution completes, as expected.
I also introduced an arbitrary error in `fetch` to ensure that the error
was immediately propagated.
## Summary
When running under `--no-deps`, we don't need to pre-fetch, because
pre-fetching fetches the _distribution_ metadata. But with `--no-deps`,
we only need the package metadata for the top-level requirements. We
never need distribution metadata.
Incidentally, this will fix https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2300.
## Test Plan
- `cargo test`
- `./target/debug/uv pip install --verbose --no-cache-dir --no-deps
--reinstall ddtrace==2.6.2 debugpy==1.8.1 ecdsa==0.18.0
editorconfig==0.12.4 --verbose` in a Python 3.10 Docker contain
repeatedly.
## Summary
It turns out that when we iterate over the incompatibilities of a
package, PubGrub will _also_ show us the inverse dependencies. I suspect
this was rare, because we have a version check at the bottom... So, this
specifically required that you had some dependency that didn't end up
appearing in the output resolution, but that matched the version
constraints of the package you care about.
In this case, `langchain-community` depends on `langchain-core`. So we
were seeing an incompatibility like:
```rust
FromDependencyOf(Package(PackageName("langchain-community"), None, None), Range { segments: [(Included("0.0.10"), Included("0.0.10")), (Included("0.0.11"), Included("0.0.11"))] }, Package(PackageName("langchain-core"), None, None), Range { segments: [(Included("0.1.8"), Excluded("0.2"))] })
```
Where we were iterating over `langchain-core`, and looking for version
`0.0.11`... which happens to match `langchain-community`.
(`langchain-community was omitted from the resolution; hence, it didn't
exist in the map.)
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2358.
Extends the "compatibility" types introduced in #1293 to apply to source
distributions as well as wheels.
- We now track the most-relevant incompatible source distribution
- Exclude newer, Python requirements, and yanked versions are all
tracked as incompatibilities in the new model (this lets us remove
`DistMetadata`!)
## Summary
PyPI now supports Metadata 2.2, which means distributions with Metadata
2.2-compliant metadata will start to appear. The upside is that if a
source distribution includes a `PKG-INFO` file with (1) a metadata
version of 2.2 or greater, and (2) no dynamic fields (at least, of the
fields we rely on), we can read the metadata from the `PKG-INFO` file
directly rather than running _any_ of the PEP 517 build hooks.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2009.
## Summary
This PR removes the URL conflict errors when the output of a `uv pip
compile` is used as a constraint to a subsequent `uv pip compile`.
If you run `uv pip compile`, the output file will contain your Git
dependencies, but pinned to a specific commit, like:
```
git+https://github.com/pallets/werkzeug@32e69512134c2f8183c6438b2b2e13fd24e9d19f
```
If you then use the output as a constraint to a subsequent resolution
(e.g., perhaps you require
`git+https://github.com/pallets/werkzeug@main`), we currently fail. I
think this is a reasonable workflow to support when all of these
requirements are coming from _your own_ dependencies. So we now assume
when resolving that the former is a more precise variant of the latter.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1903.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2266.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
This PR adds support for pip's `--no-build-isolation`. When enabled,
build requirements won't be installed during PEP 517-style builds, but
the source environment _will_ be used when executing the build steps
themselves.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1715.
## Summary
When determining "direct" dependencies, we need to ensure that we
respect markers. In the linked issue, the user had an optional
dependency like:
```toml
[project.optional-dependencies]
dev = [
"setuptools>=64",
"setuptools_scm>=8"
]
```
By not respecting markers, we tried to resolve `setuptools` to the
lowest-available version. However, since `setuptools>=64` _isn't_
enabled (since it's optional), we won't respect _that_ constraint.
To be consistent, we need to omit optional dependencies just as we will
at resolution time.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2203.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
If a pre-release marker is present on a requirement in a constraint
file, we should allow pre-releases for that package.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2063.
## Summary
Internal refactor to `PrioritizedDistribution` that I think should
reduce the size? Although the motivation here is simplicity, not perf.
Instead of storing:
```rust
/// The highest-priority, installable wheel for the package version.
compatible_wheel: Option<(DistMetadata, TagPriority)>,
/// The most-relevant, incompatible wheel for the package version.
incompatible_wheel: Option<(DistMetadata, IncompatibleWheel)>,
```
We now store:
```rust
wheel: Option<(DistMetadata, WheelCompatibility)>,
```
Where `WheelCompatibility` is an enum of `TagPriority` or
`IncompatibleWheel`.
## Summary
`PythonPlatform` only exists to format paths to directories within
virtual environments based on a root and an OS, so it's now
`VirtualenvLayout`.
`Virtualenv` is now used for non-virtual environment Pythons, so it's
now `PythonEnvironment`.
## Summary
This PR adds a `--python` flag that allows users to provide a specific
Python interpreter into which `uv` should install packages. This would
replace the `VIRTUAL_ENV=` workaround that folks have been using to
install into arbitrary, system environments, while _also_ actually being
correct for installing into non-virtual environments, where the bin and
site-packages paths can differ.
The approach taken here is to use `sysconfig.get_paths()` to get the
correct paths from the interpreter, and then use those for determining
the `bin` and `site-packages` directories, rather than constructing them
based on hard-coded expectations for each platform.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1396.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1779.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1988.
## Test Plan
- Verified that, on my Windows machine, I was able to install `requests`
into a global environment with: `cargo run pip install requests --python
'C:\\Users\\crmarsh\\AppData\\Local\\Programs\\Python\\Python3.12\\python.exe`,
then `python` and `import requests`.
- Verified that, on macOS, I was able to install `requests` into a
global environment installed via Homebrew with: `cargo run pip install
requests --python $(which python3.8)`.
Address a few pedantic lints
lints are separated into separate commits so they can be reviewed
individually.
I've not added enforcement for any of these lints, but that could be
added if desirable.
## Summary
Even when pre-releases are "allowed", per PEP 440, `pydantic<2.0.0`
should _not_ include pre-releases. This PR modifies the specifier
translation to treat `pydantic<2.0.0` as `pydantic<2.0.0.min0`, where
`min` is an internal-only version segment that's invisible to users.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1641.
## Summary
In uv, we're going to use `--no-emit-package` for this, to convey that
the package will be included in the resolution but not in the output
file. It also mirrors flags like `--emit-index-url`.
We're also including an `--unsafe-package` alias.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1415.
We don't have test coverage for this, but a term can reference an
incompatibility with root and then we'll display the internal 'root'
package to the user.
Raised in https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1855
<!--
Thank you for contributing to uv! To help us out with reviewing, please
consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
To integrate `uv` into `pixi` I need to specify a custom
`ResolverProvider` to be able to specify that some packages are already
installed by conda and should not be touched. However, some of the types
required to implement your own `ResolverProvider` were not accessible
through the public API. This PR basically adds them.
## Test Plan
I didnt add an explicit test for this.
## Summary
This revives a PR from long ago
(https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/383 and
https://github.com/zanieb/pubgrub/pull/24) that modifies how we deal
with dependencies that are declared multiple times within a single
package.
To quote from the originating PR:
> Uses an experimental pubgrub branch (#370) that allows us to handle
multiple version ranges for a single dependency to the solver which
results in better error messages because the derivation tree contains
all of the relevant versions. Previously, the version ranges were merged
(by us) in the resolver before handing them to pubgrub since only one
range could be provided per package. Since we don't merge the versions
anymore, we no longer give the solver an empty range for conflicting
requirements; instead the solver comes to that conclusion from the
provided versions. You can see the improved error message for direct
dependencies in [this
snapshot](https://github.com/astral-sh/puffin/pull/383/files#diff-a0437f2c20cde5e2f15199a3bf81a102b92580063268417847ec9c793a115bd0).
The main issue with that PR was around its handling of URL dependencies,
so this PR _also_ refactors how we handle those. Previously, we stored
URL dependencies on `PubGrubPackage`, but they were omitted from the
hash and equality implementations of `PubGrubPackage`. This led to some
really careful codepaths wherein we had to ensure that we always visited
URLs before non-URL packages, so that the URL-inclusive versions were
included in any hashmaps, etc. I considered preserving this approach,
but it would require us to rely on lots of internal details of PubGrub
(since we'd now be relying on PubGrub to merge those packages in the
"right" order).
So, instead, we now _always_ set the URL on a given package, whenever
that package was _given_ a URL upfront. I think this is easier to reason
about: if the user provided a URL for `flask`, then we should just
always add the URL for `flask`. If we see some other URL for `flask`, we
error, like before. If we see some unknown URL for `flask`, we error,
like before.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1522.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1821.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1615.
## Summary
We still need to wait for the distribution metadata (for direct
dependencies), even when resolving with `--no-deps`, since we rely on it
to report diagnostics to the user.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1801.
## Summary
Hello there! The motivation for this feature is described here #1678
## Test Plan
I've added unit tests and also tested this manually on my work project
by comparing it to the original `pip-compile` output - it looks much
like the `pip-compile` generated lock file.
## Summary
The `DefaultResolverProvider` struct was not public. This PR exposes it
so we can build our own and use this as a fallback.
## Test Plan
I did not explicitly test this trivial change.
## Summary
If an editable package declares a direct URL requirement, we currently
error since it's not considered an "allowed" requirement. We need to add
those URLs to the allow-list.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1603.
## Summary
This was just a missing line -- we have `dependencies.remove(&package);`
in the ~identical branch above, but it must've been an oversight to omit
it here.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1467.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
If you're developing on a package like `attrs` locally, and it has a
recursive extra like `attrs[dev]`, it turns out that we then try to find
the `attrs` in `attrs[dev]` from the registry, rather than recognizing
that it's part of the editable.
This PR fixes the issue by making editables slightly more first-class
throughout the resolver. Instead of mocking metadata, we explicitly
check for extras in various places. Part of the problem here is that we
treated editables as URL dependencies, but when we saw an _extra_ like
`attrs[dev]`, we didn't map that back to the URL. So now, we treat them
as registry dependencies, but with the appropriate guardrails
throughout.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1447.
## Test Plan
- Cloned `attrs`.
- Ran `cargo run venv && cargo run pip install -e ".[dev]" -v`.
First, replace all usages in files in-place. I used my editor for this.
If someone wants to add a one-liner that'd be fun.
Then, update directory and file names:
```
# Run twice for nested directories
find . -type d -print0 | xargs -0 rename s/puffin/uv/g
find . -type d -print0 | xargs -0 rename s/puffin/uv/g
# Update files
find . -type f -print0 | xargs -0 rename s/puffin/uv/g
```
Then add all the files again
```
# Add all the files again
git add crates
git add python/uv
# This one needs a force-add
git add -f crates/uv-trampoline
```