## Summary
This is what I consider to be the "real" fix for #8072. We now treat
directory and path URLs as separate `ParsedUrl` types and
`RequirementSource` types. This removes a lot of `.is_dir()` forking
within the `ParsedUrl::Path` arms and makes some states impossible
(e.g., you can't have a `.whl` path that is editable). It _also_ fixes
the `direct_url.json` for direct URLs that refer to files. Previously,
we wrote out to these as if they were installed as directories, which is
just wrong.
By splitting `path` into a lockable, relative (or absolute) and an
absolute installable path and by splitting between urls and paths by
dist type, we can store relative paths in the lockfile.
When creating a lockfile, lock the combined dependencies for all
packages in a workspace. This make the lockfile independent of where you
are in the workspace.
Fixes#3983
## Summary
This PR separates "gathering the requirements" from the rest of the
metadata (e.g., version), which isn't required when installing a
package's _dependencies_ (as opposed to installing the package itself).
It thus ensures that we don't need to build a package when a static
`pyproject.toml` is provided in `pip compile`.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/4040.
## Summary
Given `install -e dagster`, we need to assume that the user meant
`install -e ./dagster`, even though `install dagster` should _not_ be
treated as `install ./dagster`. I suspect pip will change this in the
future (since `pip install dagster` does _not_ meant `pip install
./dagster`) but for now it's what users expect.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3994.
## Summary
This PR ensures that if a lockfile already contains a resolved reference
(e.g., you locked with `main` previously, and it locked to a specific
commit), and you run `uv lock`, we use the same SHA, even if it's not
the latest SHA for that tag. This avoids upgrading Git dependencies
without `--upgrade`.
Closes#3920.
## Summary
This will help prevent bugs like #3934 by unifying the implementations
for editables and non-editable unnamed requirements. Specifically, both
of these now go through the same parsing paths and use the same struct
representations (with the exception that the editable flag is flipped in
the first case):
```
-e ./foo/bar
./foo/bar
```
We also now support PEP 508 in editable URLs. It turns out this is just
a limitation in pip, so it's correct to support it. For example, this
now works:
```
-e black[d] @ file://${PROJECT_ROOT}/scripts/packages/black_editable
```
Closes#3941.
Closes#3942.
With the change, we remove the special casing of workspace dependencies
and resolve `tool.uv` for all git and directory distributions. This
gives us support for non-editable workspace dependencies and path
dependencies in other workspaces. It removes a lot of special casing
around workspaces. These changes are the groundwork for supporting
`tool.uv` with dynamic metadata.
The basis for this change is moving `Requirement` from
`distribution-types` to `pypi-types` and the lowering logic from
`uv-requirements` to `uv-distribution`. This changes should be split out
in separate PRs.
I've included an example workspace `albatross-root-workspace2` where
`bird-feeder` depends on `a` from another workspace `ab`. There's a
bunch of failing tests and regressed error messages that still need
fixing. It does fix the audited package count for the workspace tests.
## Summary
In general, it's not quite right to filter preferences by `--reinstall`
-- we still want to respect existing versions, we just don't want to
respect _installed_ versions. But now that the installed versions and
preferences are decoupled, we can remove this (`--reinstall` is enforced
on the installed versions via the `Exclusions` struct that we pass to
the resolver).
While I was here, I also cleaned up the lockfile preference code to
better match the structure for `requirements.txt`.
## Summary
This PR just ensures that when running `uv lock` (or `uv run`), we lock
with all extras. When we later install, we'll also _install_ with all
extras, but that will be changed in a future PR.
## Summary
There are a few behavior changes in here:
- We now enforce `--require-hashes` for editables, like pip. So if you
use `--require-hashes` with an editable requirement, we'll reject it. I
could change this if it seems off.
- We now treat source tree requirements, editable or not (e.g., both `-e
./black` and `./black`) as if `--refresh` is always enabled. This
doesn't mean that we _always_ rebuild them; but if you pass
`--reinstall`, then yes, we always rebuild them. I think this is an
improvement and is close to how editables work today.
Closes#3844.
Closes#2695.
Add workspace support when using `-r <path>/pyproject.toml` or `-e
<path>` in the pip interface. It is limited to all-editable
static-metadata workspaces, and tests only include a single main
workspace, ignoring path dependencies in another workspace. This can be
considered the MVP for workspace support: You can create a workspace,
you can install from it, but some options and conveniences are still
missing. I'll file follow-up tickets (support in lockfiles, support path
deps in other workspace, #3625)
There is also support in `uv run`, but we need
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3700 first to properly support
using different current projects in the bluejay interface, currently the
resolution and therefore the lockfile depends on the current project.
I'd do this change first (it's big enough already), then #3700, and then
add workspace support properly to bluejay.
Fixes#3404
## Summary
We actually _already_ ignore these (preferences only apply to versions,
not URLs), it just happens later on. This PR thus just avoids crashing.
The behavior is unchanged.
Closes#3822.
When parsing requirements from any source, directly parse the url parts
(and reject unsupported urls) instead of parsing url parts at a later
stage. This removes a bunch of error branches and concludes the work
parsing url parts once and passing them around everywhere.
Many usages of the assembled `VerbatimUrl` remain, but these can be
removed incrementally.
Please review commit-by-commit.
## Summary
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3715.
## Test Plan
```
❯ echo "/../test" | cargo run pip compile -
error: Couldn't parse requirement in `-` at position 0
Caused by: path could not be normalized: /../test
/../test
^^^^^^^^
❯ echo "-e /../test" | cargo run pip compile -
error: Invalid URL in `-`: `/../test`
Caused by: path could not be normalized: /../test
Caused by: cannot normalize a relative path beyond the base directory
```
I don't really understand why this only happens on windows clippy and
not on linux too, but as usual, boxing the error variant fixes it.
Fixup for #3585
Add minimal support for workspace discovery, only used for determining
paths in the bluejay commands.
We can now discover the workspace structure, namely that the
`pyproject.toml` of a package belongs to a workspace `pyproject.toml`
with members and exclusion. The globbing logic is inspired by cargo. We
don't resolve `workspace = true` metadata declarations yet.
This is split out from workspaces support, which needs editables in the
bluejay commands. It consists mainly of refactorings:
* Move the `editable` module one level up.
* Introduce a `BuiltEditableMetadata` type for `(LocalEditable,
Metadata23, Requirements)`.
* Add editables to `InstalledPackagesProvider` so we can use
`EmptyInstalledPackages` for them.
## Summary
This PR introduces parallelism to the resolver. Specifically, we can
perform PubGrub resolution on a separate thread, while keeping all I/O
on the tokio thread. We already have the infrastructure set up for this
with the channel and `OnceMap`, which makes this change relatively
simple. The big change needed to make this possible is removing the
lifetimes on some of the types that need to be shared between the
resolver and pubgrub thread.
A related PR, https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/1163, found that
adding `yield_now` calls improved throughput. With optimal scheduling we
might be able to get away with everything on the same thread here.
However, in the ideal pipeline with perfect prefetching, the resolution
and prefetching can run completely in parallel without depending on one
another. While this would be very difficult to achieve, even with our
current prefetching pattern we see a consistent performance improvement
from parallelism.
This does also require reverting a few of the changes from
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/3413, but not all of them. The
sharing is isolated to the resolver task.
## Test Plan
On smaller tasks performance is mixed with ~2% improvements/regressions
on both sides. However, on medium-large resolution tasks we see the
benefits of parallelism, with improvements anywhere from 10-50%.
```
./scripts/requirements/jupyter.in
Benchmark 1: ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 29.2 ms ± 1.8 ms [User: 20.3 ms, System: 29.8 ms]
Range (min … max): 26.4 ms … 36.0 ms 91 runs
Benchmark 2: ./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 25.5 ms ± 1.0 ms [User: 19.5 ms, System: 25.5 ms]
Range (min … max): 23.6 ms … 27.8 ms 99 runs
Summary
./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm) ran
1.15 ± 0.08 times faster than ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
```
```
./scripts/requirements/boto3.in
Benchmark 1: ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 487.1 ms ± 6.2 ms [User: 464.6 ms, System: 61.6 ms]
Range (min … max): 480.0 ms … 497.3 ms 10 runs
Benchmark 2: ./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 430.8 ms ± 9.3 ms [User: 529.0 ms, System: 77.2 ms]
Range (min … max): 417.1 ms … 442.5 ms 10 runs
Summary
./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm) ran
1.13 ± 0.03 times faster than ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
```
```
./scripts/requirements/airflow.in
Benchmark 1: ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 478.1 ms ± 18.8 ms [User: 482.6 ms, System: 205.0 ms]
Range (min … max): 454.7 ms … 508.9 ms 10 runs
Benchmark 2: ./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm)
Time (mean ± σ): 308.7 ms ± 11.7 ms [User: 428.5 ms, System: 209.5 ms]
Range (min … max): 287.8 ms … 323.1 ms 10 runs
Summary
./target/profiling/parallel (resolve-warm) ran
1.55 ± 0.08 times faster than ./target/profiling/baseline (resolve-warm)
```
## Summary
I think this is overall good change because it explicitly encodes (in
the type system) something that was previously implicit. I'm not a huge
fan of the names here, open to input.
It covers some of https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3506 but I
don't think it _closes_ it.
## Summary
This PR consolidates the concurrency limits used throughout `uv` and
exposes two limits, `UV_CONCURRENT_DOWNLOADS` and
`UV_CONCURRENT_BUILDS`, as environment variables.
Currently, `uv` has a number of concurrent streams that it buffers using
relatively arbitrary limits for backpressure. However, many of these
limits are conflated. We run a relatively small number of tasks overall
and should start most things as soon as possible. What we really want to
limit are three separate operations:
- File I/O. This is managed by tokio's blocking pool and we should not
really have to worry about it.
- Network I/O.
- Python build processes.
Because the current limits span a broad range of tasks, it's possible
that a limit meant for network I/O is occupied by tasks performing
builds, reading from the file system, or even waiting on a `OnceMap`. We
also don't limit build processes that end up being required to perform a
download. While this may not pose a performance problem because our
limits are relatively high, it does mean that the limits do not do what
we want, making it tricky to expose them to users
(https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1205,
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3311).
After this change, the limits on network I/O and build processes are
centralized and managed by semaphores. All other tasks are unbuffered
(note that these tasks are still bounded, so backpressure should not be
a problem).
## Summary
Ensures that we track the origins for requirements regardless of whether
they come from `pyproject.toml` or `setup.py` or `setup.cfg`.
Closes#3480.
This commit touches a lot of code, but the conceptual change here is
pretty simple: make it so we can run the resolver without providing a
`MarkerEnvironment`. This also indicates that the resolver should run in
universal mode. That is, the effect of a missing marker environment is
that all marker expressions that reference the marker environment are
evaluated to `true`. That is, they are ignored. (The only markers we
evaluate in that context are extras, which are the only markers that
aren't dependent on the environment.)
One interesting change here is that a `Resolver` no longer needs an
`Interpreter`. Previously, it had only been using it to construct a
`PythonRequirement`, by filling in the installed version from the
`Interpreter` state. But we now construct a `PythonRequirement`
explicitly since its `target` Python version should no longer be tied to
the `MarkerEnvironment`. (Currently, the marker environment is mutated
such that its `python_full_version` is derived from multiple sources,
including the CLI, which I found a touch confusing.)
The change in behavior can now be observed through the
`--unstable-uv-lock-file` flag. First, without it:
```
$ cat requirements.in
anyio>=4.3.0 ; sys_platform == "linux"
anyio<4 ; sys_platform == "darwin"
$ cargo run -qp uv -- pip compile -p3.10 requirements.in
anyio==4.3.0
exceptiongroup==1.2.1
# via anyio
idna==3.7
# via anyio
sniffio==1.3.1
# via anyio
typing-extensions==4.11.0
# via anyio
```
And now with it:
```
$ cargo run -qp uv -- pip compile -p3.10 requirements.in --unstable-uv-lock-file
x No solution found when resolving dependencies:
`-> Because you require anyio>=4.3.0 and anyio<4, we can conclude that the requirements are unsatisfiable.
```
This is expected at this point because the marker expressions are being
explicitly ignored, *and* there is no forking done yet to account for
the conflict.
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1343. This is kinda a first
draft at the moment, but does at least mostly work locally (barring some
bits of the test suite that seem to not work for me in general).
## Test Plan
Mostly running the existing tests and checking the revised output is
sane
## Outstanding issues
Most of these come down to "AFAIK, the existing tools don't support
these patterns, but `uv` does" and so I'm not sure there's an existing
good answer here! Most of the answers so far are "whatever was easiest
to build"
- [x] ~~Is "-r pyproject.toml" correct? Should it show something else or
get skipped entirely~~ No it wasn't. Fixed in
3044fa8b86
- [ ] If the requirements file is stdin, that just gets skipped. Should
it be recorded?
- [ ] Overrides get shown as "--override<override.txt>". Correct?
- [x] ~~Some of the tests (e.g.
`dependency_excludes_non_contiguous_range_of_compatible_versions`) make
assumptions about the order of package versions being outputted, which
this PR breaks. I'm not sure if the text is fairly arbitrary and can be
replaced or whether the behaviour needs fixing?~~ - fixed by removing
the custom pubgrub PartialEq/Hash
- [ ] Are all the `TrackedFromStr` et al changes needed, or is there an
easier way? I don't think so, I think it's necessary to track these sort
of things fairly comprehensively to make this feature work, and this
sort of invasive change feels necessary, but happy to be proved wrong
there :)
- [x] ~~If you have a requirement coming in from two or more different
requirements files only one turns up. I've got a closed-source example
for this (can go into more detail if needed), mostly consisting of a
complicated set of common deps creating a larger set. It's a rarer case,
but worth considering.~~ 042432b200
- [ ] Doesn't add annotations for `setup.py` yet
- This is pretty hard, as the correct location to insert the path is
`crates/pypi-types/src/metadata.rs`'s `parse_pkg_info`, which as it's
based off a source distribution has entirely thrown away such matters as
"where did this package requirement get built from". Could add "`built
package name`" as a dep, but that's a little odd.
When using `tool.uv.sources`, we warn that requirements have a bound,
i.e. at least a lower version constraint.
When using a library, the symbols you import were introduced in
different versions, creating an implicit lower bound. This warning makes
this explicit. This is crucial to prevent backtracking resolvers from
selecting an ancient versions that is not compatible (or worse, doesn't
build), and a performance optimization on top.
This feature is gated to `tool.uv.sources` (as it should have been to
begin with for #3263/#3443) to not unnecessarily break legacy workflows.
It is also helpful specifically when using a `tool.uv.sources` section
that contains constraints that are not published to pypi, e.g. for
workspace dependencies. We can adjust those later to e.g. not constrain
workspace dependencies with `publish = false`, but i think it's the
right setting to start with.
## Summary
It's not clear to me that this should exist at all, but it's causing
errors in projects that don't use `tool.uv.sources`, so we should
definitely remove it for now.
We now correctly emit relative paths in `uv pip compile` with
`tool.uv.sources` path inputs.
`tool.uv.sources` is mainly intended to be used with the uv lock file
over requirements.txt, but it's good to have basic `uv pip` support
working.
Fixes#3366
## Summary
All of the resolver code is run on the main thread, so a lot of the
`Send` bounds and uses of `DashMap` and `Arc` are unnecessary. We could
also switch to using single-threaded versions of `Mutex` and `Notify` in
some places, but there isn't really a crate that provides those I would
be comfortable with using.
The `Arc` in `OnceMap` can't easily be removed because of the uv-auth
code which uses the
[reqwest-middleware](https://docs.rs/reqwest-middleware/latest/reqwest_middleware/trait.Middleware.html)
crate, that seems to adds unnecessary `Send` bounds because of
`async-trait`. We could duplicate the code and create a `OnceMapLocal`
variant, but I don't feel that's worth it.
Only allow using `tool.uv.sources` with preview mode, the design isn't
finalized yet.
Not sure what to label this, do we want a preview section and label for
the release notes?
## Summary
We need to partition the editable and non-editable requirements. As-is,
`editable = true` requirements were still being installed as
non-editable.
## Introduction
PEP 621 is limited. Specifically, it lacks
* Relative path support
* Editable support
* Workspace support
* Index pinning or any sort of index specification
The semantics of urls are a custom extension, PEP 440 does not specify
how to use git references or subdirectories, instead pip has a custom
stringly format. We need to somehow support these while still stying
compatible with PEP 621.
## `tool.uv.source`
Drawing inspiration from cargo, poetry and rye, we add `tool.uv.sources`
or (for now stub only) `tool.uv.workspace`:
```toml
[project]
name = "albatross"
version = "0.1.0"
dependencies = [
"tqdm >=4.66.2,<5",
"torch ==2.2.2",
"transformers[torch] >=4.39.3,<5",
"importlib_metadata >=7.1.0,<8; python_version < '3.10'",
"mollymawk ==0.1.0"
]
[tool.uv.sources]
tqdm = { git = "https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm", rev = "cc372d09dcd5a5eabdc6ed4cf365bdb0be004d44" }
importlib_metadata = { url = "https://github.com/python/importlib_metadata/archive/refs/tags/v7.1.0.zip" }
torch = { index = "torch-cu118" }
mollymawk = { workspace = true }
[tool.uv.workspace]
include = [
"packages/mollymawk"
]
[tool.uv.indexes]
torch-cu118 = "https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118"
```
See `docs/specifying_dependencies.md` for a detailed explanation of the
format. The basic gist is that `project.dependencies` is what ends up on
pypi, while `tool.uv.sources` are your non-published additions. We do
support the full range or PEP 508, we just hide it in the docs and
prefer the exploded table for easier readability and less confusing with
actual url parts.
This format should eventually be able to subsume requirements.txt's
current use cases. While we will continue to support the legacy `uv pip`
interface, this is a piece of the uv's own top level interface. Together
with `uv run` and a lockfile format, you should only need to write
`pyproject.toml` and do `uv run`, which generates/uses/updates your
lockfile behind the scenes, no more pip-style requirements involved. It
also lays the groundwork for implementing index pinning.
## Changes
This PR implements:
* Reading and lowering `project.dependencies`,
`project.optional-dependencies` and `tool.uv.sources` into a new
requirements format, including:
* Git dependencies
* Url dependencies
* Path dependencies, including relative and editable
* `pip install` integration
* Error reporting for invalid `tool.uv.sources`
* Json schema integration (works in pycharm, see below)
* Draft user-level docs (see `docs/specifying_dependencies.md`)
It does not implement:
* No `pip compile` testing, deprioritizing towards our own lockfile
* Index pinning (stub definitions only)
* Development dependencies
* Workspace support (stub definitions only)
* Overrides in pyproject.toml
* Patching/replacing dependencies
One technically breaking change is that we now require user provided
pyproject.toml to be valid wrt to PEP 621. Included files still fall
back to PEP 517. That means `pip install -r requirements.txt` requires
it to be valid while `pip install -r requirements.txt` with `-e .` as
content falls back to PEP 517 as before.
## Implementation
The `pep508` requirement is replaced by a new `UvRequirement` (name up
for bikeshedding, not particularly attached to the uv prefix). The still
existing `pep508_rs::Requirement` type is a url format copied from pip's
requirements.txt and doesn't appropriately capture all features we
want/need to support. The bulk of the diff is changing the requirement
type throughout the codebase.
We still use `VerbatimUrl` in many places, where we would expect a
parsed/decomposed url type, specifically:
* Reading core metadata except top level pyproject.toml files, we fail a
step later instead if the url isn't supported.
* Allowed `Urls`.
* `PackageId` with a custom `CanonicalUrl` comparison, instead of
canonicalizing urls eagerly.
* `PubGrubPackage`: We eventually convert the `VerbatimUrl` back to a
`Dist` (`Dist::from_url`), instead of remembering the url.
* Source dist types: We use verbatim url even though we know and require
that these are supported urls we can and have parsed.
I tried to make improve the situation be replacing `VerbatimUrl`, but
these changes would require massive invasive changes (see e.g.
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/3253). A main problem is the ref
`VersionOrUrl` and applying overrides, which assume the same
requirement/url type everywhere. In its current form, this PR increases
this tech debt.
I've tried to split off PRs and commits, but the main refactoring is
still a single monolith commit to make it compile and the tests pass.
## Demo
Adding
d1ae3b85d5/pyproject.json
as json schema (v7) to pycharm for `pyproject.toml`, you can try the IDE
support already:
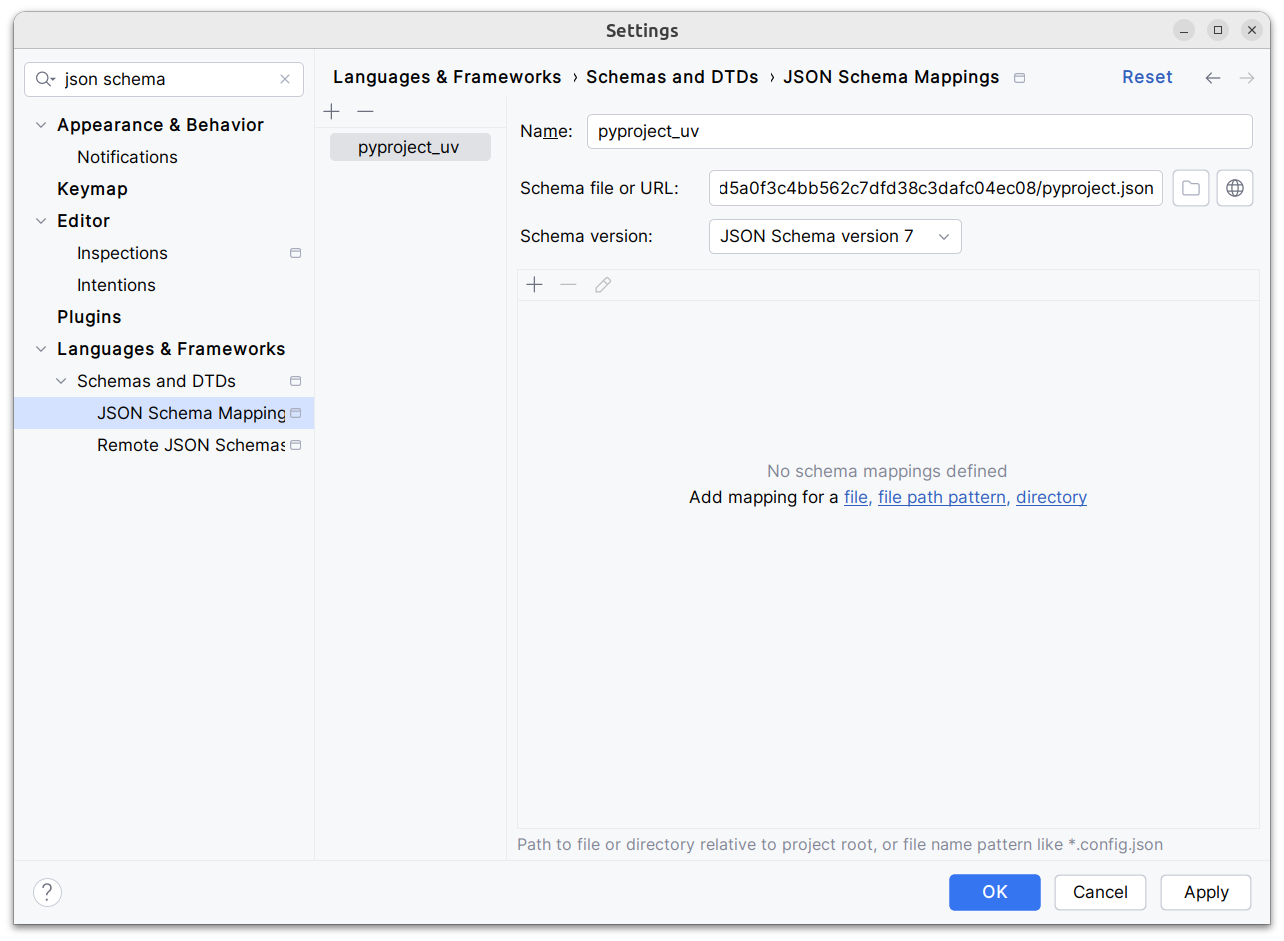
[dove.webm](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/assets/6826232/c293c272-c80b-459d-8c95-8c46a8d198a1)
## Summary
No behavior changes, but the idea here is that we move the argument
normalization code (e.g., create an `Upgrade` struct from `--upgrade`
and `--upgrade-package`) into the `settings.rs` file, where we build the
common settings structs.
This reduces a lot of the logic and duplication across commands in
`main.rs`.
In addition to the requested requirements, we include requirements from
a `pyproject.toml` file if it exists and install the current directory.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3104
## Summary
This PR enables `--require-hashes` with unnamed requirements. The key
change is that `PackageId` becomes `VersionId` (since it refers to a
package at a specific version), and the new `PackageId` consists of
_either_ a package name _or_ a URL. The hashes are keyed by `PackageId`,
so we can generate the `RequiredHashes` before we have names for all
packages, and enforce them throughout.
Closes#2979.
## Summary
This PR enables hash generation for URL requirements when the user
provides `--generate-hashes` to `pip compile`. While we include the
hashes from the registry already, today, we omit hashes for URLs.
To power hash generation, we introduce a `HashPolicy` abstraction:
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum HashPolicy<'a> {
/// No hash policy is specified.
None,
/// Hashes should be generated (specifically, a SHA-256 hash), but not validated.
Generate,
/// Hashes should be validated against a pre-defined list of hashes. If necessary, hashes should
/// be generated so as to ensure that the archive is valid.
Validate(&'a [HashDigest]),
}
```
All of the methods on the distribution database now accept this policy,
instead of accepting `&'a [HashDigest]`.
Closes#2378.
## Summary
This PR modifies the distribution database to return both the
`Metadata23` and the computed hashes when clients request metadata.
No behavior changes, but this will be necessary to power
`--generate-hashes`.
## Summary
This PR adds support for hash-checking mode in `pip install` and `pip
sync`. It's a large change, both in terms of the size of the diff and
the modifications in behavior, but it's also one that's hard to merge in
pieces (at least, with any test coverage) since it needs to work
end-to-end to be useful and testable.
Here are some of the most important highlights:
- We store hashes in the cache. Where we previously stored pointers to
unzipped wheels in the `archives` directory, we now store pointers with
a set of known hashes. So every pointer to an unzipped wheel also
includes its known hashes.
- By default, we don't compute any hashes. If the user runs with
`--require-hashes`, and the cache doesn't contain those hashes, we
invalidate the cache, redownload the wheel, and compute the hashes as we
go. For users that don't run with `--require-hashes`, there will be no
change in performance. For users that _do_, the only change will be if
they don't run with `--generate-hashes` -- then they may see some
repeated work between resolution and installation, if they use `pip
compile` then `pip sync`.
- Many of the distribution types now include a `hashes` field, like
`CachedDist` and `LocalWheel`.
- Our behavior is similar to pip, in that we enforce hashes when pulling
any remote distributions, and when pulling from our own cache. Like pip,
though, we _don't_ enforce hashes if a distribution is _already_
installed.
- Hash validity is enforced in a few different places:
1. During resolution, we enforce hash validity based on the hashes
reported by the registry. If we need to access a source distribution,
though, we then enforce hash validity at that point too, prior to
running any untrusted code. (This is enforced in the distribution
database.)
2. In the install plan, we _only_ add cached distributions that have
matching hashes. If a cached distribution is missing any hashes, or the
hashes don't match, we don't return them from the install plan.
3. In the downloader, we _only_ return distributions with matching
hashes.
4. The final combination of "things we install" are: (1) the wheels from
the cache, and (2) the downloaded wheels. So this ensures that we never
install any mismatching distributions.
- Like pip, if `--require-hashes` is provided, we require that _all_
distributions are pinned with either `==` or a direct URL. We also
require that _all_ distributions have hashes.
There are a few notable TODOs:
- We don't support hash-checking mode for unnamed requirements. These
should be _somewhat_ rare, though? Since `pip compile` never outputs
unnamed requirements. I can fix this, it's just some additional work.
- We don't automatically enable `--require-hashes` with a hash exists in
the requirements file. We require `--require-hashes`.
Closes#474.
## Test Plan
I'd like to add some tests for registries that report incorrect hashes,
but otherwise: `cargo test`
Needed to prevent circular dependencies in my toolchain work (#2931). I
think this is probably a reasonable change as we move towards persistent
configuration too?
Unfortunately `BuildIsolation` needs to be in `uv-types` to avoid
circular dependencies still. We might be able to resolve that in the
future.
## Summary
Rather than storing the `redirects` on the resolver, this PR just
re-uses the "convert this URL to precise" logic when we convert to a
`Resolution` after-the-fact. I think this is a lot simpler: it removes
state from the resolver, and simplifies a lot of the hooks around
distribution fetching (e.g., `get_or_build_wheel_metadata` no longer
returns `(Metadata23, Option<Url>)`).
## Summary
This PR leverages our lookahead direct URL resolution to significantly
improve the range of Git URLs that we can accept (e.g., if a user
provides the same requirement, once as a direct dependency, and once as
a tag). We did some of this in #2285, but the solution here is more
general and works for arbitrary transitive URLs.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2614.
## Summary
Ensures that if we resolve any distributions before the resolver, we
cache the metadata in-memory.
_Also_ ensures that we lock (important!) when resolving Git
distributions.
## Summary
This PR would enable us to support transitive URL requirements. The key
idea is to leverage the fact that...
- URL requirements can only come from URL requirements.
- URL requirements identify a _specific_ version, and so don't require
backtracking.
Prior to running the "real" resolver, we recursively resolve any URL
requirements, and collect all the known URLs upfront, then pass those to
the resolver as "lookahead" requirements. This means the resolver knows
upfront that if a given package is included, it _must_ use the provided
URL.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1808.
## Summary
If the user provides `uv pip install pyproject.toml`, we now prompt them
to confirm that they meant the `pyproject-toml` package (as opposed to
`uv pip install -r pyproject.toml`).
## Summary
We iterate over the project "requirements" directly in a variety of
places. However, it's not always the case that an input "requirement" on
its own will _actually_ be part of the resolution, since we support
"overrides".
Historically, then, overrides haven't worked as expected for _direct_
dependencies (and we have some tests that demonstrate the current,
"wrong" behavior). This is just a bug, but it's not really one that
comes up in practice, since it's rare to apply an override to your _own_
dependency.
However, we're now considering expanding the lookahead concept to
include local transitive dependencies. In this case, it's more and more
important that overrides and constraints are handled consistently.
This PR modifies all the locations in which we iterate over requirements
directly, and modifies them to respect overrides (and constraints, where
necessary).
## Summary
This is a trimmed-down version of
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/2684 that only applies to local
source trees for now, which enables workspace-like workflows (whereby
local packages can depend on other local packages at arbitrary depth).
Closes#2699.
## Test Plan
Added new tests.
Also cloned this MRE that was shared with me
(https://github.com/timothyjlaurent/uv-poetry-monorepo-mre), and
verified that it was installed without error:
```
❯ cargo run pip install ./uv-poetry-monorepo-mre/app --no-cache
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.15s
Running `target/debug/uv pip install ./uv-poetry-monorepo-mre/app --no-cache`
Resolved 4 packages in 1.28s
Built app @ file:///Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/uv-poetry-monorepo-mre/app
Built lib1 @ file:///Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/uv-poetry-monorepo-mre/lib1
Built lib2 @ file:///Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/uv-poetry-monorepo-mre/lib2 Downloaded 4 packages in 457ms
Installed 4 packages in 2ms
+ app==0.1.0 (from file:///Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/uv-poetry-monorepo-mre/app)
+ lib1==0.1.0 (from file:///Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/uv-poetry-monorepo-mre/lib1)
+ lib2==0.1.0 (from file:///Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/uv-poetry-monorepo-mre/lib2)
+ ruff==0.3.4
```
## Summary
This PR enables the resolver to "accept" URLs, prereleases, and local
version specifiers for direct dependencies of path dependencies. As a
result, `uv pip install .` and `uv pip install -e .` now behave
identically, in that neither has a restriction on URL dependencies and
the like.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2643.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1853.
## Summary
Now that we're resolving metadata more aggressively for local sources,
it's worth doing this. We now pull metadata from the `pyproject.toml`
directly if it's statically-defined.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2629.
This is driving me a little crazy and is becoming a larger problem in
#2596 where I need to move more types (like `Upgrade` and `Reinstall`)
into this crate. Anything that's shared across our core resolver,
install, and build crates needs to be defined in this crate to avoid
cyclic dependencies. We've outgrown it being a single file with some
shared traits.
There are no behavioral changes here.
If you pass a `pyproject.toml` that use Hatch's context formatting API,
we currently fail because the dependencies aren't valid under PEP 508.
This PR makes the static metadata parsing a little more relaxed, so that
we appropriately fall back to PEP 517 there.
## Summary
Passing `pyproject.toml` or `setup.py` to `pip uninstall` is a bit
strange, since it will often require running a resolution to resolve the
dependencies (e.g., build the project), which means we also need to
accept `--index-url` and friends.
## Summary
When a user passes a `pyproject.toml` to `pip compile` (e.g., `uv pip
compile pyproject.toml`), we extract the requirements from the
`pyproject.toml` directly. However... that isn't always possible (as
seen in the linked issues). When it's _not_, we instead need to run the
PEP 517 build hooks to identify the metadata.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1624.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1644.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
I don't see a great reason to allow this, and it adds a lot of
complexity, so `pyproject.toml` files are now limited to `pip compile`
and `pip install -r` -- they can't be passed as `-c` or `--override`.
## Summary
Closes Issue:
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2626
## Test Plan
```
cargo run -- pip install -r dev-requirements.txt -r requirements.txt
```
where both requirements files have same `--index-url`