## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1343. This is kinda a first
draft at the moment, but does at least mostly work locally (barring some
bits of the test suite that seem to not work for me in general).
## Test Plan
Mostly running the existing tests and checking the revised output is
sane
## Outstanding issues
Most of these come down to "AFAIK, the existing tools don't support
these patterns, but `uv` does" and so I'm not sure there's an existing
good answer here! Most of the answers so far are "whatever was easiest
to build"
- [x] ~~Is "-r pyproject.toml" correct? Should it show something else or
get skipped entirely~~ No it wasn't. Fixed in
3044fa8b86
- [ ] If the requirements file is stdin, that just gets skipped. Should
it be recorded?
- [ ] Overrides get shown as "--override<override.txt>". Correct?
- [x] ~~Some of the tests (e.g.
`dependency_excludes_non_contiguous_range_of_compatible_versions`) make
assumptions about the order of package versions being outputted, which
this PR breaks. I'm not sure if the text is fairly arbitrary and can be
replaced or whether the behaviour needs fixing?~~ - fixed by removing
the custom pubgrub PartialEq/Hash
- [ ] Are all the `TrackedFromStr` et al changes needed, or is there an
easier way? I don't think so, I think it's necessary to track these sort
of things fairly comprehensively to make this feature work, and this
sort of invasive change feels necessary, but happy to be proved wrong
there :)
- [x] ~~If you have a requirement coming in from two or more different
requirements files only one turns up. I've got a closed-source example
for this (can go into more detail if needed), mostly consisting of a
complicated set of common deps creating a larger set. It's a rarer case,
but worth considering.~~ 042432b200
- [ ] Doesn't add annotations for `setup.py` yet
- This is pretty hard, as the correct location to insert the path is
`crates/pypi-types/src/metadata.rs`'s `parse_pkg_info`, which as it's
based off a source distribution has entirely thrown away such matters as
"where did this package requirement get built from". Could add "`built
package name`" as a dep, but that's a little odd.
It turns out setuptools often uses Metadata-Version 2.1 in their
PKG-INFO:
4e766834d7/setuptools/dist.py (L64)
`Metadata23` requires Metadata-Version of at least 2.2.
This means that uv doesn't actually recognise legacy editable
installations from the most common way you'd actually get legacy
editable installations (works great for most legacy editables I make at
work though!)
Anyway, over here we only need the version and don't care about anything
else. Rather than make a `Metadata21`, I just add a version field to
`Metadata10`. The one slightly tricky thing is that only
Metadata-Version 1.2 and greater guarantee that the [version number is
PEP 440 compatible](https://peps.python.org/pep-0345/#version), so I
store the version in `Metadata10` as a `String` and only parse to
`Version` at time of use.
Also did you know that back in 2004, paramiko had a pokemon based
versioning system?
Pubgrub got a new feature where all unavailability is a custom, instead
of the reasonless `UnavailableDependencies` and our custom `String` type
previously (https://github.com/pubgrub-rs/pubgrub/pull/208). This PR
introduces a `UnavailableReason` that tracks either an entire version
being unusable, or a specific version. The error messages now also track
this difference properly.
The pubgrub commit is our main rebased onto the merged
https://github.com/pubgrub-rs/pubgrub/pull/208, i'll push
`konsti/main-rebase-generic-reason` to `main` after checking for rebase
problems.
This change allows switching out the url type for requirements. The
original idea was to allow different types for different requirement
origins, so that core metadata reads can ban non-pep 508 requirements
while we only allow them for requirements.txt. This didn't work out
because we expect `&Requirement`s from all sources to match.
I also tried to split `pep508_rs` into a PEP 508 compliant crate and
into our extensions, but they are to tightly coupled.
I think this change is an improvement still as it reduces the hardcoded
dependence on `VerbatimUrl`.
## Summary
Users often find themselves dropped into environments that contain
`.egg-info` packages. While we won't support installing these, it's not
hard to support identifying them (e.g., in `pip freeze`) and
_uninstalling_ them.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2841.
Closes#2928.
Closes#3341.
## Test Plan
Ran `cargo run pip freeze --python
/opt/homebrew/Caskroom/miniforge/base/envs/TEST/bin/python`, with an
environment that includes `pip` as an `.egg-info`
(`/opt/homebrew/Caskroom/miniforge/base/envs/TEST/lib/python3.12/site-packages/pip-24.0-py3.12.egg-info`):
```
cffi @ file:///Users/runner/miniforge3/conda-bld/cffi_1696001825047/work
pip==24.0
pycparser @ file:///home/conda/feedstock_root/build_artifacts/pycparser_1711811537435/work
setuptools==69.5.1
wheel==0.43.0
```
Then ran `cargo run pip uninstall`, verified that `pip` was uninstalled,
and no longer listed in `pip freeze`.
## Summary
We need to partition the editable and non-editable requirements. As-is,
`editable = true` requirements were still being installed as
non-editable.
## Introduction
PEP 621 is limited. Specifically, it lacks
* Relative path support
* Editable support
* Workspace support
* Index pinning or any sort of index specification
The semantics of urls are a custom extension, PEP 440 does not specify
how to use git references or subdirectories, instead pip has a custom
stringly format. We need to somehow support these while still stying
compatible with PEP 621.
## `tool.uv.source`
Drawing inspiration from cargo, poetry and rye, we add `tool.uv.sources`
or (for now stub only) `tool.uv.workspace`:
```toml
[project]
name = "albatross"
version = "0.1.0"
dependencies = [
"tqdm >=4.66.2,<5",
"torch ==2.2.2",
"transformers[torch] >=4.39.3,<5",
"importlib_metadata >=7.1.0,<8; python_version < '3.10'",
"mollymawk ==0.1.0"
]
[tool.uv.sources]
tqdm = { git = "https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm", rev = "cc372d09dcd5a5eabdc6ed4cf365bdb0be004d44" }
importlib_metadata = { url = "https://github.com/python/importlib_metadata/archive/refs/tags/v7.1.0.zip" }
torch = { index = "torch-cu118" }
mollymawk = { workspace = true }
[tool.uv.workspace]
include = [
"packages/mollymawk"
]
[tool.uv.indexes]
torch-cu118 = "https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118"
```
See `docs/specifying_dependencies.md` for a detailed explanation of the
format. The basic gist is that `project.dependencies` is what ends up on
pypi, while `tool.uv.sources` are your non-published additions. We do
support the full range or PEP 508, we just hide it in the docs and
prefer the exploded table for easier readability and less confusing with
actual url parts.
This format should eventually be able to subsume requirements.txt's
current use cases. While we will continue to support the legacy `uv pip`
interface, this is a piece of the uv's own top level interface. Together
with `uv run` and a lockfile format, you should only need to write
`pyproject.toml` and do `uv run`, which generates/uses/updates your
lockfile behind the scenes, no more pip-style requirements involved. It
also lays the groundwork for implementing index pinning.
## Changes
This PR implements:
* Reading and lowering `project.dependencies`,
`project.optional-dependencies` and `tool.uv.sources` into a new
requirements format, including:
* Git dependencies
* Url dependencies
* Path dependencies, including relative and editable
* `pip install` integration
* Error reporting for invalid `tool.uv.sources`
* Json schema integration (works in pycharm, see below)
* Draft user-level docs (see `docs/specifying_dependencies.md`)
It does not implement:
* No `pip compile` testing, deprioritizing towards our own lockfile
* Index pinning (stub definitions only)
* Development dependencies
* Workspace support (stub definitions only)
* Overrides in pyproject.toml
* Patching/replacing dependencies
One technically breaking change is that we now require user provided
pyproject.toml to be valid wrt to PEP 621. Included files still fall
back to PEP 517. That means `pip install -r requirements.txt` requires
it to be valid while `pip install -r requirements.txt` with `-e .` as
content falls back to PEP 517 as before.
## Implementation
The `pep508` requirement is replaced by a new `UvRequirement` (name up
for bikeshedding, not particularly attached to the uv prefix). The still
existing `pep508_rs::Requirement` type is a url format copied from pip's
requirements.txt and doesn't appropriately capture all features we
want/need to support. The bulk of the diff is changing the requirement
type throughout the codebase.
We still use `VerbatimUrl` in many places, where we would expect a
parsed/decomposed url type, specifically:
* Reading core metadata except top level pyproject.toml files, we fail a
step later instead if the url isn't supported.
* Allowed `Urls`.
* `PackageId` with a custom `CanonicalUrl` comparison, instead of
canonicalizing urls eagerly.
* `PubGrubPackage`: We eventually convert the `VerbatimUrl` back to a
`Dist` (`Dist::from_url`), instead of remembering the url.
* Source dist types: We use verbatim url even though we know and require
that these are supported urls we can and have parsed.
I tried to make improve the situation be replacing `VerbatimUrl`, but
these changes would require massive invasive changes (see e.g.
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/3253). A main problem is the ref
`VersionOrUrl` and applying overrides, which assume the same
requirement/url type everywhere. In its current form, this PR increases
this tech debt.
I've tried to split off PRs and commits, but the main refactoring is
still a single monolith commit to make it compile and the tests pass.
## Demo
Adding
d1ae3b85d5/pyproject.json
as json schema (v7) to pycharm for `pyproject.toml`, you can try the IDE
support already:
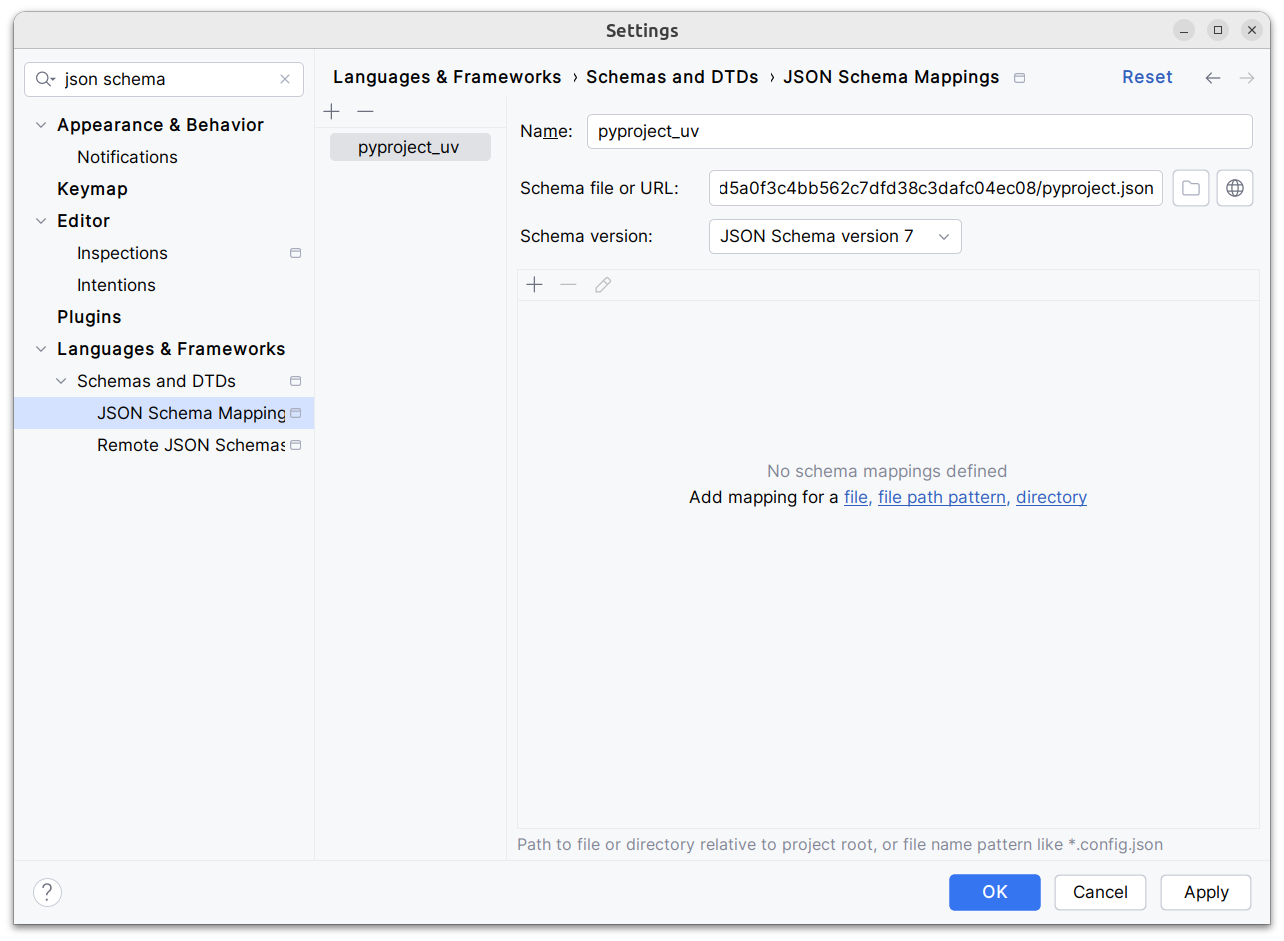
[dove.webm](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/assets/6826232/c293c272-c80b-459d-8c95-8c46a8d198a1)
In *some* places in our crates, `serde` (and `rkyv`) are optional
dependencies. I believe this was done out of reasons of "good sense,"
that is, it follows a Rust ecosystem pattern where serde integration
tends to be an opt-in crate feature. (And similarly for `rkyv`.)
However, ultimately, `uv` itself requires `serde` and `rkyv` to
function. Since our crates are strictly internal, there are limited
consumers for our crates without `serde` (and `rkyv`) enabled. I think
one possibility is that optional `serde` (and `rkyv`) integration means
that someone can do this:
cargo test -p pep440_rs
And this will run tests _without_ `serde` or `rkyv` enabled. That in
turn could lead to faster iteration time by reducing compile times. But,
I'm not sure this is worth supporting. The iterative compilation times
of
individual crates are probably fast enough in debug mode, even with
`serde` and `rkyv` enabled. Namely, `serde` and `rkyv` themselves
shouldn't need to be re-compiled in most cases. On `main`:
```
from-scratch: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --lib` 0.685
incremental: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --lib` 0.278s
from-scratch: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --features serde,rkyv --lib` 3.948s
incremental: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --features serde,rkyv --lib` 0.321s
```
So while a from-scratch build does take significantly longer, an
incremental build is about the same.
The benefit of doing this change is two-fold:
1. It brings out crates into alignment with "reality." In particular,
some crates were _implicitly_ relying on `serde` being enabled
without explicitly declaring it. This technically means that our
`Cargo.toml`s were wrong in some cases, but it is hard to observe it
because of feature unification in a Cargo workspace.
2. We no longer need to deal with the cognitive burden of writing
`#[cfg_attr(feature = "serde", ...)]` everywhere.
This is meant to be a base on which to build. There are some parts
which are implicitly incomplete and others which are explicitly
incomplete. The latter are indicated by TODO comments.
Here is a non-exhaustive list of incomplete things. In many cases, these
are incomplete simply because the data isn't present in a
`ResolutionGraph`. Future work will need to refactor our resolver so
that this data is correctly passed down.
* Not all wheels are included. Only the "selected" wheel for the current
distribution is included.
* Marker expressions are always absent.
* We don't emit hashes for certainly kinds of distributions (direct
URLs, git, and path).
* We don't capture git information from a dependency specification.
Right now, we just always emit "default branch."
There are perhaps also other changes we might want to make to the format
of a more cosmetic nature. Right now, all arrays are encoded using
whatever the `toml` crate decides to do. But we might want to exert more
control over this. For example, by using inline tables or squashing more
things into strings (like I did for `Source` and `Hash`). I think the
main trade-off here is that table arrays are somewhat difficult to read
(especially without indentation), where as squashing things down into a
more condensed format potentially makes future compatible additions
harder.
I also went pretty light on the documentation here than what I would
normally do. That's primarily because I think this code is going to
go through some evolution and I didn't want to spend too much time
documenting something that is likely to change.
Finally, here's an example of the lock file format in TOML for the
`anyio` dependency. I generated it with the following command:
```
cargo run -p uv -- pip compile -p3.10 ~/astral/tmp/reqs/anyio.in --unstable-uv-lock-file
```
And that writes out a `uv.lock` file:
```toml
version = 1
[[distribution]]
name = "anyio"
version = "4.3.0"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "2f20c40b45242c0b33774da0e2e34f/anyio-4.3.0-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:048e05d0f6caeed70d731f3db756d35dcc1f35747c8c403364a8332c630441b8"
[[distribution.dependencies]]
name = "exceptiongroup"
version = "1.2.1"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.dependencies]]
name = "idna"
version = "3.7"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.dependencies]]
name = "sniffio"
version = "1.3.1"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.dependencies]]
name = "typing-extensions"
version = "4.11.0"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution]]
name = "exceptiongroup"
version = "1.2.1"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "79fe92dd414cadab75055b0ae00b33/exceptiongroup-1.2.1-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:5258b9ed329c5bbdd31a309f53cbfb0b155341807f6ff7606a1e801a891b29ad"
[[distribution]]
name = "idna"
version = "3.7"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "741d8c8280948df2ea0eda2c8b79e8/idna-3.7-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:82fee1fc78add43492d3a1898bfa6d8a904cc97d8427f683ed8e798d07761aa0"
[[distribution]]
name = "sniffio"
version = "1.3.1"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "75a9c94214239abab1ea2cc8f38b40/sniffio-1.3.1-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:2f6da418d1f1e0fddd844478f41680e794e6051915791a034ff65e5f100525a2"
[[distribution]]
name = "typing-extensions"
version = "4.11.0"
source = "registry+https://pypi.org/simple"
[[distribution.wheel]]
url = "936e2092671b43269810cd589ceaf5/typing_extensions-4.11.0-py3-none-any.whl"
hash = "sha256:c1f94d72897edaf4ce775bb7558d5b79d8126906a14ea5ed1635921406c0387a"
```
## Summary
I found some of these too bare (e.g., when they _just_ show a package
name with no other information). For me, this makes it easier to
differentiate error message copy from data. But open to other opinions.
Take a look at the fixture changes and LMK!
Previously, we got `pypi_types::DirectUrl` (the pypa spec
direct_url.json format) and `distribution_types::DirectUrl` (an enum of
all the url types we support). This lead me to confusion, so i'm
renaming the latter one to the more appropriate `ParsedUrl`.
Add a dedicated error type for direct url parsing. This change is broken
out from the new uv requirement type, which uses direct url parsing
internally.
## Summary
resolves https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3106
## Test Plan
added a simple test where the password provided in `UV_INDEX_URL` is
hidden in the output as expected.
## Summary
In all of these ID types, we pass values to `cache_key::digest` prior to
passing to `DistributionId` or `ResourceId`. The `DistributionId` and
`ResourceId` are then hashed later, since they're used as keys in hash
maps.
It seems wasteful to hash the value, then hash the hashed value? So this
PR modifies those structs to be enums that can take one of a fixed set
of types.
## Summary
This PR enables `--require-hashes` with unnamed requirements. The key
change is that `PackageId` becomes `VersionId` (since it refers to a
package at a specific version), and the new `PackageId` consists of
_either_ a package name _or_ a URL. The hashes are keyed by `PackageId`,
so we can generate the `RequiredHashes` before we have names for all
packages, and enforce them throughout.
Closes#2979.
## Summary
This PR enables hash generation for URL requirements when the user
provides `--generate-hashes` to `pip compile`. While we include the
hashes from the registry already, today, we omit hashes for URLs.
To power hash generation, we introduce a `HashPolicy` abstraction:
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum HashPolicy<'a> {
/// No hash policy is specified.
None,
/// Hashes should be generated (specifically, a SHA-256 hash), but not validated.
Generate,
/// Hashes should be validated against a pre-defined list of hashes. If necessary, hashes should
/// be generated so as to ensure that the archive is valid.
Validate(&'a [HashDigest]),
}
```
All of the methods on the distribution database now accept this policy,
instead of accepting `&'a [HashDigest]`.
Closes#2378.
## Summary
This represents a change to `--require-hashes` in the event that we
don't find a matching hash from the registry. The behavior in this PR is
closer to pip's.
Prior to this PR, if a distribution had no reported hash, or only
mismatched hashes, we would mark it as incompatible. Now, we mark it as
compatible, but we use the hash-agreement as part of the ordering, such
that we prefer any distribution with a matching hash, then any
distribution with no hash, then any distribution with a mismatched hash.
As a result, if an index reports incorrect hashes, but the user provides
the correct one, resolution now succeeds, where it would've failed.
Similarly, if an index omits hashes altogether, but the user provides
the correct one, resolution now succeeds, where it would've failed.
If we end up picking a distribution whose hash ultimately doesn't match,
we'll reject it later, after resolution.
## Summary
This PR adds support for hash-checking mode in `pip install` and `pip
sync`. It's a large change, both in terms of the size of the diff and
the modifications in behavior, but it's also one that's hard to merge in
pieces (at least, with any test coverage) since it needs to work
end-to-end to be useful and testable.
Here are some of the most important highlights:
- We store hashes in the cache. Where we previously stored pointers to
unzipped wheels in the `archives` directory, we now store pointers with
a set of known hashes. So every pointer to an unzipped wheel also
includes its known hashes.
- By default, we don't compute any hashes. If the user runs with
`--require-hashes`, and the cache doesn't contain those hashes, we
invalidate the cache, redownload the wheel, and compute the hashes as we
go. For users that don't run with `--require-hashes`, there will be no
change in performance. For users that _do_, the only change will be if
they don't run with `--generate-hashes` -- then they may see some
repeated work between resolution and installation, if they use `pip
compile` then `pip sync`.
- Many of the distribution types now include a `hashes` field, like
`CachedDist` and `LocalWheel`.
- Our behavior is similar to pip, in that we enforce hashes when pulling
any remote distributions, and when pulling from our own cache. Like pip,
though, we _don't_ enforce hashes if a distribution is _already_
installed.
- Hash validity is enforced in a few different places:
1. During resolution, we enforce hash validity based on the hashes
reported by the registry. If we need to access a source distribution,
though, we then enforce hash validity at that point too, prior to
running any untrusted code. (This is enforced in the distribution
database.)
2. In the install plan, we _only_ add cached distributions that have
matching hashes. If a cached distribution is missing any hashes, or the
hashes don't match, we don't return them from the install plan.
3. In the downloader, we _only_ return distributions with matching
hashes.
4. The final combination of "things we install" are: (1) the wheels from
the cache, and (2) the downloaded wheels. So this ensures that we never
install any mismatching distributions.
- Like pip, if `--require-hashes` is provided, we require that _all_
distributions are pinned with either `==` or a direct URL. We also
require that _all_ distributions have hashes.
There are a few notable TODOs:
- We don't support hash-checking mode for unnamed requirements. These
should be _somewhat_ rare, though? Since `pip compile` never outputs
unnamed requirements. I can fix this, it's just some additional work.
- We don't automatically enable `--require-hashes` with a hash exists in
the requirements file. We require `--require-hashes`.
Closes#474.
## Test Plan
I'd like to add some tests for registries that report incorrect hashes,
but otherwise: `cargo test`
## Summary
If we build a source distribution from the registry, and the version
doesn't match that of the filename, we should error, just as we do for
mismatched package names. However, we should also backtrack here, which
we didn't previously.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2953.
## Test Plan
Verified that `cargo run pip install docutils --verbose --no-cache
--reinstall` installs `docutils==0.21` instead of the invalid
`docutils==0.21.post1`.
In the logs, I see:
```
WARN Unable to extract metadata for docutils: Package metadata version `0.21` does not match given version `0.21.post1`
```
## Summary
Right now, we have a `Hashes` representation that looks like:
```rust
/// A dictionary mapping a hash name to a hex encoded digest of the file.
///
/// PEP 691 says multiple hashes can be included and the interpretation is left to the client.
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Eq, PartialEq, Default, Deserialize)]
pub struct Hashes {
pub md5: Option<Box<str>>,
pub sha256: Option<Box<str>>,
pub sha384: Option<Box<str>>,
pub sha512: Option<Box<str>>,
}
```
It stems from the PyPI API, which returns a dictionary of hashes.
We tend to pass these around as a vector of `Vec<Hashes>`. But it's a
bit strange because each entry in that vector could contain multiple
hashes. And it makes it difficult to ask questions like "Is
`sha256:ab21378ca980a8` in the set of hashes"?
This PR instead treats `Hashes` as the PyPI-internal type, and uses a
new `Vec<HashDigest>` everywhere in our own APIs.
## Summary
We have a heuristic in `File` that attempts to detect whether a URL is
absolute or relative. However, `contains("://")` is prone to false
positive. In the linked issues, the URLs look like:
```
/packages/5a/d8/4d75d1e4287ad9d051aab793c68f902c9c55c4397636b5ee540ebd15aedf/pytz-2005k.tar.bz2?hash=597b596dc1c2c130cd0a57a043459c3bd6477c640c07ac34ca3ce8eed7e6f30c&remote=4d75d1e4287636b5ee540ebd15aedf/pytz-2005k.tar.bz2#sha256=597b596dc1c2c130cd0a57a043459c3bd6477c640c07ac34ca3ce8eed7e6f30c
```
Which is relative, but includes `://`.
Instead, we should determine whether the URL has a _scheme_ which
matches the `Url` crate internally.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2899.
With pubgrub being fast for complex ranges, we can now compute the next
n candidates without taking a performance hit. This speeds up cold cache
`urllib3<1.25.4` `boto3` from maybe 40s - 50s to ~2s. See docstrings for
details on the heuristics.
**Before**

**After**

---
We need two parts of the prefetching, first looking for compatible
version and then falling back to flat next versions. After we selected a
boto3 version, there is only one compatible botocore version remaining,
so when won't find other compatible candidates for prefetching. We see
this as a pattern where we only prefetch boto3 (stack bars), but not
botocore (sequential requests between the stacked bars).

The risk is that we're completely wrong with the guess and cause a lot
of useless network requests. I think this is acceptable since this
mechanism only triggers when we're already on the bad path and we should
simply have fetched all versions after some seconds (assuming a fast
index like pypi).
---
It would be even better if the pubgrub state was copy-on-write so we
could simulate more progress than we actually have; currently we're
guessing what the next version is which could be completely wrong, but i
think this is still a valuable heuristic.
Fixes#170.
## Summary
I noticed in #2769 that I was now stripping `.git` suffixes from Git
URLs after resolving to a precise commit. This PR cleans up the internal
caching to use a better canonical representation: a `RepositoryUrl`
along with a `GitReference`, instead of a `GitUrl` which can contain
non-canonical data. This gives us both better fidelity (preserving the
`.git`, along with any casing that the user provided when defining the
URL) and is overall cleaner and more robust.
## Summary
Ensures that if we resolve any distributions before the resolver, we
cache the metadata in-memory.
_Also_ ensures that we lock (important!) when resolving Git
distributions.
Previously, we did not consider installed distributions as candidates
while performing resolution. Here, we update the resolver to use
installed distributions that satisfy requirements instead of pulling new
distributions from the registry.
The implementation details are as follows:
- We now provide `SitePackages` to the `CandidateSelector`
- If an installed distribution satisfies the requirement, we prefer it
over remote distributions
- We do not want to allow installed distributions in some cases, i.e.,
upgrade and reinstall
- We address this by introducing an `Exclusions` type which tracks
installed packages to ignore during selection
- There's a new `ResolvedDist` wrapper with `Installed(InstalledDist)`
and `Installable(Dist)` variants
- This lets us pass already installed distributions throughout the
resolver
The user-facing behavior is thoroughly covered in the tests, but
briefly:
- Installing a package that depends on an already-installed package
prefers the local version over the index
- Installing a package with a name that matches an already-installed URL
package does not reinstall from the index
- Reinstalling (--reinstall) a package by name _will_ pull from the
index even if an already-installed URL package is present
- To reinstall the URL package, you must specify the URL in the request
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1661
Addresses:
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1476
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1856
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2093
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2282
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2383
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2560
## Test plan
- [x] Reproduction at `charlesnicholson/uv-pep420-bug` passes
- [x] Unit test for editable package
([#1476](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1476))
- [x] Unit test for previously installed package with empty registry
- [x] Unit test for local non-editable package
- [x] Unit test for new version available locally but not in registry
([#2093](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2093))
- ~[ ] Unit test for wheel not available in registry but already
installed locally
([#2282](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2282))~ (seems
complicated and not worthwhile)
- [x] Unit test for install from URL dependency then with matching
version ([#2383](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2383))
- [x] Unit test for install of new package that depends on installed
package does not change version
([#2560](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2560))
- [x] Unit test that `pip compile` does _not_ consider installed
packages
## Summary
This PR enables the resolver to "accept" URLs, prereleases, and local
version specifiers for direct dependencies of path dependencies. As a
result, `uv pip install .` and `uv pip install -e .` now behave
identically, in that neither has a restriction on URL dependencies and
the like.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2643.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1853.
## Summary
`uv` was failing to install requirements defined like:
```
file://localhost/Users/crmarsh/Downloads/iniconfig-2.0.0-py3-none-any.whl
```
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2652.
## Summary
Closes Issue:
- https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2626
## Test Plan
```
cargo run -- pip install -r dev-requirements.txt -r requirements.txt
```
where both requirements files have same `--index-url`
## Summary
This PR enables the source distribution database to be used with unnamed
requirements (i.e., URLs without a package name). The (significant)
upside here is that we can now use PEP 517 hooks to resolve unnamed
requirement metadata _and_ reuse any computation in the cache.
The changes to `crates/uv-distribution/src/source/mod.rs` are quite
extensive, but mostly mechanical. The core idea is that we introduce a
new `BuildableSource` abstraction, which can either be a distribution,
or an unnamed URL:
```rust
/// A reference to a source that can be built into a built distribution.
///
/// This can either be a distribution (e.g., a package on a registry) or a direct URL.
///
/// Distributions can _also_ point to URLs in lieu of a registry; however, the primary distinction
/// here is that a distribution will always include a package name, while a URL will not.
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy)]
pub enum BuildableSource<'a> {
Dist(&'a SourceDist),
Url(SourceUrl<'a>),
}
```
All the methods on the source distribution database now accept
`BuildableSource`. `BuildableSource` has a `name()` method, but it
returns `Option<&PackageName>`, and everything is required to work with
and without a package name.
The main drawback of this approach (which isn't a terrible one) is that
we can no longer include the package name in the cache. (We do continue
to use the package name for registry-based distributions, since those
always have a name.). The package name was included in the cache route
for two reasons: (1) it's nice for debugging; and (2) we use it to power
`uv cache clean flask`, to identify the entries that are relevant for
Flask.
To solve this, I changed the `uv cache clean` code to look one level
deeper. So, when we want to determine whether to remove the cache entry
for a given URL, we now look into the directory to see if there are any
wheels that match the package name. This isn't as nice, but it does work
(and we have test coverage for it -- all passing).
I also considered removing the package name from the cache routes for
non-registry _wheels_, for consistency... But, it would require a cache
bump, and it didn't feel important enough to merit that.