## Summary
First part of https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/5093.
Remaining:
- Global settings
- `pip`-specific settings (some will be copied-over from here)
- Auto-generating the "Possible values" for enums
Add support for path dependencies from a package in one workspace to a
package in another workspace, which it self has workspace dependencies.
Say we have a main workspace with packages `a` and `b`, and a second
workspace with `c` and `d`. We have `a -> b`, `b -> c`, `c -> d`. This
would previously lead to a mangled path for `d`, which is now fixed.
Like distribution paths, we split workspace paths into an absolute
install path and a relative (or absolute, if the user provided an
absolute path) lock path.
Part of https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3943
## Summary
When range requests aren't supported, we fall back to streaming the
wheel, stopping as soon as we hit a `METADATA` file. This is a small
optimization, but the downside is that we don't get to cache the
resulting wheel...
We don't know whether `METADATA` will be at the beginning or end of the
wheel, but it _seems_ like a better tradeoff to download and cache the
entire wheel?
Closes: https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/5088.
Sort of a revert of: https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/1792.
## Summary
Workaround the `stream_wheel` not retry issue
[found](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3514#issuecomment-2229820667)
in #3514, it's not a perfect solution but I think it's acceptable
because the error should not occur frequently.
## Test Plan
Manually using `iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp -dport 3128 -j REJECT
--reject-with tcp-reset` to inject connection reset error to the HTTP
proxy that proxies PyPI requests.
```
error: Failed to prepare distributions
Caused by: Failed to fetch wheel: piqp==0.4.1
Caused by: Request failed after 3 retries
Caused by: error sending request for url (09ade94dfdd3c368ac505b6ca09831/piqp-0.4.1-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl)
Caused by: client error (Connect)
Caused by: tcp connect error: Connection refused (os error 111)
Caused by: Connection refused (os error 111)
```
## Summary
So this PR introduces change to how `Array` of dependencies
representation is reformatted while `PyProjectTomlMut` is manipulated.
These changes are here for it to respect the original indentation.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/5009
## Test Plan
Using `pyproject.toml` like
```
[project]
name = "project"
version = "0.1.0"
requires-python = ">=3.12"
dependencies = [
"requests"
]
```
Executed
```
$ uv add httpx
```
And expected in `pyproject.toml`
```
[project]
name = "project"
version = "0.1.0"
requires-python = ">=3.12"
dependencies = [
"requests",
"httpx",
]
```
Preserving original indentation
This name should lead to less confusion. Unfortunately this is a
"breaking cache change" so everyone's cache will be invalidated. I'm not
sure if we should support a rename-on-upgrade.
edit: We can make the breaking change next time we bump the version
## Summary
Use the lockfile to prefill the `InMemoryIndex` used by the resolver.
This enables us to resolve completely from the lockfile without making
any network requests/builds if the requirements are unchanged. It also
means that if new requirements are added we can still avoid most I/O
during resolution, partially addressing
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3925.
The main limitation of this PR is that resolution from the lockfile can
fail if new versions are requested that are not present in the lockfile,
in which case we have to perform a fresh resolution. Fixing this would
likely require lazy version/metadata requests by `VersionMap` (this is
different from the lazy parsing we do, the list of versions in a
`VersionMap` is currently immutable).
Resolves https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3892.
## Test Plan
Added a `deterministic!` macro that ensures that a resolve from the
lockfile and a clean resolve result in the same lockfile output for all
our current tests.
## Summary
We currently store wheel URLs in an unparsed state because we don't have
a stable parsed representation to use with rykv. Unfortunately this
means we end up reparsing unnecessarily in a lot of places, especially
when constructing a `Lock`. This PR adds a `UrlString` type that lets us
avoid reparsing without losing the validity of the `Url`.
## Test Plan
Shaves off another ~10 ms from
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/4860.
```
➜ transformers hyperfine "../../uv/target/profiling/uv lock" "../../uv/target/profiling/baseline lock" --warmup 3
Benchmark 1: ../../uv/target/profiling/uv lock
Time (mean ± σ): 120.9 ms ± 2.5 ms [User: 126.0 ms, System: 80.6 ms]
Range (min … max): 116.8 ms … 125.7 ms 23 runs
Benchmark 2: ../../uv/target/profiling/baseline lock
Time (mean ± σ): 129.9 ms ± 4.2 ms [User: 127.1 ms, System: 86.1 ms]
Range (min … max): 123.4 ms … 141.2 ms 23 runs
Summary
../../uv/target/profiling/uv lock ran
1.07 ± 0.04 times faster than ../../uv/target/profiling/baseline lock
```
In #3514 and #2755, users had intermittent network errors, but it was
not always clear whether we had already retried these requests or not.
Building upon https://github.com/TrueLayer/reqwest-middleware/pull/159,
this PR adds the number of retries to the error message, so we can see
at first glance where we're missing retries and where we might need to
change retry settings.
Example error trace:
```
Could not connect, are you offline?
Caused by: Request failed after 3 retries
Caused by: error sending request for url (https://pypi.org/simple/uv/)
Caused by: client error (Connect)
Caused by: dns error: failed to lookup address information: Name or service not known
Caused by: failed to lookup address information: Name or service not known
```
This code is ugly since i'm missing a better pattern for attaching
context to reqwest middleware errors in
https://github.com/TrueLayer/reqwest-middleware/pull/159.
## Summary
You can now add `managed = false` under `[tool.uv]` in a
`pyproject.toml` to explicitly opt out of the project and workspace
APIs.
If a project sets `managed = false`, we will (1) _not_ discover it as a
workspace root, and (2) _not_ discover it as a workspace member (similar
to using `exclude` in the workspace parent).
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/4551.
## Summary
This PR dodges some of the bigger issues raised by
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/4554 and
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/4555 by _not_ changing any of the
bigger semantics around syncing and instead merely changing virtual
workspace roots to sync all packages in the workspace (rather than
erroring due to being unable to find a project).
Closes#4541.
## Summary
- Adds a `--extra` flag to `uv add` that allows activating extras
without the PEP508 syntax.
- `uv add` now errors if the update is ambiguous (e.g. the dependency is
present twice with different markers)
- `uv add` is smarter about updates. For example, `uv add flask==3.0.0`
followed by `uv add flask --extra dotenv` preserves the previous version
specifier.
Resolves https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/4419.
## Summary
If the package _isn't_ marked as `workspace = true`, locking will fail
given:
```rust
let workspace_package_declared =
// We require that when you use a package that's part of the workspace, ...
!workspace.packages().contains_key(&requirement.name)
// ... it must be declared as a workspace dependency (`workspace = true`), ...
|| matches!(
source,
Some(Source::Workspace {
// By using toml, we technically support `workspace = false`.
workspace: true,
..
})
)
// ... except for recursive self-inclusion (extras that activate other extras), e.g.
// `framework[machine_learning]` depends on `framework[cuda]`.
|| &requirement.name == project_name;
if !workspace_package_declared {
return Err(LoweringError::UndeclaredWorkspacePackage);
}
```
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/4552.
## Summary
It turns out that the Git fetch implementation is initializing its own
client, which can be really expensive on macOS (due to loading native
certificates) _and_ bypasses any of our middleware. This PR modifies the
Git implementation to accept a shared client.
## Summary
I might be mistaken, but I think we need to read the header from the
response, not the request. The request would only contain headers that
we set.
I verified (with extra logging) that the request header is `None` while
PyPI returns a valid length in the response header.
## Summary
This will make `uv lock` read `override-dependencies` from the
`[tool.uv]` section of `pyproject.toml`.
Resolves#4108
This [other](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/4446) implementation
touches more code but seems more consistent.
## Test Plan
Unit test
Previously, distributions created through `Source::Workspace` would have
the absolute path as lock path. This didn't cause any problems, since in
`Urls` we would later overwrite those urls with the correct one created
from being workspace members by path.
Changing the order surfaced this. This change emits the correct lock
path. I've manually checked the difference with `dbg!`, this is not
observable on main, but on the diverging urls branch it fixes lockfile
creation.
## Summary
After this change, `uv add` will try to use `tool.uv.sources` for all
source requirements. If a source cannot be resolved, i.e. an ambiguous
Git reference is provided, it will error. Git references can be
specified with the `--tag`, `--branch`, or `--rev` arguments. Editables
are also supported with `--editable`.
Users can opt-out of `tool.uv.sources` support with the `--raw` flag,
which will force uv to use `project.dependencies`.
Part of https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3959.
## Summary
Implements `uv add foo --workspace`, which adds `foo` as a workspace
dependency with the corresponding `tool.uv.sources` entry.
Part of https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3959.
## Summary
Because the workspace member itself is part of the resolution, adding
the workspace name for the project leads to confusing errors, like:
```
❯ cargo run lock --preview
Compiling uv v0.2.11 (/Users/crmarsh/workspace/puffin/crates/uv)
Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 1.79s
Running `/Users/crmarsh/workspace/puffin/target/debug/uv lock --preview`
× No solution found when resolving dependencies:
╰─▶ Because only albatross==0.1.0 is available and albatross==0.1.0 depends on anyio<=3, we can conclude that all versions of albatross depend on anyio<=3.
And because bird-feeder==1.0.0 depends on anyio>=4.3.0,<5 and only bird-feeder==1.0.0 is available, we can conclude that all versions of albatross and all versions of bird-feeder are incompatible.
And because albatross depends on albatross and bird-feeder, we can conclude that the requirements are unsatisfiable.
```
(Notice "albatross depends on albatross".)
Previously, `b` in the test case would have been incorrectly locked to
the path of `a`. I've moved `relative_to` into uv-fs since it's now used
in two different places.
Previously failing lockfile when `a/pyproject.toml` and
`a/b/pyproject.toml` exist (not in a workspace) and `a` was depending on
`b`:
```toml
version = 1
requires-python = ">=3.11, <3.13"
[[distribution]]
name = "b"
version = "0.1.0"
source = "directory+/home/konsti/projects/uv/a"
sdist = { path = "/home/konsti/projects/uv/a" }
[[distribution]]
name = "black"
version = "0.1.0"
source = "editable+."
sdist = { path = "." }
[[distribution.dependencies]]
name = "b"
version = "0.1.0"
source = "directory+/home/konsti/projects/uv/a"
```
Updates `--no-binary <package>` to take precedence over `--only-binary
:all:` and `--only-binary <package>` to take precedence over
`--no-binary :all:`.
I'm not entirely sure about this behavior, e.g. maybe I provided
`--only-binary :all:` later on the command line and really want it to
override those earlier arguments of `--no-binary <package>` for safety.
Right now we just fail to solve though since we can't satisfy the
overlapping requests.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/4063
## Summary
This is what I consider to be the "real" fix for #8072. We now treat
directory and path URLs as separate `ParsedUrl` types and
`RequirementSource` types. This removes a lot of `.is_dir()` forking
within the `ParsedUrl::Path` arms and makes some states impossible
(e.g., you can't have a `.whl` path that is editable). It _also_ fixes
the `direct_url.json` for direct URLs that refer to files. Previously,
we wrote out to these as if they were installed as directories, which is
just wrong.
By splitting `path` into a lockable, relative (or absolute) and an
absolute installable path and by splitting between urls and paths by
dist type, we can store relative paths in the lockfile.
## Summary
Adds handling for a few cases to improve interoperability with Poetry:
- If the `project` schema is invalid, we now raise a hard error, rather
than treating the metadata as dynamic and then falling back to the build
backend. This could cause problems, I'm not sure. It's stricter than
before.
- If the project contains `tool.poetry` but omits
`project.dependencies`, we now treat it as dynamic. We could go even
further and treat _any_ Poetry project as dynamic, but then we'd be
ignoring user-declared dependencies, which is also confusing.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/4142.
When creating a lockfile, lock the combined dependencies for all
packages in a workspace. This make the lockfile independent of where you
are in the workspace.
Fixes#3983
## Summary
Externally, development dependencies are currently structured as a flat
list of PEP 580-compatible requirements:
```toml
[tool.uv]
dev-dependencies = ["werkzeug"]
```
When locking, we lock all development dependencies; when syncing, users
can provide `--dev`.
Internally, though, we model them as dependency groups, similar to
Poetry, PDM, and [PEP 735](https://peps.python.org/pep-0735). This
enables us to change out the user-facing frontend without changing the
internal implementation, once we've decided how these should be exposed
to users.
A few important decisions encoded in the implementation (which we can
change later):
1. Groups are enabled globally, for all dependencies. This differs from
extras, which are enabled on a per-requirement basis. Note, however,
that we'll only discover groups for uv-enabled packages anyway.
2. Installing a group requires installing the base package. We rely on
this in PubGrub to ensure that we resolve to the same version (even
though we only expect groups to come from workspace dependencies anyway,
which are unique). But anyway, that's encoded in the resolver right now,
just as it is for extras.
## Summary
If `Requires-Python` is omitted in `uv lock` or `uv run`, we now warn
and default to `>=` the current minor version.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/4050.
## Summary
This PR separates "gathering the requirements" from the rest of the
metadata (e.g., version), which isn't required when installing a
package's _dependencies_ (as opposed to installing the package itself).
It thus ensures that we don't need to build a package when a static
`pyproject.toml` is provided in `pip compile`.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/4040.
We know that `[project]` must exist for each workspace member, so we can
store it directly and avoid going through the `.and_then()` when we need
to access it. This requires cloning the struct due to lack of
self-referential structs. An alternative would taking the `Project` from
`PyProjectToml` instead, but this could be confusing when passing the
`PyProjectToml` around.
Add a `--package` option that allows switching the current project in
the workspace. Wherever you are in a workspace, you should be able to
run with any other project as root. This is the uv equivalent of `cargo
run -p`.
I don't love the `--package` name, esp. since `-p` is already taken and
in general to many things start with p already.
Part of this change is moving the workspace discovery of
`ProjectWorkspace` to `Workspace` itself.
## Usage
In albatross-virtual-workspace:
```console
$ uv venv
$ uv run --preview --package bird-feeder python -c "import albatross"
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/bird-feeder
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/seeds
Built 2 editables in 167ms
Resolved 5 packages in 4ms
Installed 5 packages in 1ms
+ anyio==4.4.0
+ bird-feeder==1.0.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/bird-feeder)
+ idna==3.6
+ seeds==1.0.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/seeds)
+ sniffio==1.3.1
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'albatross'
$ uv venv
$ uv run --preview --package albatross python -c "import albatross"
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/albatross
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/bird-feeder
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/seeds
Built 3 editables in 173ms
Resolved 7 packages in 6ms
Installed 7 packages in 1ms
+ albatross==0.1.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/albatross)
+ anyio==4.4.0
+ bird-feeder==1.0.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/bird-feeder)
+ idna==3.6
+ seeds==1.0.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-virtual-workspace/packages/seeds)
+ sniffio==1.3.1
+ tqdm==4.66.4
```
In albatross-root-workspace:
```console
$ uv venv
$ uv run --preview --package bird-feeder python -c "import albatross"
Using Python 3.12.3 interpreter at: /home/konsti/.local/bin/python3
Creating virtualenv at: .venv
Activate with: source .venv/bin/activate
Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.10s
Running `/home/konsti/projects/uv/target/debug/uv run --preview --package bird-feeder python -c 'import albatross'`
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace/packages/bird-feeder
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace/packages/seeds Built 2 editables in 161ms
Resolved 5 packages in 4ms
Installed 5 packages in 1ms
+ anyio==4.4.0
+ bird-feeder==1.0.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace/packages/bird-feeder)
+ idna==3.6
+ seeds==1.0.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace/packages/seeds)
+ sniffio==1.3.1
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'albatross'
$ uv venv
$ cargo run run --preview --package albatross python -c "import albatross"
Using Python 3.12.3 interpreter at: /home/konsti/.local/bin/python3
Creating virtualenv at: .venv
Activate with: source .venv/bin/activate
Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.13s
Running `/home/konsti/projects/uv/target/debug/uv run --preview --package albatross python -c 'import albatross'`
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace/packages/bird-feeder
Built file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace/packages/seeds
Built 3 editables in 168ms
Resolved 7 packages in 5ms
Installed 7 packages in 1ms
+ albatross==0.1.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace)
+ anyio==4.4.0
+ bird-feeder==1.0.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace/packages/bird-feeder)
+ idna==3.6
+ seeds==1.0.0 (from file:///home/konsti/projects/uv/scripts/workspaces/albatross-root-workspace/packages/seeds)
+ sniffio==1.3.1
+ tqdm==4.66.4
```
## Summary
This PR removes the static resolver map:
```rust
static RESOLVED_GIT_REFS: Lazy<Mutex<FxHashMap<RepositoryReference, GitSha>>> =
Lazy::new(Mutex::default);
```
With a `GitResolver` struct that we now pass around on the
`BuildContext`. There should be no behavior changes here; it's purely an
internal refactor with an eye towards making it cleaner for us to
"pre-populate" the list of resolved SHAs.
Move `Metadata`, `MetadataLoweringError` and `ArchiveMetadata` into
their own file `metadata.rs` in `uv-distribution`, moving it out from
`lib.rs`. No functional changes.
With the change, we remove the special casing of workspace dependencies
and resolve `tool.uv` for all git and directory distributions. This
gives us support for non-editable workspace dependencies and path
dependencies in other workspaces. It removes a lot of special casing
around workspaces. These changes are the groundwork for supporting
`tool.uv` with dynamic metadata.
The basis for this change is moving `Requirement` from
`distribution-types` to `pypi-types` and the lowering logic from
`uv-requirements` to `uv-distribution`. This changes should be split out
in separate PRs.
I've included an example workspace `albatross-root-workspace2` where
`bird-feeder` depends on `a` from another workspace `ab`. There's a
bunch of failing tests and regressed error messages that still need
fixing. It does fix the audited package count for the workspace tests.
## Summary
We currently rely on libgit2 for most git-related functionality.
However, libgit2 has long-standing performance issues, as well as lags
significantly behind git in terms of new features. For these reasons we
now use the git CLI by default for fetching repositories
(https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/1781). This PR completely drops
libgit2 in favor of the git CLI for all git-related functionality, which
should allow us to use features such as partial clones and sparse
checkouts in the future for performance.
There is also a lot of technical debt in the current git code as it's
mostly taken from Cargo. Switching to the git CLI *vastly* simplifies
the `uv-git` codebase.
Eventually we might want to look into switching to
[`gitoxide`](https://github.com/Byron/gitoxide), but it's currently too
immature for our use case.
## Summary
There are a few behavior changes in here:
- We now enforce `--require-hashes` for editables, like pip. So if you
use `--require-hashes` with an editable requirement, we'll reject it. I
could change this if it seems off.
- We now treat source tree requirements, editable or not (e.g., both `-e
./black` and `./black`) as if `--refresh` is always enabled. This
doesn't mean that we _always_ rebuild them; but if you pass
`--reinstall`, then yes, we always rebuild them. I think this is an
improvement and is close to how editables work today.
Closes#3844.
Closes#2695.
When parsing requirements from any source, directly parse the url parts
(and reject unsupported urls) instead of parsing url parts at a later
stage. This removes a bunch of error branches and concludes the work
parsing url parts once and passing them around everywhere.
Many usages of the assembled `VerbatimUrl` remain, but these can be
removed incrementally.
Please review commit-by-commit.
## Summary
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3715.
## Test Plan
```
❯ echo "/../test" | cargo run pip compile -
error: Couldn't parse requirement in `-` at position 0
Caused by: path could not be normalized: /../test
/../test
^^^^^^^^
❯ echo "-e /../test" | cargo run pip compile -
error: Invalid URL in `-`: `/../test`
Caused by: path could not be normalized: /../test
Caused by: cannot normalize a relative path beyond the base directory
```
## Summary
Uncertain about this, but we don't actually need the full
`SourceDistFilename`, only the name and version -- and we often have
that information already (as in the lockfile routines). So by flattening
the fields onto `RegistrySourceDist`, we can avoid re-parsing for
information we already have.
Our current flow of data from "simple registry package" to "final
resolved distribution" goes through a number of types:
* `SimpleMetadata` is the API response from a registry that includes all
published versions for a package. Each version has an assortment of
metadata
associated with it.
* `VersionFiles` is the aforementioned metadata. It is split in two: a
group of files for source distributions and a group of files for wheels.
* `PrioritizedDist` collects a subset of the files from `VersionFiles`
to form a selection of the "best" sdist and the "best" wheel for the
current environment.
* `CompatibleDist` is created from a borrowed `PrioritizedDist` that,
perhaps among other things, encapsulates the decision of whether to pick
an sdist or a wheel. (This decision depends both on compatibility and
the action being performed. e.g., When doing installation, a
`CompatibleDist` will sometimes select an sdist over a wheel.)
* `ResolvedDistRef` is like a `ResolvedDist`, but borrows a `Dist`.
* `ResolvedDist` is the almost-final-form of a distribution in a
resolution and is created from a `ResolvedDistRef`.
* `AnnotatedResolvedDist` is a new data type that is the actual final
form of a distribution that a universal lock file cares about. It
bundles a `ResolvedDist` with some metadata needed to generate a lock
file.
One of the requirements of a universal lock file is that we include all
wheels (and maybe all source distributions? but at least one if it's
present) associated with a distribution. But the above flow of data (in
the step from `VersionFiles` to `PrioritizedDist`) drops all wheels
except for the best one.
To remedy this, in this PR, we rejigger `PrioritizedDist`,
`CompatibleDist` and `ResolvedDistRef` so that all wheel data is
preserved. And when a `ResolvedDistRef` is finally turned into a
`ResolvedDist`, we copy all of the wheel data. And finally, we adjust
the `Lock` constructor to read this new data and include it in the lock
file. To make this work, we also modify `RegistryBuiltDist` so that it
can contain one or more wheels instead of just one.
One shortcoming here (called out in the code as a FIXME) is that if a
source distribution is selected as the "best" thing to use (perhaps
there are no compatible wheels), then the wheels won't end up in the
lock file. I plan to fix this in a follow-up PR.
We also aren't totally consistent on source distribution naming.
Sometimes we use `sdist`. Sometimes `source`. Sometimes `source_dist`.
I think it'd be nice to just use `sdist` everywhere, but I do prefer
the type names to be `SourceDist`. And sometimes you want function
names to match the type names (i.e., `from_source_dist`), which in turn
leads to an appearance of inconsistency. I'm open to ideas.
Closes#3351
## Summary
I don't love this, but it turns out that setuptools is not robust to
parallel builds: https://github.com/pypa/setuptools/issues/3119. As a
result, if you run uv from multiple processes, and they each attempt to
build the same source distribution, you can hit failures.
This PR applies an advisory lock to the source distribution directory.
We apply it unconditionally, even if we ultimately find something in the
cache and _don't_ do a build, which helps ensure that we only build the
distribution once (and wait for that build to complete) rather than
kicking off builds from each thread.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3512.
## Test Plan
Ran:
```sh
#!/bin/bash
make_venv(){
target/debug/uv venv $1
source $1/bin/activate
target/debug/uv pip install opentracing --no-deps --verbose
}
for i in {1..8}
do
make_venv ./$1/$i &
done
```
## Summary
I think this is overall good change because it explicitly encodes (in
the type system) something that was previously implicit. I'm not a huge
fan of the names here, open to input.
It covers some of https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3506 but I
don't think it _closes_ it.
## Summary
This PR consolidates the concurrency limits used throughout `uv` and
exposes two limits, `UV_CONCURRENT_DOWNLOADS` and
`UV_CONCURRENT_BUILDS`, as environment variables.
Currently, `uv` has a number of concurrent streams that it buffers using
relatively arbitrary limits for backpressure. However, many of these
limits are conflated. We run a relatively small number of tasks overall
and should start most things as soon as possible. What we really want to
limit are three separate operations:
- File I/O. This is managed by tokio's blocking pool and we should not
really have to worry about it.
- Network I/O.
- Python build processes.
Because the current limits span a broad range of tasks, it's possible
that a limit meant for network I/O is occupied by tasks performing
builds, reading from the file system, or even waiting on a `OnceMap`. We
also don't limit build processes that end up being required to perform a
download. While this may not pose a performance problem because our
limits are relatively high, it does mean that the limits do not do what
we want, making it tricky to expose them to users
(https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/1205,
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/3311).
After this change, the limits on network I/O and build processes are
centralized and managed by semaphores. All other tasks are unbuffered
(note that these tasks are still bounded, so backpressure should not be
a problem).
## Summary
All of the resolver code is run on the main thread, so a lot of the
`Send` bounds and uses of `DashMap` and `Arc` are unnecessary. We could
also switch to using single-threaded versions of `Mutex` and `Notify` in
some places, but there isn't really a crate that provides those I would
be comfortable with using.
The `Arc` in `OnceMap` can't easily be removed because of the uv-auth
code which uses the
[reqwest-middleware](https://docs.rs/reqwest-middleware/latest/reqwest_middleware/trait.Middleware.html)
crate, that seems to adds unnecessary `Send` bounds because of
`async-trait`. We could duplicate the code and create a `OnceMapLocal`
variant, but I don't feel that's worth it.
## Introduction
PEP 621 is limited. Specifically, it lacks
* Relative path support
* Editable support
* Workspace support
* Index pinning or any sort of index specification
The semantics of urls are a custom extension, PEP 440 does not specify
how to use git references or subdirectories, instead pip has a custom
stringly format. We need to somehow support these while still stying
compatible with PEP 621.
## `tool.uv.source`
Drawing inspiration from cargo, poetry and rye, we add `tool.uv.sources`
or (for now stub only) `tool.uv.workspace`:
```toml
[project]
name = "albatross"
version = "0.1.0"
dependencies = [
"tqdm >=4.66.2,<5",
"torch ==2.2.2",
"transformers[torch] >=4.39.3,<5",
"importlib_metadata >=7.1.0,<8; python_version < '3.10'",
"mollymawk ==0.1.0"
]
[tool.uv.sources]
tqdm = { git = "https://github.com/tqdm/tqdm", rev = "cc372d09dcd5a5eabdc6ed4cf365bdb0be004d44" }
importlib_metadata = { url = "https://github.com/python/importlib_metadata/archive/refs/tags/v7.1.0.zip" }
torch = { index = "torch-cu118" }
mollymawk = { workspace = true }
[tool.uv.workspace]
include = [
"packages/mollymawk"
]
[tool.uv.indexes]
torch-cu118 = "https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118"
```
See `docs/specifying_dependencies.md` for a detailed explanation of the
format. The basic gist is that `project.dependencies` is what ends up on
pypi, while `tool.uv.sources` are your non-published additions. We do
support the full range or PEP 508, we just hide it in the docs and
prefer the exploded table for easier readability and less confusing with
actual url parts.
This format should eventually be able to subsume requirements.txt's
current use cases. While we will continue to support the legacy `uv pip`
interface, this is a piece of the uv's own top level interface. Together
with `uv run` and a lockfile format, you should only need to write
`pyproject.toml` and do `uv run`, which generates/uses/updates your
lockfile behind the scenes, no more pip-style requirements involved. It
also lays the groundwork for implementing index pinning.
## Changes
This PR implements:
* Reading and lowering `project.dependencies`,
`project.optional-dependencies` and `tool.uv.sources` into a new
requirements format, including:
* Git dependencies
* Url dependencies
* Path dependencies, including relative and editable
* `pip install` integration
* Error reporting for invalid `tool.uv.sources`
* Json schema integration (works in pycharm, see below)
* Draft user-level docs (see `docs/specifying_dependencies.md`)
It does not implement:
* No `pip compile` testing, deprioritizing towards our own lockfile
* Index pinning (stub definitions only)
* Development dependencies
* Workspace support (stub definitions only)
* Overrides in pyproject.toml
* Patching/replacing dependencies
One technically breaking change is that we now require user provided
pyproject.toml to be valid wrt to PEP 621. Included files still fall
back to PEP 517. That means `pip install -r requirements.txt` requires
it to be valid while `pip install -r requirements.txt` with `-e .` as
content falls back to PEP 517 as before.
## Implementation
The `pep508` requirement is replaced by a new `UvRequirement` (name up
for bikeshedding, not particularly attached to the uv prefix). The still
existing `pep508_rs::Requirement` type is a url format copied from pip's
requirements.txt and doesn't appropriately capture all features we
want/need to support. The bulk of the diff is changing the requirement
type throughout the codebase.
We still use `VerbatimUrl` in many places, where we would expect a
parsed/decomposed url type, specifically:
* Reading core metadata except top level pyproject.toml files, we fail a
step later instead if the url isn't supported.
* Allowed `Urls`.
* `PackageId` with a custom `CanonicalUrl` comparison, instead of
canonicalizing urls eagerly.
* `PubGrubPackage`: We eventually convert the `VerbatimUrl` back to a
`Dist` (`Dist::from_url`), instead of remembering the url.
* Source dist types: We use verbatim url even though we know and require
that these are supported urls we can and have parsed.
I tried to make improve the situation be replacing `VerbatimUrl`, but
these changes would require massive invasive changes (see e.g.
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/3253). A main problem is the ref
`VersionOrUrl` and applying overrides, which assume the same
requirement/url type everywhere. In its current form, this PR increases
this tech debt.
I've tried to split off PRs and commits, but the main refactoring is
still a single monolith commit to make it compile and the tests pass.
## Demo
Adding
d1ae3b85d5/pyproject.json
as json schema (v7) to pycharm for `pyproject.toml`, you can try the IDE
support already:
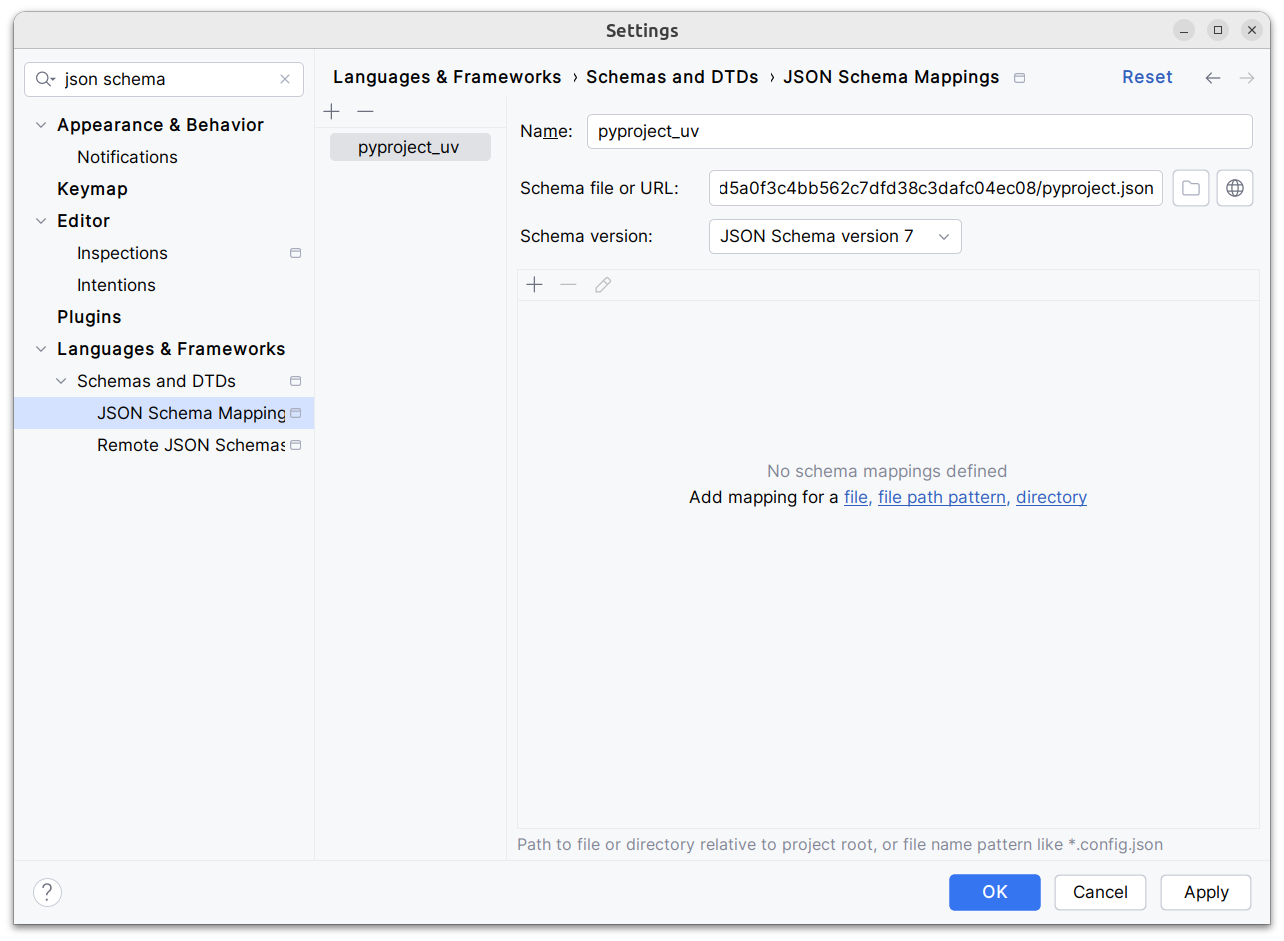
[dove.webm](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/assets/6826232/c293c272-c80b-459d-8c95-8c46a8d198a1)
In *some* places in our crates, `serde` (and `rkyv`) are optional
dependencies. I believe this was done out of reasons of "good sense,"
that is, it follows a Rust ecosystem pattern where serde integration
tends to be an opt-in crate feature. (And similarly for `rkyv`.)
However, ultimately, `uv` itself requires `serde` and `rkyv` to
function. Since our crates are strictly internal, there are limited
consumers for our crates without `serde` (and `rkyv`) enabled. I think
one possibility is that optional `serde` (and `rkyv`) integration means
that someone can do this:
cargo test -p pep440_rs
And this will run tests _without_ `serde` or `rkyv` enabled. That in
turn could lead to faster iteration time by reducing compile times. But,
I'm not sure this is worth supporting. The iterative compilation times
of
individual crates are probably fast enough in debug mode, even with
`serde` and `rkyv` enabled. Namely, `serde` and `rkyv` themselves
shouldn't need to be re-compiled in most cases. On `main`:
```
from-scratch: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --lib` 0.685
incremental: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --lib` 0.278s
from-scratch: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --features serde,rkyv --lib` 3.948s
incremental: `cargo test -p pep440_rs --features serde,rkyv --lib` 0.321s
```
So while a from-scratch build does take significantly longer, an
incremental build is about the same.
The benefit of doing this change is two-fold:
1. It brings out crates into alignment with "reality." In particular,
some crates were _implicitly_ relying on `serde` being enabled
without explicitly declaring it. This technically means that our
`Cargo.toml`s were wrong in some cases, but it is hard to observe it
because of feature unification in a Cargo workspace.
2. We no longer need to deal with the cognitive burden of writing
`#[cfg_attr(feature = "serde", ...)]` everywhere.
## Summary
I found some of these too bare (e.g., when they _just_ show a package
name with no other information). For me, this makes it easier to
differentiate error message copy from data. But open to other opinions.
Take a look at the fixture changes and LMK!
Add a dedicated error type for direct url parsing. This change is broken
out from the new uv requirement type, which uses direct url parsing
internally.
## Summary
If there are no hashes for a given package, we now return
`Validate(&[])` so that the policy is impossible to satisfy. Previously,
we returned `None`, which is always satisfied.
We don't really ever expect to hit this, because we detect this case in
the resolver and raise a different error. But if we have a bug
somewhere, it's better to fail with an error than silently let the
package through.
## Summary
This PR enables `--require-hashes` with unnamed requirements. The key
change is that `PackageId` becomes `VersionId` (since it refers to a
package at a specific version), and the new `PackageId` consists of
_either_ a package name _or_ a URL. The hashes are keyed by `PackageId`,
so we can generate the `RequiredHashes` before we have names for all
packages, and enforce them throughout.
Closes#2979.
## Summary
Similar to `Revision`, we now store IDs in the `Archive` entires rather
than absolute paths. This makes the cache robust to moves, etc.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2908.
## Summary
This PR formalizes some of the concepts we use in the cache for
"pointers to things".
In the wheel cache, we have files like
`annotated_types-0.6.0-py3-none-any.http`. This represents an unzipped
wheel, cached alongside an HTTP caching policy. We now have a struct for
this to encapsulate the logic: `HttpArchivePointer`.
Similarly, we have files like `annotated_types-0.6.0-py3-none-any.rev`.
This represents an unzipped local wheel, alongside with a timestamp. We
now have a struct for this to encapsulate the logic:
`LocalArchivePointer`.
We have similar structs for source distributions too.
## Summary
This PR enables hash generation for URL requirements when the user
provides `--generate-hashes` to `pip compile`. While we include the
hashes from the registry already, today, we omit hashes for URLs.
To power hash generation, we introduce a `HashPolicy` abstraction:
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq)]
pub enum HashPolicy<'a> {
/// No hash policy is specified.
None,
/// Hashes should be generated (specifically, a SHA-256 hash), but not validated.
Generate,
/// Hashes should be validated against a pre-defined list of hashes. If necessary, hashes should
/// be generated so as to ensure that the archive is valid.
Validate(&'a [HashDigest]),
}
```
All of the methods on the distribution database now accept this policy,
instead of accepting `&'a [HashDigest]`.
Closes#2378.
## Summary
This PR modifies the distribution database to return both the
`Metadata23` and the computed hashes when clients request metadata.
No behavior changes, but this will be necessary to power
`--generate-hashes`.
## Summary
This PR adds support for hash-checking mode in `pip install` and `pip
sync`. It's a large change, both in terms of the size of the diff and
the modifications in behavior, but it's also one that's hard to merge in
pieces (at least, with any test coverage) since it needs to work
end-to-end to be useful and testable.
Here are some of the most important highlights:
- We store hashes in the cache. Where we previously stored pointers to
unzipped wheels in the `archives` directory, we now store pointers with
a set of known hashes. So every pointer to an unzipped wheel also
includes its known hashes.
- By default, we don't compute any hashes. If the user runs with
`--require-hashes`, and the cache doesn't contain those hashes, we
invalidate the cache, redownload the wheel, and compute the hashes as we
go. For users that don't run with `--require-hashes`, there will be no
change in performance. For users that _do_, the only change will be if
they don't run with `--generate-hashes` -- then they may see some
repeated work between resolution and installation, if they use `pip
compile` then `pip sync`.
- Many of the distribution types now include a `hashes` field, like
`CachedDist` and `LocalWheel`.
- Our behavior is similar to pip, in that we enforce hashes when pulling
any remote distributions, and when pulling from our own cache. Like pip,
though, we _don't_ enforce hashes if a distribution is _already_
installed.
- Hash validity is enforced in a few different places:
1. During resolution, we enforce hash validity based on the hashes
reported by the registry. If we need to access a source distribution,
though, we then enforce hash validity at that point too, prior to
running any untrusted code. (This is enforced in the distribution
database.)
2. In the install plan, we _only_ add cached distributions that have
matching hashes. If a cached distribution is missing any hashes, or the
hashes don't match, we don't return them from the install plan.
3. In the downloader, we _only_ return distributions with matching
hashes.
4. The final combination of "things we install" are: (1) the wheels from
the cache, and (2) the downloaded wheels. So this ensures that we never
install any mismatching distributions.
- Like pip, if `--require-hashes` is provided, we require that _all_
distributions are pinned with either `==` or a direct URL. We also
require that _all_ distributions have hashes.
There are a few notable TODOs:
- We don't support hash-checking mode for unnamed requirements. These
should be _somewhat_ rare, though? Since `pip compile` never outputs
unnamed requirements. I can fix this, it's just some additional work.
- We don't automatically enable `--require-hashes` with a hash exists in
the requirements file. We require `--require-hashes`.
Closes#474.
## Test Plan
I'd like to add some tests for registries that report incorrect hashes,
but otherwise: `cargo test`
To get more insights into test performance, allow instrumenting tests
with tracing-durations-export.
Usage:
```shell
# A single test
TRACING_DURATIONS_TEST_ROOT=$(pwd)/target/test-traces cargo test --features tracing-durations-export --test pip_install_scenarios no_binary -- --exact
# All tests
TRACING_DURATIONS_TEST_ROOT=$(pwd)/target/test-traces cargo nextest run --features tracing-durations-export
```
Then we can e.g. look at
`target/test-traces/pip_install_scenarios::no_binary.svg` and see the
builds it performs:

## Summary
If we build a source distribution from the registry, and the version
doesn't match that of the filename, we should error, just as we do for
mismatched package names. However, we should also backtrack here, which
we didn't previously.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/issues/2953.
## Test Plan
Verified that `cargo run pip install docutils --verbose --no-cache
--reinstall` installs `docutils==0.21` instead of the invalid
`docutils==0.21.post1`.
In the logs, I see:
```
WARN Unable to extract metadata for docutils: Package metadata version `0.21` does not match given version `0.21.post1`
```
Needed to prevent circular dependencies in my toolchain work (#2931). I
think this is probably a reasonable change as we move towards persistent
configuration too?
Unfortunately `BuildIsolation` needs to be in `uv-types` to avoid
circular dependencies still. We might be able to resolve that in the
future.
## Summary
When you specify a source distribution via a path, it can either be a
path to an archive (like a `.tar.gz` file), or a source tree (a
directory). Right now, we handle both paths through the same methods in
the source database. This PR splits them up into separate handlers.
This will make hash generation a little easier, since we need to
generate hashes for archives, but _can't_ generate hashes for source
trees.
It also means that we can now store the unzipped source distribution in
the cache (in the case of archives), and avoid unzipping the source
distribution needlessly on every invocation; and, overall, let's un
enforce clearer expectations between the two routes (e.g., what errors
are possible vs. not), at the cost of duplicating some code.
Closes#2760 (incidentally -- not exactly the motivation for the change,
but it did accomplish it).
## Summary
I think this is a much clearer name for this concept: the set of
"versions" of a given wheel or source distribution. We also use
"Manifest" elsewhere to refer to the set of requirements, constraints,
etc., so this was overloaded.