This PR adds a syntax error if the parser encounters a `TryStmt` that
has except clauses both with and without a star.
The displayed error points to each except clause that contradicts the
original except clause kind. So, for example,
```python
try:
....
except: #<-- we assume this is the desired except kind
....
except*: #<--- error will point here
....
except*: #<--- and here
....
```
Closes#14860
This adds support for `type[Any]`, which represents an unknown type (not
an instance of an unknown type), and `type`, which we are choosing to
interpret as `type[object]`.
Closes#14546
## Summary
This is already several hundred lines of code, and it will get more
complex with call-signature checking.
## Test Plan
This is a pure code move; the moved code wasn't changed, just imports.
Existing tests pass.
## Summary
Add a `is_fully_static` premise to the equivalence on subtyping property tests.
## Test Plan
```
cargo test -p red_knot_python_semantic -- --ignored types::property_tests::stable
```
Without this, `cargo insta test` re-compiles every time it is run, even
if there are no changes. With this, I can re-run `cargo insta test` (or
other `cargo build` commands) without it resulting in re-compiles.
I made an identical change to uv a while back:
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv/pull/6825
## Summary
This is the second PR out of three that adds support for
enabling/disabling lint rules in Red Knot. You may want to take a look
at the [first PR](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14869) in this
stack to familiarize yourself with the used terminology.
This PR adds a new syntax to define a lint:
```rust
declare_lint! {
/// ## What it does
/// Checks for references to names that are not defined.
///
/// ## Why is this bad?
/// Using an undefined variable will raise a `NameError` at runtime.
///
/// ## Example
///
/// ```python
/// print(x) # NameError: name 'x' is not defined
/// ```
pub(crate) static UNRESOLVED_REFERENCE = {
summary: "detects references to names that are not defined",
status: LintStatus::preview("1.0.0"),
default_level: Level::Warn,
}
}
```
A lint has a name and metadata about its status (preview, stable,
removed, deprecated), the default diagnostic level (unless the
configuration changes), and documentation. I use a macro here to derive
the kebab-case name and extract the documentation automatically.
This PR doesn't yet add any mechanism to discover all known lints. This
will be added in the next and last PR in this stack.
## Documentation
I documented some rules but then decided that it's probably not my best
use of time if I document all of them now (it also means that I play
catch-up with all of you forever). That's why I left some rules
undocumented (marked with TODO)
## Where is the best place to define all lints?
I'm not sure. I think what I have in this PR is fine but I also don't
love it because most lints are in a single place but not all of them. If
you have ideas, let me know.
## Why is the message not part of the lint, unlike Ruff's `Violation`
I understand that the main motivation for defining `message` on
`Violation` in Ruff is to remove the need to repeat the same message
over and over again. I'm not sure if this is an actual problem. Most
rules only emit a diagnostic in a single place and they commonly use
different messages if they emit diagnostics in different code paths,
requiring extra fields on the `Violation` struct.
That's why I'm not convinced that there's an actual need for it and
there are alternatives that can reduce the repetition when creating a
diagnostic:
* Create a helper function. We already do this in red knot with the
`add_xy` methods
* Create a custom `Diagnostic` implementation that tailors the entire
diagnostic and pre-codes e.g. the message
Avoiding an extra field on the `Violation` also removes the need to
allocate intermediate strings as it is commonly the place in Ruff.
Instead, Red Knot can use a borrowed string with `format_args`
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
This PR introduces a structured `DiagnosticId` instead of using a plain
`&'static str`. It is the first of three in a stack that implements a
basic rules infrastructure for Red Knot.
`DiagnosticId` is an enum over all known diagnostic codes. A closed enum
reduces the risk of accidentally introducing two identical diagnostic
codes. It also opens the possibility of generating reference
documentation from the enum in the future (not part of this PR).
The enum isn't *fully closed* because it uses a `&'static str` for lint
names. This is because we want the flexibility to define lints in
different crates, and all names are only known in `red_knot_linter` or
above. Still, lower-level crates must already reference the lint names
to emit diagnostics. We could define all lint-names in `DiagnosticId`
but I decided against it because:
* We probably want to share the `DiagnosticId` type between Ruff and Red
Knot to avoid extra complexity in the diagnostic crate, and both tools
use different lint names.
* Lints require a lot of extra metadata beyond just the name. That's why
I think defining them close to their implementation is important.
In the long term, we may also want to support plugins, which would make
it impossible to know all lint names at compile time. The next PR in the
stack introduces extra syntax for defining lints.
A closed enum does have a few disadvantages:
* rustc can't help us detect unused diagnostic codes because the enum is
public
* Adding a new diagnostic in the workspace crate now requires changes to
at least two crates: It requires changing the workspace crate to add the
diagnostic and the `ruff_db` crate to define the diagnostic ID. I
consider this an acceptable trade. We may want to move `DiagnosticId` to
its own crate or into a shared `red_knot_diagnostic` crate.
## Preventing duplicate diagnostic identifiers
One goal of this PR is to make it harder to introduce ambiguous
diagnostic IDs, which is achieved by defining a closed enum. However,
the enum isn't fully "closed" because it doesn't explicitly list the IDs
for all lint rules. That leaves the possibility that a lint rule and a
diagnostic ID share the same name.
I made the names unambiguous in this PR by separating them into
different namespaces by using `lint/<rule>` for lint rule codes. I don't
mind the `lint` prefix in a *Ruff next* context, but it is a bit weird
for a standalone type checker. I'd like to not overfocus on this for now
because I see a few different options:
* We remove the `lint` prefix and add a unit test in a top-level crate
that iterates over all known lint rules and diagnostic IDs to ensure the
names are non-overlapping.
* We only render `[lint]` as the error code and add a note to the
diagnostic mentioning the lint rule. This is similar to clippy and has
the advantage that the header line remains short
(`lint/some-long-rule-name` is very long ;))
* Any other form of adjusting the diagnostic rendering to make the
distinction clear
I think we can defer this decision for now because the `DiagnosticId`
contains all the relevant information to change the rendering
accordingly.
## Why `Lint` and not `LintRule`
I see three kinds of diagnostics in Red Knot:
* Non-suppressable: Reveal type, IO errors, configuration errors, etc.
(any `DiagnosticId`)
* Lints: code-related diagnostics that are suppressable.
* Lint rules: The same as lints, but they can be enabled or disabled in
the configuration. The majority of lints in Red Knot and the Ruff
linter.
Our current implementation doesn't distinguish between lints and Lint
rules because we aren't aware of a suppressible code-related lint that
can't be configured in the configuration. The only lint that comes to my
mind is maybe `division-by-zero` if we're 99.99% sure that it is always
right. However, I want to keep the door open to making this distinction
in the future if it proves useful.
Another reason why I chose lint over lint rule (or just rule) is that I
want to leave room for a future lint rule and lint phase concept:
* lint is the *what*: a specific code smell, pattern, or violation
* the lint rule is the *how*: I could see a future `LintRule` trait in
`red_knot_python_linter` that provides the necessary hooks to run as
part of the linter. A lint rule produces diagnostics for exactly one
lint. A lint rule differs from all lints in `red_knot_python_semantic`
because they don't run as "rules" in the Ruff sense. Instead, they're a
side-product of type inference.
* the lint phase is a different form of *how*: A lint phase can produce
many different lints in a single pass. This is a somewhat common pattern
in Ruff where running one analysis collects the necessary information
for finding many different lints
* diagnostic is the *presentation*: Unlike a lint, the diagnostic isn't
the what, but how a specific lint gets presented. I expect that many
lints can use one generic `LintDiagnostic`, but a few lints might need
more flexibility and implement their custom diagnostic rendering (at
least custom `Diagnostic` implementation).
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Add replacement fixes to deprecated arguments of a DAG.
Ref #14582#14626
## Test Plan
Diff was verified and snapshots were updated.
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
Per suggestion in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14802#discussion_r1875455417
This is a bit less error-prone and allows us to handle both expressions
in the current scope or a different scope. Also, there's currently no
need for this method outside of `TypeInferenceBuilder`, so no reason to
expose it in `types.rs`.
## Test Plan
Pure refactor, no functional change; existing tests pass.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Part 1 of the big change introduced in #14828. This temporarily causes
all fixes for `round(...)` to be considered unsafe, but they will
eventually be enhanced.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run` and `cargo insta test`.
## Summary
Close#11243. Fix `pytest-parametrize-names-wrong-type (PT006)` to edit
both `argnames` and `argvalues` if both of them are single-element
tuples/lists.
```python
# Before fix
@pytest.mark.parametrize(("x",), [(1,), (2,)])
def test_foo(x):
...
# After fix:
@pytest.mark.parametrize("x", [1, 2])
def test_foo(x):
...
```
## Test Plan
New test cases
This PR introduces three changes to the diagnostic and fix behavior
(still under preview) for [boolean-chained-comparison
(PLR1716)](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/boolean-chained-comparison/#boolean-chained-comparison-plr1716).
1. We now offer a _fix_ in the case of parenthesized expressions like
`(a < b) and b < c`. The fix will merge the chains of comparisons and
then balance parentheses by _adding_ parentheses to one side of the
expression.
2. We now trigger a diagnostic (and fix) in the case where some
comparisons have multiple comparators like `a < b < c and c < d`.
3. When adjacent comparators are parenthesized, we prefer the left
parenthesization and apply the replacement to the whole parenthesized
range. So, for example, `a < (b) and ((b)) < c` becomes `a < (b) < c`.
While these seem like somewhat disconnected changes, they are actually
related. If we only offered (1), then we would see the following fix
behavior:
```diff
- (a < b) and b < c and ((c < d))
+ (a < b < c) and ((c < d))
```
This is because the fix which add parentheses to the first pair of
comparisons overlaps with the fix that removes the `and` between the
second two comparisons. So the latter fix is deferred. However, the
latter fix does not get a second chance because, upon the next lint
iteration, there is no violation of `PLR1716`.
Upon adopting (2), however, both fixes occur by the time ruff completes
several iterations and we get:
```diff
- (a < b) and b < c and ((c < d))
+ ((a < b < c < d))
```
Finally, (3) fixes a previously unobserved bug wherein the autofix for
`a < (b) and b < c` used to result in `a<(b<c` which gives a syntax
error. It could in theory have been fixed in a separate PR, but seems to
be on theme here.
----------
- Closes#13524
- (1), (2), and (3) are implemented in separate commits for ease of
review and modification.
- Technically a user can trigger an error in ruff (by reaching max
iterations) if they have a humongous boolean chained comparison with
differing parentheses levels.
## Summary
Minor change for the documentation of COM818 rule. This was a block
called “In the event that a tuple is intended”, but the suggested change
did not produce a tuple.
## Test Plan
```python
>>> import json
>>> (json.dumps({"bar": 1}),) # this is a tuple
('{"bar": 1}',)
>>> (json.dumps({"bar": 1})) # not a tuple
'{"bar": 1}'
```
Improves error message for [except*](https://peps.python.org/pep-0654/)
(Rules: B025, B029, B030, B904)
Example python snippet:
```python
try:
a = 1
except* ValueError:
a = 2
except* ValueError:
a = 2
try:
pass
except* ():
pass
try:
pass
except* 1: # error
pass
try:
raise ValueError
except* ValueError:
raise UserWarning
```
Error messages
Before:
```
$ ruff check --select=B foo.py
foo.py:6:9: B025 try-except block with duplicate exception `ValueError`
foo.py:11:1: B029 Using `except ():` with an empty tuple does not catch anything; add exceptions to handle
foo.py:16:9: B030 `except` handlers should only be exception classes or tuples of exception classes
foo.py:22:5: B904 Within an `except` clause, raise exceptions with `raise ... from err` or `raise ... from None` to distinguish them from errors in exception handling
Found 4 errors.
```
After:
```
$ ruff check --select=B foo.py
foo.py:6:9: B025 try-except* block with duplicate exception `ValueError`
foo.py:11:1: B029 Using `except* ():` with an empty tuple does not catch anything; add exceptions to handle
foo.py:16:9: B030 `except*` handlers should only be exception classes or tuples of exception classes
foo.py:22:5: B904 Within an `except*` clause, raise exceptions with `raise ... from err` or `raise ... from None` to distinguish them from errors in exception handling
Found 4 errors.
```
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/14791
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
This adds support for `type[a.X]`, where the `type` special form is
applied to a qualified name that resolves to a class literal. This works
for both nested classes and classes imported from another module.
Closes#14545
## Summary
Inferred and declared types for function parameters, in the function
body scope.
Fixes#13693.
## Test Plan
Added mdtests.
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Airflow 3.0 removes various deprecated functions, members, modules, and
other values. They have been deprecated in 2.x, but the removal causes
incompatibilities that we want to detect. This PR deprecates the
following names.
* in `DAG`
* `sla_miss_callback` was removed
* in `airflow.operators.trigger_dagrun.TriggerDagRunOperator`
* `execution_date` was removed
* in `airflow.operators.weekday.DayOfWeekSensor`,
`airflow.operators.datetime.BranchDateTimeOperator` and
`airflow.operators.weekday.BranchDayOfWeekOperator`
* `use_task_execution_day` was removed in favor of
`use_task_logical_date`
The full list of rules we will extend
https://github.com/apache/airflow/issues/44556
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
A test fixture is included in the PR.
## Summary
`typing.Never` and `typing.LiteralString` are only conditionally
exported from `typing` for Python versions 3.11 and later. We run the
Markdown tests with the default Python version of 3.9, so here we change
the import to `typing_extensions` instead, and add a new test to make
sure we'll continue to understand the `typing`-version of these symbols
for newer versions.
This didn't cause problems so far, as we don't understand
`sys.version_info` branches yet.
## Test Plan
New Markdown tests to make sure this will continue to work in the
future.
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/14778
The formatter incorrectly removed the inner implicitly concatenated
string for following single-line f-string:
```py
f"{'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' 'a' if True else ""}"
# formatted
f"{ if True else ''}"
```
This happened because I changed the `RemoveSoftlinesBuffer` in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14489 to remove any content
wrapped in `if_group_breaks`. After all, it emulates an *all flat*
layout. This works fine when `if_group_breaks` is only used to **add**
content if the gorup breaks. It doesn't work if the same content is
rendered differently depending on if the group fits using
`if_group_breaks` and `if_groups_fits` because the enclosing `group`
might still *break* if the entire content exceeds the line-length limit.
This PR fixes this by unwrapping any `if_group_fits` content by removing
the `if_group_fits` start and end tags.
## Test Plan
added test
## Summary
This adds support for specifying the target Python version from a
Markdown test. It is a somewhat limited ad-hoc solution, but designed to
be future-compatible. TOML blocks can be added to arbitrary sections in
the Markdown block. They have the following format:
````markdown
```toml
[tool.knot.environment]
target-version = "3.13"
```
````
So far, there is nothing else that can be configured, but it should be
straightforward to extend this to things like a custom typeshed path.
This is in preparation for the statically-known branches feature where
we are going to have to specify the target version for lots of tests.
## Test Plan
- New Markdown test that fails without the explicitly specified
`target-version`.
- Manually tested various error paths when specifying a wrong
`target-version` field.
- Made sure that running tests is as fast as before.
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/14807
I suspect that this broke when we updated notify, although I'm not quiet
sure how this *ever* worked...
The problem was that the file watcher didn't skip over `Access` events,
but Ruff itself accesses the `pyproject.toml` when checking the project.
That means, Ruff triggers `Access` events but it also schedules a
re-check on every `Access` event... and this goes one forever.
This PR skips over `Access` and `Other` event. `Access` events are
uninteresting because they're only reads, they don't change any file
metadata or content.
The `Other` events should be rare and are mainly to inform about file
watcher changes... we don't need those.
I also added an explicit handling for the `Rescan` event. File watchers
emit a `Rescan` event if they failed to capture some file watching
changes
and it signals that the program should assume that all files might have
changed (the program should do a rescan to *get up to date*).
## Test Plan
I tested that Ruff no longer loops when running `check --watch`. I
verified that Ruff rechecks file after making content changes.
## Summary
This is related to #13778, more specifically
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13778#issuecomment-2513556004.
This PR adds various test cases where a keyword is being where an
identifier is expected. The tests are to make sure that red knot doesn't
panic, raises the syntax error and the identifier is added to the symbol
table. The final part allows editor related features like renaming the
symbol.
## Summary
`typing_extensions` has a `>=3.13` re-export for the `typing.NoDefault`
singleton, but not for `typing._NoDefaultType`. This causes problems as
soon as we understand `sys.version_info` branches, so we explicity
switch to `typing._NoDefaultType` for Python 3.13 and later.
This is a part of #14759 that I thought might make sense to break out
and merge in isolation.
## Test Plan
New test that will become more meaningful with #12700
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
## Summary
- Instead of seven (more or less similar) `setup_db` functions, use just
one in a single central place.
- For every test that needs customization beyond that, offer a
`TestDbBuilder` that can control the Python target version, custom
typeshed, and pre-existing files.
The main motivation for this is that we're soon going to need
customization of the Python version, and I didn't feel like adding this
to each of the existing `setup_db` functions.
## Summary
This changeset contains various improvements concerning non-fully-static
types and their relationships:
- Make sure that non-fully-static types do not participate in
equivalence or subtyping.
- Clarify what `Type::is_equivalent_to` actually implements.
- Introduce `Type::is_fully_static`
- New tests making sure that multiple `Any`/`Unknown`s inside unions and
intersections are collapsed.
closes#14524
## Test Plan
- Added new unit tests for union and intersection builder
- Added new unit tests for `Type::is_equivalent_to`
- Added new unit tests for `Type::is_subtype_of`
- Added new property test making sure that non-fully-static types do not
participate in subtyping
We already had a representation for the Any type, which we would use
e.g. for expressions without type annotations. We now recognize
`typing.Any` as a way to refer to this type explicitly. Like other
special forms, this is tracked correctly through aliasing, and isn't
confused with local definitions that happen to have the same name.
Closes#14544
## Summary
Minor change that uses two plain classes `A` and `B` instead of
`typing.Sized` and `typing.Hashable`.
The motivation is twofold: I remember that I was confused when I first
saw this test. Was there anything specific to `Sized` and `Hashable`
that was relevant here? (there is, these classes are not overlapping;
and you can build a proper intersection from them; but that's true for
almost all non-builtin classes).
I now ran into another problem while working on #14758: `Sized` and
`Hashable` are protocols that we don't fully understand yet. This
causing some trouble when trying to infer whether these are fully-static
types or not.
Closes: #14676
I think the consensus generally was to keep the rule as-is, but expand
the docs.
## Summary
Expands the docs for TC006 with an explanation for why the type
expression is always quoted, including mention of another potential
benefit to this style.
When fixing an invalid escape sequence in an f-string, each f-string
element is analyzed for valid escape characters prior to creating the
diagnostic and fix. This allows us to safely prefix with `r` to create a
raw string if no valid escape characters were found anywhere in the
f-string, and otherwise insert backslashes.
This fixes a bug in the original implementation: each "f-string part"
was treated separately, so it was not possible to tell whether a valid
escape character was or would be used elsewhere in the f-string.
Progress towards #11491 but format specifiers are not handled in this
PR.
## Summary
This PR makes changes to the `AIR001` rule as per
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14627#discussion_r1860212307.
Additionally,
* Avoid returning the `Diagnostic` and update the checker in the rule
logic for consistency
* Remove test case for different keyword position (I don't think it's
required here)
## Test Plan
Add test cases for multiple operators from various modules.
## Summary
Just some minor followups to the recently merged RUF052 rule, that was
added in bf0fd04:
- Some small tweaks to the docs
- A minor code-style nit
- Some more tests for my peace of mind, just to check that the new
methods on the semantic model are working correctly
I'm adding the "internal" label as this doesn't deserve a changelog
entry. RUF052 is a new rule that hasn't been released yet.
## Test Plan
`cargo test -p ruff_linter`
## Summary
This PR adds a new `property_tests` module with quickcheck-based tests
that verify certain properties of types. The following properties are
currently checked:
* `is_equivalent_to`:
* is reflexive: `T` is equivalent to itself
* `is_subtype_of`:
* is reflexive: `T` is a subtype of `T`
* is antisymmetric: if `S <: T` and `T <: S`, then `S` is equivalent to
`T`
* is transitive: `S <: T` & `T <: U` => `S <: U`
* `is_disjoint_from`:
* is irreflexive: `T` is not disjoint from `T`
* is symmetric: `S` disjoint from `T` => `T` disjoint from `S`
* `is_assignable_to`:
* is reflexive
* `negate`:
* is an involution: `T.negate().negate()` is equivalent to `T`
There are also some tests that validate higher-level properties like:
* `S <: T` implies that `S` is not disjoint from `T`
* `S <: T` implies that `S` is assignable to `T`
* A singleton type must also be single-valued
These tests found a few bugs so far:
- #14177
- #14195
- #14196
- #14210
- #14731
Some additional notes:
- Quickcheck-based property tests are non-deterministic and finding
counter-examples might take an arbitrary long time. This makes them bad
candidates for running in CI (for every PR). We can think of running
them in a cron-job way from time to time, similar to fuzzing. But for
now, it's only possible to run them locally (see instructions in source
code).
- Some tests currently find false positive "counterexamples" because our
understanding of equivalence of types is not yet complete. We do not
understand that `int | str` is the same as `str | int`, for example.
These tests are in a separate `property_tests::flaky` module.
- Properties can not be formulated in every way possible, due to the
fact that `is_disjoint_from` and `is_subtype_of` can produce false
negative answers.
- The current shrinking implementation is very naive, which leads to
counterexamples that are very long (`str & Any & ~tuple[Any] &
~tuple[Unknown] & ~Literal[""] & ~Literal["a"] | str & int & ~tuple[Any]
& ~tuple[Unknown]`), requiring the developer to simplify manually. It
has not been a major issue so far, but there is a comment in the code
how this can be improved.
- The tests are currently implemented using a macro. This is a single
commit on top which can easily be reverted, if we prefer the plain code
instead. With the macro:
```rs
// `S <: T` implies that `S` can be assigned to `T`.
type_property_test!(
subtype_of_implies_assignable_to, db,
forall types s, t. s.is_subtype_of(db, t) => s.is_assignable_to(db, t)
);
```
without the macro:
```rs
/// `S <: T` implies that `S` can be assigned to `T`.
#[quickcheck]
fn subtype_of_implies_assignable_to(s: Ty, t: Ty) -> bool {
let db = get_cached_db();
let s = s.into_type(&db);
let t = t.into_type(&db);
!s.is_subtype_of(&*db, t) || s.is_assignable_to(&*db, t)
}
```
## Test Plan
```bash
while cargo test --release -p red_knot_python_semantic --features property_tests types::property_tests; do :; done
```
## Summary
`KnownInstance::instance_fallback` may return instances of supertypes.
For example, it returns an instance of `_SpecialForm` for `Literal`.
This means it can't be used on the right-hand side of `is_subtype_of`
relationships, because it might lead to false positives.
I can lead to false negatives on the left hand side of `is_subtype_of`,
but this is at least a known limitation. False negatives are fine for
most applications, but false positives can lead to wrong results in
intersection-simplification, for example.
closes#14731
## Test Plan
Added regression test
## Summary
Simplify tuples containing `Never` to `Never`:
```py
from typing import Never
def never() -> Never: ...
reveal_type((1, never(), "foo")) # revealed: Never
```
I should note that mypy and pyright do *not* perform this
simplification. I don't know why.
There is [only one
place](5137fcc9c8/crates/red_knot_python_semantic/src/types/infer.rs (L1477-L1484))
where we use `TupleType::new` directly (instead of `Type::tuple`, which
changes behavior here). This appears when creating `TypeVar`
constraints, and it looks to me like it should stay this way, because
we're using `TupleType` to store a list of constraints there, instead of
an actual type. We also store `tuple[constraint1, constraint2, …]` as
the type for the `constraint1, constraint2, …` tuple expression. This
would mean that we infer a type of `tuple[str, Never]` for the following
type variable constraints, without simplifying it to `Never`. This seems
like a weird edge case that's maybe not worth looking further into?!
```py
from typing import Never
# vvvvvvvvvv
def f[T: (str, Never)](x: T):
pass
```
## Test Plan
- Added a new unit test. Did not add additional Markdown tests as that
seems superfluous.
- Tested the example above using red knot, mypy, pyright.
- Verified that this allows us to remove `contains_never` from the
property tests
(https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14178#discussion_r1866473192)
This PR improves on #14477 by:
- Ensuring user's do not require the module alias "__debug__", which is unassignable
- Validating the linter settings for
`lint.flake8-import-conventions.extend-aliases` (whereas previously we
only did this for `lint.flake8-import-conventions.aliases`).
Closes#14662
Resolves https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/14547 by delegating
narrowing to `E` for `bool(E)` where `E` is some expression.
This change does not include other builtin class constructors which
should also work in this position, like `int(..)` or `float(..)`, as the
original issue does not mention these. It should be easy enough to add
checks for these as well if we want to.
I don't see a lot of markdown tests for malformed input, maybe there's a
better place for the no args and too many args cases to go?
I did see after the fact that it looks like this task was intended for a
new hire.. my apologies. I got here from
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13694, which is marked
help-wanted.
---------
Co-authored-by: David Peter <mail@david-peter.de>
This PR extends the Decimal parsing used in [verbose-decimal-constructor
(FURB157)](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/verbose-decimal-constructor/)
to better handle non-finite `Decimal` objects, avoiding some false
negatives.
Closes#14587
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
## Summary
Seeing the fuzzing results from @dhruvmanila in #13778, I think we can
re-enable these tests. We also had one regression that would have been
caught by these tests, so there is some value in having them enabled.
## Summary
- Check if `hashlib` and `crypt` imports have been seen for `FURB181`
and `S324`
- Mark the fix for `FURB181` as safe: I think it was accidentally marked
as unsafe in the first place. The rule does not support user-defined
classes as the "fix safety" section suggests.
- Removed `hashlib._Hash`, as it's not part of the `hashlib` module.
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
## Test Plan
Updated the test snapshots
## Summary
Closes: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/14593
The final type of a variable after if-statement without explicit else
branch should be similar to having an explicit else branch.
## Test Plan
Originally failed test cases from the bug are added.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
`bool()` is equal to `False`, and we infer `Literal[False]` for it. Which
means that the test here will fail as soon as we treat the body of
this `if` as unreachable.
## Summary
This came up as part of #12927 when implementing
`SemanticModel::simulate_runtime_load`.
Should be fairly self-explanatory, if the scope returns a binding with
`BindingKind::Annotation` the bottom part of the loop gets skipped, so
there's no chance for `seen_function` to have been updated. So unless
there's something subtle going on here, like function scopes never
containing bindings with `BindingKind::Annotation`, this seems like a
bug.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run`
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug in the f-string formatting to not consider the
escaped newlines for `is_multiline`. This is done by checking if the
f-string is triple-quoted or not similar to normal string literals.
This is not required to be gated behind preview because the logic change
for `is_multiline` was added in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14454.
## Test Plan
Add a test case which formats differently on `main`:
https://play.ruff.rs/ea3c55c2-f0fe-474e-b6b8-e3365e0ede5e
## Summary
This PR gets rid of the `requirements.in` and `requirements.txt` files
in the `scripts/fuzz-parser` directory, and replaces them with
`pyproject.toml` and `uv.lock` files. The script is renamed from
`fuzz-parser` to `py-fuzzer` (since it can now also be used to fuzz
red-knot as well as the parser, following
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14566), and moved from the
`scripts/` directory to the `python/` directory, since it's now a
(uv)-pip-installable project in its own right.
I've been resisting this for a while, because conceptually this script
just doesn't feel "complicated" enough to me for it to be a full-blown
package. However, I think it's time to do this. Making it a proper
package has several advantages:
- It means we can run it from the project root using `uv run` without
having to activate a virtual environment and ensure that all required
dependencies are installed into that environment
- Using a `pyproject.toml` file means that we can express that the
project requires Python 3.12+ to run properly; this wasn't possible
before
- I've been running mypy on the project locally when I've been working
on it or reviewing other people's PRs; now I can put the mypy config for
the project in the `pyproject.toml` file
## Test Plan
I manually tested that all the commands detailed in
`python/py-fuzzer/README.md` work for me locally.
---------
Co-authored-by: David Peter <sharkdp@users.noreply.github.com>
## Summary
fixes: #14608
The logic that was only applied for 3.12+ target version needs to be
applied for other versions as well.
## Test Plan
I've moved the existing test cases for 3.12 only to `f_string.py` so
that it's tested against the default target version.
I think we should probably enabled testing for two target version (pre
3.12 and 3.12) but it won't highlight any issue because the parser
doesn't consider this. Maybe we should enable this once we have target
version specific syntax errors in place
(https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/6591).
## Summary
Fix panics related to expressions without inferred types in invalid
syntax examples like:
```py
x: f"Literal[{1 + 2}]" = 3
```
where the `1 + 2` expression (and its sub-expressions) inside the
annotation did not have an inferred type.
## Test Plan
Added new corpus test.
## Summary
Remove entry that was prevously fixed in
5a30ec0df6.
## Test Plan
```sh
cargo test -p red_knot_workspace -- --ignored linter_af linter_gz
```
## Summary
This is about the easiest patch that I can think of. It has a drawback
in that there is no real guarantee this won't happen again. I think this
might be acceptable, given that all of this is a temporary thing.
And we also add a new CI job to prevent regressions like this in the
future.
For the record though, I'm listing alternative approaches I thought of:
- We could get rid of the debug/release distinction and just add `@Todo`
type metadata everywhere. This has possible affects on runtime. The main
reason I didn't follow through with this is that the size of `Type`
increases. We would either have to adapt the `assert_eq_size!` test or
get rid of it. Even if we add messages everywhere and get rid of the
file-and-line-variant in the enum, it's not enough to get back to the
current release-mode size of `Type`.
- We could generally discard `@Todo` meta information when using it in
tests. I think this would be a huge drawback. I like that we can have
the actual messages in the mdtest. And make sure we get the expected
`@Todo` type, not just any `@Todo`. It's also helpful when debugging
tests.
closes#14594
## Test Plan
```rs
cargo nextest run --release
```
## Summary
fixes: #13813
This PR fixes a bug in the formatting assignment statement when the
value is an f-string.
This is resolved by using custom best fit layouts if the f-string is (a)
not already a flat f-string (thus, cannot be multiline) and (b) is not a
multiline string (thus, cannot be flattened). So, it is used in cases
like the following:
```py
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa = f"testeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee{
expression}moreeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee"
```
Which is (a) `FStringLayout::Multiline` and (b) not a multiline.
There are various other examples in the PR diff along with additional
explanation and context as code comments.
## Test Plan
Add multiple test cases for various scenarios.
## Summary
This PR implements new rule discussed
[here](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/discussions/14449).
In short, it searches for assert messages which were unintentionally
used as a expression to be matched against.
## Test Plan
`cargo test` and review of `ruff-ecosystem`
Fix#14558
## Summary
- Add `typing.NoReturn` and `typing.Never` to known instances and infer
them as `Type::Never`
- Add `is_assignable_to` cases for `Type::Never`
I skipped emitting diagnostic for when a function is annotated as
`NoReturn` but it actually returns.
## Test Plan
Added tests from
https://github.com/python/typing/blob/main/conformance/tests/specialtypes_never.py
except from generics and checking if the return value of the function
and the annotations match.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
Closes#14588
```py
x: Literal[42, "hello"] = 42 if bool_instance() else "hello"
reveal_type(x) # revealed: Literal[42] | Literal["hello"]
_ = ... if isinstance(x, str) else ...
# The `isinstance` test incorrectly narrows the type of `x`.
# As a result, `x` is revealed as Literal["hello"], but it should remain Literal[42, "hello"].
reveal_type(x) # revealed: Literal["hello"]
```
## Test Plan
mdtest included!
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
This is just a small refactor to remove the `FormatFStringPart` as it's
only used in the case when the f-string is not implicitly concatenated
in which case the only part is going to be `FString`. In implicitly
concatenated f-strings, we use `StringLike` instead.
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
Fix#14525
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
New test cases
---------
Signed-off-by: harupy <hkawamura0130@gmail.com>
## Summary
Resolves#14289
The documentation for B028 no_explicit_stacklevel is updated to be more
clear.
---------
Co-authored-by: dylwil3 <dylwil3@gmail.com>
This PR adds a sometimes-available, safe autofix for [unraw-re-pattern
(RUF039)](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/unraw-re-pattern/#unraw-re-pattern-ruf039),
which prepends an `r` prefix. It is used only when the string in
question has no backslahses (and also does not have a `u` prefix, since
that causes a syntax error.)
Closes#14527
Notes:
- Test fixture unchanged, but snapshot changed to include fix messages.
- This fix is automatically only available in preview since the rule
itself is in preview
## Summary
This fix addresses panics related to invalid syntax like the following
where a `break` statement is used in a nested definition inside a
loop:
```py
while True:
def b():
x: int
break
```
closes#14342
## Test Plan
* New corpus regression tests.
* New unit test to make sure we handle nested while loops correctly.
This test is passing on `main`, but can easily fail if the
`is_inside_loop` state isn't properly saved/restored.
## Summary
Add support for (non-generic) type aliases. The main motivation behind
this was to get rid of panics involving expressions in (generic) type
aliases. But it turned out the best way to fix it was to implement
(partial) support for type aliases.
```py
type IntOrStr = int | str
reveal_type(IntOrStr) # revealed: typing.TypeAliasType
reveal_type(IntOrStr.__name__) # revealed: Literal["IntOrStr"]
x: IntOrStr = 1
reveal_type(x) # revealed: Literal[1]
def f() -> None:
reveal_type(x) # revealed: int | str
```
## Test Plan
- Updated corpus test allow list to reflect that we don't panic anymore.
- Added Markdown-based test for type aliases (`type_alias.md`)
## Summary
Fixes a panic related to sub-expressions of `typing.Union` where we fail
to store a type for the `int, str` tuple-expression in code like this:
```
x: Union[int, str] = 1
```
relates to [my
comment](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14499#discussion_r1851794467)
on #14499.
## Test Plan
New corpus test
## Summary
Adds meta information to `Type::Todo`, allowing developers to easily
trace back the origin of a particular `@Todo` type they encounter.
Instead of `Type::Todo`, we now write either `type_todo!()` which
creates a `@Todo[path/to/source.rs:123]` type with file and line
information, or using `type_todo!("PEP 604 unions not supported")`,
which creates a variant with a custom message.
`Type::Todo` now contains a `TodoType` field. In release mode, this is
just a zero-sized struct, in order not to create any overhead. In debug
mode, this is an `enum` that contains the meta information.
`Type` implements `Copy`, which means that `TodoType` also needs to be
copyable. This limits the design space. We could intern `TodoType`, but
I discarded this option, as it would require us to have access to the
salsa DB everywhere we want to use `Type::Todo`. And it would have made
the macro invocations less ergonomic (requiring us to pass `db`).
So for now, the meta information is simply a `&'static str` / `u32` for
the file/line variant, or a `&'static str` for the custom message.
Anything involving a chain/backtrace of several `@Todo`s or similar is
therefore currently not implemented. Also because we currently don't see
any direct use cases for this, and because all of this will eventually
go away.
Note that the size of `Type` increases from 16 to 24 bytes, but only in
debug mode.
## Test Plan
- Observed the changes in Markdown tests.
- Added custom messages for all `Type::Todo`s that were revealed in the
tests
- Ran red knot in release and debug mode on the following Python file:
```py
def f(x: int) -> int:
reveal_type(x)
```
Prints `@Todo` in release mode and `@Todo(function parameter type)` in
debug mode.
Fix#14498
## Summary
This PR adds `typing.Union` support
## Test Plan
I created new tests in mdtest.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
- Expand some docs where they're unclear about the motivation, or assume
some knowledge that hasn't been introduced yet
- Add more links to external docs
- Rename PYI063 from `PrePep570PositionalArgument` to
`Pep484StylePositionalOnlyParameter`
- Rename the file `parenthesize_logical_operators.rs` to
`parenthesize_chained_operators.rs`, since the rule is called
`ParenthesizeChainedOperators`, not `ParenthesizeLogicalOperators`
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
These rules were implemented in January, have been very stable, and have
no open issues about them. They were highly requested by the community
prior to being implemented. Let's stabilise them!
## Test Plan
Ecosystem check on this PR.
## Summary
closes#14279
### Limitations of the Current Implementation
#### Incorrect Error Propagation
In the current implementation of lexicographic comparisons, if the
result of an Eq operation is Ambiguous, the comparison stops
immediately, returning a bool instance. While this may yield correct
inferences, it fails to capture unsupported-operation errors that might
occur in subsequent comparisons.
```py
class A: ...
(int_instance(), A()) < (int_instance(), A()) # should error
```
#### Weak Inference in Specific Cases
> Example: `(int_instance(), "foo") == (int_instance(), "bar")`
> Current result: `bool`
> Expected result: `Literal[False]`
`Eq` and `NotEq` have unique behavior in lexicographic comparisons
compared to other operators. Specifically:
- For `Eq`, if any non-equal pair exists within the tuples being
compared, we can immediately conclude that the tuples are not equal.
- For `NotEq`, if any equal pair exists, we can conclude that the tuples
are unequal.
```py
a = (str_instance(), int_instance(), "foo")
reveal_type(a == a) # revealed: bool
reveal_type(a != a) # revealed: bool
b = (str_instance(), int_instance(), "bar")
reveal_type(a == b) # revealed: bool # should be Literal[False]
reveal_type(a != b) # revealed: bool # should be Literal[True]
```
#### Incorrect Support for Non-Boolean Rich Comparisons
In CPython, aside from `==` and `!=`, tuple comparisons return a
non-boolean result as-is. Tuples do not convert the value into `bool`.
Note: If all pairwise `==` comparisons between elements in the tuples
return Truthy, the comparison then considers the tuples' lengths.
Regardless of the return type of the dunder methods, the final result
can still be a boolean.
```py
from __future__ import annotations
class A:
def __eq__(self, o: object) -> str:
return "hello"
def __ne__(self, o: object) -> bytes:
return b"world"
def __lt__(self, o: A) -> float:
return 3.14
a = (A(), A())
reveal_type(a == a) # revealed: bool
reveal_type(a != a) # revealed: bool
reveal_type(a < a) # revealed: bool # should be: `float | Literal[False]`
```
### Key Changes
One of the major changes is that comparisons no longer end with a `bool`
result when a pairwise `Eq` result is `Ambiguous`. Instead, the function
attempts to infer all possible cases and unions the results. This
improvement allows for more robust type inference and better error
detection.
Additionally, as the function is now optimized for tuple comparisons,
the name has been changed from the more general
`infer_lexicographic_comparison` to `infer_tuple_rich_comparison`.
## Test Plan
mdtest included
## Summary
Previously, we panicked on expressions like `f"{v:{f'0.2f'}}"` because
we did not infer types for expressions nested inside format spec
elements.
## Test Plan
```
cargo nextest run -p red_knot_workspace -- --ignored linter_af linter_gz
```
## Summary
Add type narrowing for `type(x) is C` conditions (and `else` clauses of
`type(x) is not C` conditionals):
```py
if type(x) is A:
reveal_type(x) # revealed: A
else:
reveal_type(x) # revealed: A | B
```
closes: #14431, part of: #13694
## Test Plan
New Markdown-based tests.
## Summary
This patches up various missing paths where sub-expressions of type
annotations previously had no type attached. Examples include:
```py
tuple[int, str]
# ~~~~~~~~
type[MyClass]
# ~~~~~~~
Literal["foo"]
# ~~~~~
Literal["foo", Literal[1, 2]]
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Literal[1, "a", random.illegal(sub[expr + ession])]
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
```
## Test Plan
```
cargo nextest run -p red_knot_workspace -- --ignored linter_af linter_gz
```
## Summary
Follow-up to #14371, this PR simplifies the visitor logic for list
expressions to remove the state management. We just need to make sure
that we visit the nested expressions using the `QuoteAnnotator` and not
the `Generator`. This is similar to what's being done for binary
expressions.
As per the
[grammar](https://typing.readthedocs.io/en/latest/spec/annotations.html#grammar-token-expression-grammar-annotation_expression),
list expressions can be present which can contain other type expressions
(`Callable`):
```
| <Callable> '[' <Concatenate> '[' (type_expression ',')+
(name | '...') ']' ',' type_expression ']'
(where name must be a valid in-scope ParamSpec)
| <Callable> '[' '[' maybe_unpacked (',' maybe_unpacked)*
']' ',' type_expression ']'
```
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
Resolves#12616.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run` and `cargo insta test`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
Resolves#14378.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run` and `cargo insta test`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
Disable the no-panic tests for the linter corpus, as there are too many
problems right now, requiring linter-contributors to add their test
files to the allow-list.
We can still run the tests using `cargo test -p red_knot_workspace --
--ignored linter_af linter_gz`. This is also why I left the
`crates/ruff_linter/` entries in the allow list for now, even if they
will get out of sync. But let me know if I should rather remove them.
## Summary
Implements `redundant-bool-literal`
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
`cargo test`
The ecosystem results are all correct, but for `Airflow` the rule is not
relevant due to the use of overloading (and is marked as unsafe
correctly).
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR splits the corpus tests into smaller chunks because running all
of them takes 8s on my windows machine and it's by far the longest test
in `red_knot_workspace`.
Splitting the tests has the advantage that they run in parallel. This PR
brings down the wall time from 8s to 4s.
This PR also limits the glob for the linter tests because it's common to
clone cpython into the `ruff_linter/resources/test` folder for
benchmarks (because that's what's written in the contributing guides)
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
This PR adds autofix for `redundant-numeric-union` (`PYI041`)
There are some comments below to explain the reasoning behind some
choices that might help review.
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
Resolves part of https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/14185.
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
This PR adds corrected handling of list expressions to the `Visitor`
implementation of `QuotedAnnotator` in `flake8_type_checking::helpers`.
Closes#14368
## Summary
- Add 383 files from `crates/ruff_python_parser/resources` to the test
corpus
- Add 1296 files from `crates/ruff_linter/resources` to the test corpus
- Use in-memory file system for tests
- Improve test isolation by cleaning the test environment between checks
- Add a mechanism for "known failures". Mark ~80 files as known
failures.
- The corpus test is now a lot slower (6 seconds).
Note:
While `red_knot` as a command line tool can run over all of these
files without panicking, we still have a lot of test failures caused by
explicitly "pulling" all types.
## Test Plan
Run `cargo test -p red_knot_workspace` while making sure that
- Introducing code that is known to lead to a panic fails the test
- Removing code that is known to lead to a panic from
`KNOWN_FAILURES`-files also fails the test
Fix: #13934
## Summary
Current implementation has a bug when the current annotation contains a
string with single and double quotes.
TL;DR: I think these cases happen less than other use cases of Literal.
So instead of fixing them we skip the fix in those cases.
One of the problematic cases:
```
from typing import Literal
from third_party import Type
def error(self, type1: Type[Literal["'"]]):
pass
```
The outcome is:
```
- def error(self, type1: Type[Literal["'"]]):
+ def error(self, type1: "Type[Literal[''']]"):
```
While it should be:
```
"Type[Literal['\'']"
```
The solution in this case is that we check if there’s any quotes same as
the quote style we want to use for this Literal parameter then escape
that same quote used in the string.
Also this case is not uncommon to have:
<https://grep.app/search?current=2&q=Literal["'>
But this can get more complicated for example in case of:
```
- def error(self, type1: Type[Literal["\'"]]):
+ def error(self, type1: "Type[Literal[''']]"):
```
Here we escaped the inner quote but in the generated annotation it gets
removed. Then we flip the quote style of the Literal paramter and the
formatting is wrong.
In this case the solution is more complicated.
1. When generating the string of the source code preserve the backslash.
2. After we have the annotation check if there isn’t any escaped quote
of the same type we want to use for the Literal parameter. In this case
check if we have any `’` without `\` before them. This can get more
complicated since there can be multiple backslashes so checking for only
`\’` won’t be enough.
Another problem is when the string contains `\n`. In case of
`Type[Literal["\n"]]` we generate `'Type[Literal["\n"]]'` and both
pyright and mypy reject this annotation.
https://pyright-play.net/?code=GYJw9gtgBALgngBwJYDsDmUkQWEMoAySMApiAIYA2AUAMaXkDOjUAKoiQNqsC6AXFAB0w6tQAmJYLBKMYAfQCOAVzCk5tMChjlUjOQCNytANaMGjABYAKRiUrAANLA4BGAQHJ2CLkVIVKnABEADoogTw87gCUfNRQ8VAITIyiElKksooqahpaOih6hiZmTNa29k7w3m5sHJy%2BZFRBoeE8MXEJScxAA
## Test Plan
I added test cases for the original code in the reported issue and two
more cases for backslash and new line.
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug in the Ruff language server where the
editor-specified configuration was resolved relative to the
configuration directory and not the current working directory.
The existing behavior is confusing given that this config file is
specified by the user and is not _discovered_ by Ruff itself. The
behavior of resolving this configuration file should be similar to that
of the `--config` flag on the command-line which uses the current
working directory:
3210f1a23b/crates/ruff/src/resolve.rs (L34-L48)
This creates problems where certain configuration options doesn't work
because the paths resolved in that case are relative to the
configuration directory and not the current working directory in which
the editor is expected to be in. For example, the
`lint.per-file-ignores` doesn't work as mentioned in the linked issue
along with `exclude`, `extend-exclude`, etc.
fixes: #14282
## Test Plan
Using the following directory tree structure:
```
.
├── .config
│ └── ruff.toml
└── src
└── migrations
└── versions
└── a.py
```
where, the `ruff.toml` is:
```toml
# 1. Comment this out to test `per-file-ignores`
extend-exclude = ["**/versions/*.py"]
[lint]
select = ["D"]
# 2. Comment this out to test `extend-exclude`
[lint.per-file-ignores]
"**/versions/*.py" = ["D"]
# 3. Comment both `per-file-ignores` and `extend-exclude` to test selection works
```
And, the content of `a.py`:
```py
"""Test"""
```
And, the VS Code settings:
```jsonc
{
"ruff.nativeServer": "on",
"ruff.path": ["/Users/dhruv/work/astral/ruff/target/debug/ruff"],
// For single-file mode where current working directory is `/`
// "ruff.configuration": "/tmp/ruff-repro/.config/ruff.toml",
// When a workspace is opened containing this path
"ruff.configuration": "./.config/ruff.toml",
"ruff.trace.server": "messages",
"ruff.logLevel": "trace"
}
```
I also tested out just opening the file in single-file mode where the
current working directory is `/` in VS Code. Here, the
`ruff.configuration` needs to be updated to use absolute path as shown
in the above VS Code settings.
## Summary
This PR adds support for parsing and inferring types within string
annotations.
### Implementation (attempt 1)
This is preserved in
6217f48924.
The implementation here would separate the inference of string
annotations in the deferred query. This requires the following:
* Two ways of evaluating the deferred definitions - lazily and eagerly.
* An eager evaluation occurs right outside the definition query which in
this case would be in `binding_ty` and `declaration_ty`.
* A lazy evaluation occurs on demand like using the
`definition_expression_ty` to determine the function return type and
class bases.
* The above point means that when trying to get the binding type for a
variable in an annotated assignment, the definition query won't include
the type. So, it'll require going through the deferred query to get the
type.
This has the following limitations:
* Nested string annotations, although not necessarily a useful feature,
is difficult to implement unless we convert the implementation in an
infinite loop
* Partial string annotations require complex layout because inferring
the types for stringified and non-stringified parts of the annotation
are done in separate queries. This means we need to maintain additional
information
### Implementation (attempt 2)
This is the final diff in this PR.
The implementation here does the complete inference of string annotation
in the same definition query by maintaining certain state while trying
to infer different parts of an expression and take decisions
accordingly. These are:
* Allow names that are part of a string annotation to not exists in the
symbol table. For example, in `x: "Foo"`, if the "Foo" symbol is not
defined then it won't exists in the symbol table even though it's being
used. This is an invariant which is being allowed only for symbols in a
string annotation.
* Similarly, lookup name is updated to do the same and if the symbol
doesn't exists, then it's not bounded.
* Store the final type of a string annotation on the string expression
itself and not for any of the sub-expressions that are created after
parsing. This is because those sub-expressions won't exists in the
semantic index.
Design document:
https://www.notion.so/astral-sh/String-Annotations-12148797e1ca801197a9f146641e5b71?pvs=4Closes: #13796
## Test Plan
* Add various test cases in our markdown framework
* Run `red_knot` on LibCST (contains a lot of string annotations,
specifically
https://github.com/Instagram/LibCST/blob/main/libcst/matchers/_matcher_base.py),
FastAPI (good amount of annotated code including `typing.Literal`) and
compare against the `main` branch output
## Summary
Add a typed representation of function signatures (parameters and return
type) and infer it correctly from a function.
Convert existing usage of function return types to use the signature
representation.
This does not yet add inferred types for parameters within function body
scopes based on the annotations, but it should be easy to add as a next
step.
Part of #14161 and #13693.
## Test Plan
Added tests.
Follow-up to #14287 : when checking that `name` is the same as `as_name`
in `import name as as_name`, we do not need to first do an early return
if `'.'` is found in `name`.
This PR handles a panic that occurs when applying unsafe fixes if a user
inserts a required import (I002) that has a "useless alias" in it, like
`import numpy as numpy`, and also selects PLC0414 (useless-import-alias)
In this case, the fixes alternate between adding the required import
statement, then removing the alias, until the recursion limit is
reached. See linked issue for an example.
Closes#14283
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
This fixes several panics related to invalid assignment targets. All of
these led to some a crash, previously:
```py
(x.y := 1) # only name-expressions are valid targets of named expressions
([x, y] := [1, 2]) # same
(x, y): tuple[int, int] = (2, 3) # tuples are not valid targets for annotated assignments
(x, y) += 2 # tuples are not valid targets for augmented assignments
```
closes#14321closes#14322
## Test Plan
I symlinked four files from `crates/ruff_python_parser/resources` into
the red knot corpus, as they seemed like ideal test files for this exact
scenario. I think eventually, it might be a good idea to simply include *all*
invalid-syntax examples from the parser tests into red knots corpus (I believe
we're actually not too far from that goal). Or expand the scope of the corpus
test to this directory. Then we can get rid of these symlinks again.
## Summary
This avoids a panic inside `TypeInferenceBuilder::infer_type_parameters`
when encountering generic type aliases:
```py
type ListOrSet[T] = list[T] | set[T]
```
To fix this properly, we would have to treat type aliases as being their own
annotation scope [1]. The left hand side is a definition for the type parameter
`T` which is being used in the special annotation scope on the right hand side.
Similar to how it works for generic functions and classes.
[1] https://docs.python.org/3/reference/compound_stmts.html#generic-type-aliasescloses#14307
## Test Plan
Added new example to the corpus.
When we look up the types of class bases or keywords (`metaclass`), we
currently do this little dance: if there are type params, then look up
the type using `SemanticModel` in the type-params scope, if not, look up
the type directly in the definition's own scope, with support for
deferred types.
With inference of function parameter types, I'm now adding another case
of this same dance, so I'm motivated to make it a bit more ergonomic.
Add support to `definition_expression_ty` to handle any sub-expression
of a definition, whether it is in the definition's own scope or in a
type-params sub-scope.
Related to both #13693 and #14161.
## Summary
Use the memory address to uniquely identify AST nodes, instead of
relying on source range and kind. The latter fails for ASTs resulting
from invalid syntax examples. See #14313 for details.
Also results in a 1-2% speedup
(https://codspeed.io/astral-sh/ruff/runs/67349cf55f36b36baa211360)
closes#14313
## Review
Here are the places where we use `NodeKey` directly or indirectly (via
`ExpressionNodeKey` or `DefinitionNodeKey`):
```rs
// semantic_index.rs
pub(crate) struct SemanticIndex<'db> {
// [...]
/// Map expressions to their corresponding scope.
scopes_by_expression: FxHashMap<ExpressionNodeKey, FileScopeId>,
/// Map from a node creating a definition to its definition.
definitions_by_node: FxHashMap<DefinitionNodeKey, Definition<'db>>,
/// Map from a standalone expression to its [`Expression`] ingredient.
expressions_by_node: FxHashMap<ExpressionNodeKey, Expression<'db>>,
// [...]
}
// semantic_index/builder.rs
pub(super) struct SemanticIndexBuilder<'db> {
// [...]
scopes_by_expression: FxHashMap<ExpressionNodeKey, FileScopeId>,
definitions_by_node: FxHashMap<ExpressionNodeKey, Definition<'db>>,
expressions_by_node: FxHashMap<ExpressionNodeKey, Expression<'db>>,
}
// semantic_index/ast_ids.rs
pub(crate) struct AstIds {
/// Maps expressions to their expression id.
expressions_map: FxHashMap<ExpressionNodeKey, ScopedExpressionId>,
/// Maps expressions which "use" a symbol (that is, [`ast::ExprName`]) to a use id.
uses_map: FxHashMap<ExpressionNodeKey, ScopedUseId>,
}
pub(super) struct AstIdsBuilder {
expressions_map: FxHashMap<ExpressionNodeKey, ScopedExpressionId>,
uses_map: FxHashMap<ExpressionNodeKey, ScopedUseId>,
}
```
## Test Plan
Added two failing examples to the corpus.
## Summary
Fixes a failing debug assertion that triggers for the following code:
```py
match some_int:
case x:=2:
pass
```
closes#14305
## Test Plan
Added problematic code example to corpus.
## Summary
Resolves#13217.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run` and `cargo insta test`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR improves the fix for `PYI055` to be able to handle nested and
mixed type unions.
It also marks the fix as unsafe when comments are present.
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
`pytest-raises-too-broad (PT011)` should be raised when
`expected_exception` is provided as a keyword argument.
```python
def test_foo():
with pytest.raises(ValueError): # raises PT011
raise ValueError("Can't divide 1 by 0")
# This is minor but a valid pytest.raises call
with pytest.raises(expected_exception=ValueError): # doesn't raise PT011 but should
raise ValueError("Can't divide 1 by 0")
```
`pytest.raises` doc:
https://docs.pytest.org/en/8.3.x/reference/reference.html#pytest.raises
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
Unit tests
Signed-off-by: harupy <hkawamura0130@gmail.com>
## Summary
- Emit diagnostics when looking up (possibly) unbound attributes
- More explicit test assertions for unbound symbols
- Review remaining call sites of `Symbol::ignore_possibly_unbound`. Most
of them are something like `builtins_symbol(self.db,
"Ellipsis").ignore_possibly_unbound().unwrap_or(Type::Unknown)` which
look okay to me, unless we want to emit additional diagnostics. There is
one additional case in enum literal handling, which has a TODO comment
anyway.
part of #14022
## Test Plan
New MD tests for (possibly) unbound attributes.
## Summary
This adds a new diagnostic when possibly unbound symbols are imported.
The `TODO` comment had a question mark, do I'm not sure if this is
really something that we want.
This does not touch the un*declared* case, yet.
relates to: #14022
## Test Plan
Updated already existing tests with new diagnostics
## Summary
Apart from one small functional change, this is mostly a refactoring of
the `Symbol` API:
- Rename `as_type` to the more explicit `ignore_possibly_unbound`, no
functional change
- Remove `unwrap_or_unknown` in favor of the more explicit
`.ignore_possibly_unbound().unwrap_or(Type::Unknown)`, no functional
change
- Consistently call it "possibly unbound" (not "may be unbound")
- Rename `replace_unbound_with` to `or_fall_back_to` and properly handle
boundness of the fall back. This is the only functional change (did not
have any impact on existing tests).
relates to: #14022
## Test Plan
New unit tests for `Symbol::or_fall_back_to`
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
Related to #970. Implement [`shallow-copy-environ /
W1507`](https://pylint.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_guide/messages/warning/shallow-copy-environ.html).
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
Unit test
---------
Co-authored-by: Simon Brugman <sbrugman@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
The implicit namespace package rule currently fails to detect cases like
the following:
```text
foo/
├── __init__.py
└── bar/
└── baz/
└── __init__.py
```
The problem is that we detect a root at `foo`, and then an independent
root at `baz`. We _would_ detect that `bar` is an implicit namespace
package, but it doesn't contain any files! So we never check it, and
have no place to raise the diagnostic.
This PR adds detection for these kinds of nested packages, and augments
the `INP` rule to flag the `__init__.py` file above with a specialized
message. As a side effect, I've introduced a dedicated `PackageRoot`
struct which we can pass around in lieu of Yet Another `Path`.
For now, I'm only enabling this in preview (and the approach doesn't
affect any other rules). It's a bug fix, but it may end up expanding the
rule.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13519.
## Summary
It's only safe to enforce the `x in "1234567890"` case if `x` is exactly
one character, since the set on the right has been reordered as compared
to `string.digits`. We can't know if `x` is exactly one character unless
it's a literal. And if it's a literal, well, it's kind of silly code in
the first place?
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13802.
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
Fix `await-outside-async` to allow `await` at the top-level scope of a
notebook.
```python
# foo.ipynb
await asyncio.sleep(1) # should be allowed
```
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
A unit test
## Summary
Resolves#13833.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run` and `cargo insta test`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
This PR accounts for further subtleties in `Decimal` parsing:
- Strings which are empty modulo underscores and surrounding whitespace
are skipped
- `Decimal("-0")` is skipped
- `Decimal("{integer literal that is longer than 640 digits}")` are
skipped (see linked issue for explanation)
NB: The snapshot did not need to be updated since the new test cases are
"Ok" instances and added below the diff.
Closes#14204
## Summary
Create definitions and infer types for PEP 695 type variables.
This just gives us the type of the type variable itself (the type of `T`
as a runtime object in the body of `def f[T](): ...`), with special
handling for its attributes `__name__`, `__bound__`, `__constraints__`,
and `__default__`. Mostly the support for these attributes exists
because it is easy to implement and allows testing that we are
internally representing the typevar correctly.
This PR doesn't yet have support for interpreting a typevar as a type
annotation, which is of course the primary use of a typevar. But the
information we store in the typevar's type in this PR gives us
everything we need to handle it correctly in a future PR when the
typevar appears in an annotation.
## Test Plan
Added mdtest.
## Summary
`Ty::BuiltinClassLiteral(…)` is a sub~~class~~type of
`Ty::BuiltinInstance("type")`, so it can't be disjoint from it.
## Test Plan
New `is_not_disjoint_from` test case
## Summary
Fix `Type::is_assignable_to` for union types on the left hand side (of
`.is_assignable_to`; or the right hand side of the `… = …` assignment):
`Literal[1, 2]` should be assignable to `int`.
## Test Plan
New unit tests that were previously failing.
## Summary
Minor fix to `Type::is_subtype_of` to make sure that Boolean literals
are subtypes of `int`, to match runtime semantics.
Found this while doing some property-testing experiments [1].
[1] https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14178
## Test Plan
New unit test.
## Summary
Fixes#14114. I don't think I can really describe the problems with our
current architecture (and therefore the motivations for this PR) any
better than @carljm did in that issue, so I'll just copy it out here!
---
We currently represent "known instances" (e.g. special forms like
`typing.Literal`, which are an instance of `typing._SpecialForm`, but
need to be handled differently from other instances of
`typing._SpecialForm`) as an `InstanceType` with a `known` field that is
`Some(...)`.
This makes it easy to handle a known instance as if it were a regular
instance type (by ignoring the `known` field), and in some cases (e.g.
`Type::member`) that is correct and convenient. But in other cases (e.g.
`Type::is_equivalent_to`) it is not correct, and we currently have a bug
that we would consider the known-instance type of `typing.Literal` as
equivalent to the general instance type for `typing._SpecialForm`, and
we would fail to consider it a singleton type or a single-valued type
(even though it is both.)
An instance type with `known.is_some()` is semantically quite different
from an instance type with `known.is_none()`. The former is a singleton
type that represents exactly one runtime object; the latter is an open
type that represents many runtime objects, including instances of
unknown subclasses. It is too error-prone to represent these
very-different types as a single `Type` variant. We should instead
introduce a dedicated `Type::KnownInstance` variant and force ourselves
to handle these explicitly in all `Type` variant matches.
## Possible followups
There is still a little bit of awkwardness in our current design in some
places, in that we first infer the symbol `typing.Literal` as a
`_SpecialForm` instance, and then later convert that instance-type into
a known-instance-type. We could also use this `KnownInstanceType` enum
to account for other special runtime symbols such as `builtins.Ellipsis`
or `builtins.NotImplemented`.
I think these might be worth pursuing, but I didn't do them here as they
didn't seem essential right now, and I wanted to keep the diff
relatively minimal.
## Test Plan
`cargo test -p red_knot_python_semantic`. New unit tests added for
`Type::is_subtype_of`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
This adds type inference for comparison expressions involving
intersection types.
For example:
```py
x = get_random_int()
if x != 42:
reveal_type(x == 42) # revealed: Literal[False]
reveal_type(x == 43) # bool
```
closes#13854
## Test Plan
New Markdown-based tests.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
- Get rid of `Symbol::unwrap_or` (unclear semantics, not needed anymore)
- Introduce `Type::call_dunder`
- Emit new diagnostic for possibly-unbound `__iter__` methods
- Better diagnostics for callables with possibly-unbound /
possibly-non-callable `__call__` methods
part of: #14022closes#14016
## Test Plan
- Updated test for iterables with possibly-unbound `__iter__` methods.
- New tests for callables
## Summary
- Adds basic support for `type[C]` as a red knot `Type`. Some things
might not be supported yet, like `type[Any]`.
- Adds type narrowing for `issubclass` checks.
closes#14117
## Test Plan
New Markdown-based tests
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Implementation for one of the rules in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/1348
Refurb only deals only with classes with a single base, however the rule
is valid for any base.
(`str, Enum` is common prior to `StrEnum`)
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
Flake8-builtins provides two checks for arguments (really, parameters)
of a function shadowing builtins: A002 checks function definitions, and
A006 checks lambda expressions. This PR ensures that A002 is restricted
to functions rather than lambda expressions.
Closes#14135 .
## Summary
I mirrored some of the idioms that @AlexWaygood used in the MRO work.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/14096.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Related to
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13979#discussion_r1828305790,
this PR removes the `current_unpack` state field from
`SemanticIndexBuilder` and passes the `Unpack` ingredient via the
`CurrentAssignment` -> `DefinitionNodeRef` conversion to finally store
it on `DefintionNodeKind`.
This involves updating the lifetime of `AnyParameterRef` (parameter to
`declare_parameter`) to use the `'db` lifetime. Currently, all AST nodes
stored on various enums are marked with `'a` lifetime but they're always
utilized using the `'db` lifetime.
This also removes the dedicated `'a` lifetime parameter on
`add_definition` which is currently being used in `DefinitionNodeRef`.
As mentioned, all AST nodes live through the `'db` lifetime so we can
remove the `'a` lifetime parameter from that method and use the `'db`
lifetime instead.
FURB157 suggests replacing expressions like `Decimal("123")` with
`Decimal(123)`. This PR extends the rule to cover cases where the input
string to `Decimal` can be easily transformed into an integer literal.
For example:
```python
Decimal("1__000") # fix: `Decimal(1000)`
```
Note: we do not implement the full decimal parsing logic from CPython on
the grounds that certain acceptable string inputs to the `Decimal`
constructor may be presumed purposeful on the part of the developer. For
example, as in the linked issue, `Decimal("١٢٣")` is valid and equal to
`Decimal(123)`, but we do not suggest a replacement in this case.
Closes#13807
## Summary
- Store the expression type for annotations that are starred expressions
(see [discussion
here](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14091#discussion_r1828332857))
- Use `self.store_expression_type(…)` consistently throughout, as it
makes sure that no double-insertion errors occur.
closes#14115
## Test Plan
Added an invalid-syntax example to the corpus which leads to a panic on
`main`. Also added a Markdown test with a valid-syntax example that
would lead to a panic once we implement function parameter inference.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Adds more precise type inference for `… is …` and `… is not …` identity
checks in some limited cases where we statically know the answer to be
either `Literal[True]` or `Literal[False]`.
I found this helpful while working on type inference for comparisons
involving intersection types, but I'm not sure if this is at all useful
for real world code (where the answer is most probably *not* statically
known). Note that we already have *type narrowing* for identity tests.
So while we are already able to generate constraints for things like `if
x is None`, we can now — in some limited cases — make an even stronger
conclusion and infer that the test expression itself is `Literal[False]`
(branch never taken) or `Literal[True]` (branch always taken).
## Test Plan
New Markdown tests
Handling `Literal` type in annotations.
Resolves: #13672
## Implementation
Since Literals are not a fully defined type in typeshed. I used a trick
to figure out when a special form is a literal.
When we are inferring assignment types I am checking if the type of that
assignment was resolved to typing.SpecialForm and the name of the target
is `Literal` if that is the case then I am re creating a new instance
type and set the known instance field to `KnownInstance:Literal`.
**Why not defining a new type?**
From this [issue](https://github.com/python/typeshed/issues/6219) I
learned that we want to resolve members to SpecialMethod class. So if we
create a new instance here we can rely on the member resolving in that
already exists.
## Tests
https://typing.readthedocs.io/en/latest/spec/literal.html#equivalence-of-two-literals
Since the type of the value inside Literal is evaluated as a
Literal(LiteralString, LiteralInt, ...) then the equality is only true
when types and value are equal.
https://typing.readthedocs.io/en/latest/spec/literal.html#legal-and-illegal-parameterizations
The illegal parameterizations are mostly implemented I'm currently
checking the slice expression and the slice type to make sure it's
valid.
https://typing.readthedocs.io/en/latest/spec/literal.html#shortening-unions-of-literals
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR enables red-knot to support type narrowing based on `and` and
`or` conditionals, including nested combinations and their negation (for
`elif` / `else` blocks and for `not` operator). Part of #13694.
In order to address this properly (hopefully 😅), I had to run
`NarrowingConstraintsBuilder` functions recursively. In the first commit
I introduced a minor refactor - instead of mutating `self.constraints`,
the new constraints are now returned as function return values. I also
modified the constraints map to be optional, preventing unnecessary
hashmap allocations.
Thanks @carljm for your support on this :)
The second commit contains the logic and tests for handling boolean ops,
with improvements to intersections handling in `is_subtype_of` .
As I'm still new to Rust and the internals of type checkers, I’d be more
than happy to hear any insights or suggestions.
Thank you!
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
Encountered this while running red-knot benchmarks on the `black`
codebase.
Fixes two of the issues in #13478.
## Test Plan
Added a regression test.
## Summary
Removes `Type::None` in favor of `KnownClass::NoneType.to_instance(…)`.
closes#13670
## Performance
There is a -4% performance regression on our red-knot benchmark. This is due to the fact that we now have to import `_typeshed` as a module, and infer types.
## Test Plan
Existing tests pass.
## Summary
This PR adds a new salsa query and an ingredient to resolve all the
variables involved in an unpacking assignment like `(a, b) = (1, 2)` at
once. Previously, we'd recursively try to match the correct type for
each definition individually which will result in creating duplicate
diagnostics.
This PR still doesn't solve the duplicate diagnostics issue because that
requires a different solution like using salsa accumulator or
de-duplicating the diagnostics manually.
Related: #13773
## Test Plan
Make sure that all unpack assignment test cases pass, there are no
panics in the corpus tests.
## Todo
- [x] Look at the performance regression
## Summary
The `commented-out-code` rule (ERA001) from `eradicate` is currently
flagging a very common idiom that marks Python strings as another
language, to help with syntax highlighting:

This PR adds this idiom to the list of allowed exceptions to the rule.
## Test Plan
I've added some additional test cases.
## Summary
Like https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/14063, but ensures that we
catch cases like `{1, True}` in which the items hash to the same value
despite not being identical.
## Summary
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13944
## Test Plan
Standard snapshot testing
flake8-simplify surprisingly only has a single test case
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
Removing more TODOs from the augmented assignment test suite. Now, if
the _target_ is a union, we correctly infer the union of results:
```python
if flag:
f = Foo()
else:
f = 42.0
f += 12
```
## Summary
One of the follow-ups from augmented assignment inference, now that
`Type::Unbound` has been removed.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
- Remove `Type::Unbound`
- Handle (potential) unboundness as a concept orthogonal to the type
system (see new `Symbol` type)
- Improve existing and add new diagnostics related to (potential)
unboundness
closes#13671
## Test Plan
- Update existing markdown-based tests
- Add new tests for added/modified functionality
## Summary
This PR fixes a panic which can occur in an unpack assignment when:
* (number of target expressions) - (number of tuple types) > 2
* There's a starred expression
The reason being that the `insert` panics because the index is greater
than the length.
This is an error case and so practically it should occur very rarely.
The solution is to resize the types vector to match the number of
expressions and then insert the starred expression type.
## Test Plan
Add a new test case.
## Summary
This PR creates a new `TypeCheckDiagnosticsBuilder` for the
`TypeCheckDiagnostics` struct. The main motivation behind this is to
separate the helpers required to build the diagnostics from the type
inference builder itself. This allows us to use such helpers outside of
the inference builder like for example in the unpacking logic in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13979.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
These cases aren't handled correctly yet -- some of them are waiting on
refactors to `Unbound` before fixing. Part of #12699.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
I noticed that augmented assignments on floats were yielding "not
supported" diagnostics. If the dunder isn't bound at all, we should use
binary operator semantics, rather than treating it as not-callable.
## Summary
Minor follow-up to #13917 — thanks @AlexWaygood for the post-merge
review.
- Add
SliceLiteralType::as_tuple
- Use .expect() instead of SAFETY
comment
- Match on ::try_from
result
- Add TODO comment regarding raising a diagnostic for `"foo"["bar":"baz"]`
## Summary
This PR adds support for heterogenous `tuple` annotations to red-knot.
It does the following:
- Extends `infer_type_expression` so that it understands tuple
annotations
- Changes `infer_type_expression` so that `ExprStarred` nodes in type
annotations are inferred as `Todo` rather than `Unknown` (they're valid
in PEP-646 tuple annotations)
- Extends `Type::is_subtype_of` to understand when one heterogenous
tuple type can be understood to be a subtype of another (without this
change, the PR would have introduced new false-positive errors to some
existing mdtests).
## Summary
- Add a new `Type::SliceLiteral` variant
- Infer `SliceLiteral` types for slice expressions, such as
`<int-literal>:<int-literal>:<int-literal>`.
- Infer "sliced" literal types for subscript expressions using slices,
such as `<string-literal>[<slice-literal>]`.
- Infer types for expressions involving slices of tuples:
`<tuple>[<slice-literal>]`.
closes#13853
## Test Plan
- Unit tests for indexing/slicing utility functions
- Markdown-based tests for
- Subscript expressions `tuple[slice]`
- Subscript expressions `string_literal[slice]`
- Subscript expressions `bytes_literal[slice]`
## Summary
This does two things:
- distribute negated intersections when building up intersections (i.e.
going from `A & ~(B & C)` to `(A & ~B) | (A & ~C)`) (fixing #13931)
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
This PR adds type narrowing in `and` and `or` expressions, for example:
```py
class A: ...
x: A | None = A() if bool_instance() else None
isinstance(x, A) or reveal_type(x) # revealed: None
```
## Test Plan
New mdtests 😍
## Summary
After #13918 has landed, narrowing constraint negation became easy, so
adding support for `not` operator.
## Test Plan
Added a new mdtest file for `not` expression.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
As python uses short-circuiting boolean operations in runtime, we should
mimic that logic in redknot as well.
For example, we should detect that in the following code `x` might be
undefined inside the block:
```py
if flag or (x := 1):
print(x)
```
## Test Plan
Added mdtest suit for boolean expressions.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
Add support for type narrowing in elif and else scopes as part of
#13694.
## Test Plan
- mdtest
- builder unit test for union negation.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
`ruff check` has not been the default in a long time. However, the help
message and code comment still designate it as the default. The remark
should have been removed in the deprecation PR #10169.
## Test Plan
Not tested.
## Summary
Add type narrowing for `isinstance(object, classinfo)` [1] checks:
```py
x = 1 if flag else "a"
if isinstance(x, int):
reveal_type(x) # revealed: Literal[1]
```
closes#13893
[1] https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#isinstance
## Test Plan
New Markdown-based tests in `narrow/isinstance.md`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR updates the fix generation logic for auto-quoting an annotation
to generate an edit even when there's a quote character present.
The logic uses the visitor pattern, maintaining it's state on where it
is and generating the string value one node at a time. This can be
considered as a specialized form of `Generator`. The state required to
maintain is whether we're currently inside a `typing.Literal` or
`typing.Annotated` because the string value in those types should not be
un-quoted i.e., `Generic[Literal["int"]]` should become
`"Generic[Literal['int']]`, the quotes inside the `Literal` should be
preserved.
Fixes: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9137
## Test Plan
Add various test cases to validate this change, validate the snapshots.
There are no ecosystem changes to go through.
---------
Signed-off-by: Shaygan <hey@glyphack.com>
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
A minor quality-of-life improvement: add
[`#[track_caller]`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/reference/attributes/codegen.html#the-track_caller-attribute)
attribute to `Type::expect_xyz()` methods and some `TypeInference` methods such that the panic-location
is reported one level higher up in the stack trace.
before: reports location inside the `Type::expect_class_literal()`
method. Not very useful.
```
thread 'types::infer::tests::deferred_annotation_builtin' panicked at crates/red_knot_python_semantic/src/types.rs:304:14:
Expected a Type::ClassLiteral variant
```
after: reports location at the `Type::expect_class_literal()` call site,
where the error was made.
```
thread 'types::infer::tests::deferred_annotation_builtin' panicked at crates/red_knot_python_semantic/src/types/infer.rs:4302:14:
Expected a Type::ClassLiteral variant
```
## Test Plan
Called `expect_class_literal()` on something that's not a
`Type::ClassLiteral` and saw that the error was reported at the call
site.
## Summary
* Rename `Type::Class` => `Type::ClassLiteral`
* Rename `Type::Function` => `Type::FunctionLiteral`
* Do not rename `Type::Module`
* Remove `*Literal` suffixes in `display::LiteralTypeKind` variants, as
per clippy suggestion
* Get rid of `Type::is_class()` in favor of `is_subtype_of(…, 'type')`;
modifiy `is_subtype_of` to support this.
* Add new `Type::is_xyz()` methods and use them instead of matching on
`Type` variants.
closes#13863
## Test Plan
New `is_subtype_of_class_literals` unit test.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
- Properly treat the empty intersection as being of type `object`.
- Consequently, change the simplification method to explicitly add
`Never` to the positive side of the intersection when collapsing a type
such as `int & str` to `Never`, as opposed to just clearing both the
positive and the negative side.
- Minor code improvement in `bindings_ty`: use `peekable()` to check
whether the iterator over constraints is empty, instead of handling
first and subsequent elements separately.
fixes#13870
## Test Plan
- New unit tests for `IntersectionBuilder` to make sure the empty
intersection represents `object`.
- Markdown-based regression test for the original issue in #13870
Add the following subtype relations:
- `BooleanLiteral <: object`
- `IntLiteral <: object`
- `StringLiteral <: object`
- `LiteralString <: object`
- `BytesLiteral <: object`
Added a test case for `bool <: int`.
## Test Plan
New unit tests.
Add type narrowing for `!=` expression as stated in
#13694.
### Test Plan
Add tests in new md format.
---------
Co-authored-by: David Peter <mail@david-peter.de>
## Summary
A small fix for comparisons of multiple comparators.
Instead of comparing each comparator to the leftmost item, we should
compare it to the closest item on the left.
While implementing this, I noticed that we don’t yet narrow Yoda
comparisons (e.g., `True is x`), so I didn’t change that behavior in
this PR.
## Test Plan
Added some mdtests 🎉
## Summary
Just a drive-by change that occurred to me while I was looking at
`Type::is_subtype_of`: the existing pattern for unions on the *right
hand side*:
```rs
(ty, Type::Union(union)) => union
.elements(db)
.iter()
.any(|&elem_ty| ty.is_subtype_of(db, elem_ty)),
```
is not (generally) correct if the *left hand side* is a union.
## Test Plan
Added new test cases for `is_subtype_of` and `!is_subtype_of`
## Summary
- Consistent naming: `BoolLiteral` => `BooleanLiteral` (it's mainly the
`Ty::BoolLiteral` variant that was renamed)
I tripped over this a few times now, so I thought I'll smooth it out.
- Add a new test case for `Literal[True] <: bool`, as suggested here:
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13781#discussion_r1804922827
Remove unnecessary uses of `.as_ref()`, `.iter()`, `&**` and similar, mostly in situations when iterating over variables. Many of these changes are only possible following #13826, when we bumped our MSRV to 1.80: several useful implementations on `&Box<[T]>` were only stabilised in Rust 1.80. Some of these changes we could have done earlier, however.
Implemented some points from
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12701
- Handle Unknown and Any in Unary operation
- Handle Boolean in binary operations
- Handle instances in unary operation
- Consider division by False to be division by zero
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
- Refactored comparison type inference functions in `infer.rs`: Changed
the return type from `Option` to `Result` to lay the groundwork for
providing more detailed diagnostics.
- Updated diagnostic messages.
This is a small step toward improving diagnostics in the future.
Please refer to #13787
## Test Plan
mdtest included!
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
This fixes an edge case that @carljm and I missed when implementing
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13800. Namely, if the left-hand
operand is the _exact same type_ as the right-hand operand, the
reflected dunder on the right-hand operand is never tried:
```pycon
>>> class Foo:
... def __radd__(self, other):
... return 42
...
>>> Foo() + Foo()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<python-input-1>", line 1, in <module>
Foo() + Foo()
~~~~~~^~~~~~~
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'Foo' and 'Foo'
```
This edge case _is_ covered in Brett's blog at
https://snarky.ca/unravelling-binary-arithmetic-operations-in-python/,
but I missed it amongst all the other subtleties of this algorithm. The
motivations and history behind it were discussed in
https://mail.python.org/archives/list/python-dev@python.org/thread/7NZUCODEAPQFMRFXYRMGJXDSIS3WJYIV/
## Test Plan
I added an mdtest for this cornercase.
## Summary
- Add `Type::is_disjoint_from` as a way to test whether two types
overlap
- Add a first set of simplification rules for intersection types
- `S & T = S` for `S <: T`
- `S & ~T = Never` for `S <: T`
- `~S & ~T = ~T` for `S <: T`
- `A & ~B = A` for `A` disjoint from `B`
- `A & B = Never` for `A` disjoint from `B`
- `bool & ~Literal[bool] = Literal[!bool]`
resolves one item in #12694
## Open questions:
- Can we somehow leverage the (anti) symmetry between `positive` and
`negative` contributions? I could imagine that there would be a way if
we had `Type::Not(type)`/`Type::Negative(type)`, but with the
`positive`/`negative` architecture, I'm not sure. Note that there is a
certain duplication in the `add_positive`/`add_negative` functions (e.g.
`S & ~T = Never` is implemented twice), but other rules are actually not
perfectly symmetric: `S & T = S` vs `~S & ~T = ~T`.
- I'm not particularly proud of the way `add_positive`/`add_negative`
turned out. They are long imperative-style functions with some
mutability mixed in (`to_remove`). I'm happy to look into ways to
improve this code *if we decide to go with this approach* of
implementing a set of ad-hoc rules for simplification.
- ~~Is it useful to perform simplifications eagerly in
`add_positive`/`add_negative`? (@carljm)~~ This is what I did for now.
## Test Plan
- Unit tests for `Type::is_disjoint_from`
- Observe changes in Markdown-based tests
- Unit tests for `IntersectionBuilder::build()`
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
Minor cleanup and consistent formatting of the Markdown-based tests.
- Removed lots of unnecessary `a`, `b`, `c`, … variables.
- Moved test assertions (`# revealed:` comments) closer to the tested
object.
- Always separate `# revealed` and `# error` comments from the code by
two spaces, according to the discussion
[here](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13746/files#r1799385758).
This trades readability for consistency in some cases.
- Fixed some headings
## Summary
This pull request resolves some rule thrashing identified in #12427 by
allowing for unused arguments when using `NotImplementedError` with a
variable per [this
comment](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12427#issuecomment-2384727468).
**Note**
This feels a little heavy-handed / edge-case-prone. So, to be clear, I'm
happy to scrap this code and just update the docs to communicate that
`abstractmethod` and friends should be used in this scenario (or
similar). Just let me know what you'd like done!
fixes: #12427
## Test Plan
I added a test-case to the existing `ARG.py` file and ran...
```sh
cargo run -p ruff -- check crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/flake8_unused_arguments/ARG.py --no-cache --preview --select ARG002
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR updates the language server to avoid indexing the workspace for
single-file mode.
**What's a single-file mode?**
When a user opens the file directly in an editor, and not the folder
that represents the workspace, the editor usually can't determine the
workspace root. This means that during initializing the server, the
`workspaceFolders` field will be empty / nil.
Now, in this case, the server defaults to using the current working
directory which is a reasonable default assuming that the directory
would point to the one where this open file is present. This would allow
the server to index the directory itself for any config file, if
present.
It turns out that in VS Code the current working directory in the above
scenario is the system root directory `/` and so the server will try to
index the entire root directory which would take a lot of time. This is
the issue as described in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/issues/627. To reproduce, refer
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/issues/627#issuecomment-2401440767.
This PR updates the indexer to avoid traversing the workspace to read
any config file that might be present. The first commit
(8dd2a31eef)
refactors the initialization and introduces two structs `Workspaces` and
`Workspace`. The latter struct includes a field to determine whether
it's the default workspace. The second commit
(61fc39bdb6)
utilizes this field to avoid traversing.
Closes: #11366
## Editor behavior
This is to document the behavior as seen in different editors. The test
scenario used has the following directory tree structure:
```
.
├── nested
│ ├── nested.py
│ └── pyproject.toml
└── test.py
```
where, the contents of the files are:
**test.py**
```py
import os
```
**nested/nested.py**
```py
import os
import math
```
**nested/pyproject.toml**
```toml
[tool.ruff.lint]
select = ["I"]
```
Steps:
1. Open `test.py` directly in the editor
2. Validate that it raises the `F401` violation
3. Open `nested/nested.py` in the same editor instance
4. This file would raise only `I001` if the `nested/pyproject.toml` was
indexed
### VS Code
When (1) is done from above, the current working directory is `/` which
means the server will try to index the entire system to build up the
settings index. This will include the `nested/pyproject.toml` file as
well. This leads to bad user experience because the user would need to
wait for minutes for the server to finish indexing.
This PR avoids that by not traversing the workspace directory in
single-file mode. But, in VS Code, this means that per (4), the file
wouldn't raise `I001` but only raise two `F401` violations because the
`nested/pyproject.toml` was never resolved.
One solution here would be to fix this in the extension itself where we
would detect this scenario and pass in the workspace directory that is
the one containing this open file in (1) above.
### Neovim
**tl;dr** it works as expected because the client considers the presence
of certain files (depending on the server) as the root of the workspace.
For Ruff, they are `pyproject.toml`, `ruff.toml`, and `.ruff.toml`. This
means that the client notifies us as the user moves between single-file
mode and workspace mode.
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13770#issuecomment-2416608055
### Helix
Same as Neovim, additional context in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13770#issuecomment-2417362097
### Sublime Text
**tl;dr** It works similar to VS Code except that the current working
directory of the current process is different and thus the config file
is never read. So, the behavior remains unchanged with this PR.
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13770#issuecomment-2417362097
### Zed
Zed seems to be starting a separate language server instance for each
file when the editor is running in a single-file mode even though all
files have been opened in a single editor instance.
(Separated the logs into sections separated by a single blank line
indicating 3 different server instances that the editor started for 3
files.)
```
0.000053375s INFO main ruff_server::server: No workspace settings found for file:///Users/dhruv/projects/ruff-temp, using default settings
0.009448792s INFO main ruff_server::session::index: Registering workspace: /Users/dhruv/projects/ruff-temp
0.009906334s DEBUG ruff:main ruff_server::resolve: Included path via `include`: /Users/dhruv/projects/ruff-temp/test.py
0.011775917s INFO ruff:main ruff_server::server: Configuration file watcher successfully registered
0.000060583s INFO main ruff_server::server: No workspace settings found for file:///Users/dhruv/projects/ruff-temp/nested, using default settings
0.010387125s INFO main ruff_server::session::index: Registering workspace: /Users/dhruv/projects/ruff-temp/nested
0.011061875s DEBUG ruff:main ruff_server::resolve: Included path via `include`: /Users/dhruv/projects/ruff-temp/nested/nested.py
0.011545208s INFO ruff:main ruff_server::server: Configuration file watcher successfully registered
0.000059125s INFO main ruff_server::server: No workspace settings found for file:///Users/dhruv/projects/ruff-temp/nested, using default settings
0.010857583s INFO main ruff_server::session::index: Registering workspace: /Users/dhruv/projects/ruff-temp/nested
0.011428958s DEBUG ruff:main ruff_server::resolve: Included path via `include`: /Users/dhruv/projects/ruff-temp/nested/other.py
0.011893792s INFO ruff:main ruff_server::server: Configuration file watcher successfully registered
```
## Test Plan
When using the `ruff` server from this PR, we see that the server starts
quickly as seen in the logs. Next, when I switch to the release binary,
it starts indexing the root directory.
For more details, refer to the "Editor Behavior" section above.
Summary
---------
PEP 695 Generics introduce a scope inside a class statement's arguments
and keywords.
```
class C[T](A[T]): # the T in A[T] is not from the global scope but from a type-param-specfic scope
...
```
When doing inference on the class bases, we currently have been doing
base class expression lookups in the global scope. Not an issue without
generics (since a scope is only created when generics are present).
This change instead makes sure to stop the global scope inference from
going into expressions within this sub-scope. Since there is a separate
scope, `check_file` and friends will trigger inference on these
expressions still.
Another change as a part of this is making sure that `ClassType` looks
up its bases in the right scope.
Test Plan
----------
`cargo test --package red_knot_python_semantic generics` will run the
markdown test that previously would panic due to scope lookup issues
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
This reverts https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13799, and restores
the previous behavior, which I think was the most pragmatic and useful
version of the divide-by-zero error, if we will emit it at all.
In general, a type checker _does_ emit diagnostics when it can detect
something that will definitely be a problem for some inhabitants of a
type, but not others. For example, `x.foo` if `x` is typed as `object`
is a type error, even though some inhabitants of the type `object` will
have a `foo` attribute! The correct fix is to make your type annotations
more precise, so that `x` is assigned a type which definitely has the
`foo` attribute.
If we will emit it divide-by-zero errors, it should follow the same
logic. Dividing an inhabitant of the type `int` by zero may not emit an
error, if the inhabitant is an instance of a subclass of `builtins.int`
that overrides division. But it may emit an error (more likely it will).
If you don't want the diagnostic, you can clarify your type annotations
to require an instance of your safe subclass.
Because the Python type system doesn't have the ability to explicitly
reflect the fact that divide-by-zero is an error in type annotations
(e.g. for `int.__truediv__`), or conversely to declare a type as safe
from divide-by-zero, or include a "nonzero integer" type which it is
always safe to divide by, the analogy doesn't fully apply. You can't
explicitly mark your subclass of `int` as safe from divide-by-zero, we
just semi-arbitrarily choose to silence the diagnostic for subclasses,
to avoid false positives.
Also, if we fully followed the above logic, we'd have to error on every
`int / int` because the RHS `int` might be zero! But this would likely
cause too many false positives, because of the lack of a "nonzero
integer" type.
So this is just a pragmatic choice to emit the diagnostic when it is
very likely to be an error. It's unclear how useful this diagnostic is
in practice, but this version of it is at least very unlikely to cause
harm.
If the LHS is just `int` or `float` type, that type includes custom
subclasses which can arbitrarily override division behavior, so we
shouldn't emit a divide-by-zero error in those cases.
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Add type inference for comparisons involving union types. For example:
```py
one_or_two = 1 if flag else 2
reveal_type(one_or_two <= 2) # revealed: Literal[True]
reveal_type(one_or_two <= 1) # revealed: bool
reveal_type(one_or_two <= 0) # revealed: Literal[False]
```
closes#13779
## Test Plan
See `resources/mdtest/comparison/unions.md`
## Summary
Fixes the bug described in #13514 where an unbound public type defaulted
to the type or `Unknown`, whereas it should only be the type if unbound.
## Test Plan
Added a new test case
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
This PR adds a debug assertion that asserts that `TypeInference::extend`
is only called on results that have the same scope.
This is critical because `expressions` uses `ScopedExpressionId` that
are local and merging expressions from different
scopes would lead to incorrect expression types.
We could consider storing `scope` only on `TypeInference` for debug
builds. Doing so has the advantage that the `TypeInference` type is
smaller of which we'll have many. However, a `ScopeId` is a `u32`... so
it shouldn't matter that much and it avoids storing the `scope` both on
`TypeInference` and `TypeInferenceBuilder`
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
This PR implements comparisons for (tuple, tuple).
It will close#13688 and complete an item in #13618 once merged.
## Test Plan
Basic tests are included for (tuple, tuple) comparisons.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
Just a small simplification to remove some unnecessary complexity here.
Rather than using separate branches for subscript expressions involving
boolean literals, we can simply convert them to integer literals and
reuse the logic in the `IntLiteral` branches.
## Test Plan
`cargo test -p red_knot_python_semantic`
## Summary
This PR adds support for unpacking tuple expression in an assignment
statement where the target expression can be a tuple or a list (the
allowed sequence targets).
The implementation introduces a new `infer_assignment_target` which can
then be used for other targets like the ones in for loops as well. This
delegates it to the `infer_definition`. The final implementation uses a
recursive function that visits the target expression in source order and
compares the variable node that corresponds to the definition. At the
same time, it keeps track of where it is on the assignment value type.
The logic also accounts for the number of elements on both sides such
that it matches even if there's a gap in between. For example, if
there's a starred expression like `(a, *b, c) = (1, 2, 3)`, then the
type of `a` will be `Literal[1]` and the type of `b` will be
`Literal[2]`.
There are a couple of follow-ups that can be done:
* Use this logic for other target positions like `for` loop
* Add diagnostics for mis-match length between LHS and RHS
## Test Plan
Add various test cases using the new markdown test framework.
Validate that existing test cases pass.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
Porting infer tests to new markdown tests framework.
Link to the corresponding issue: #13696
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
- Fix a bug with `… is not …` type guards.
Previously, in an example like
```py
x = [1]
y = [1]
if x is not y:
reveal_type(x)
```
we would infer a type of `list[int] & ~list[int] == Never` for `x`
inside the conditional (instead of `list[int]`), since we built a
(negative) intersection with the type of the right hand side (`y`).
However, as this example shows, this assumption can only be made for
singleton types (types with a single inhabitant) such as `None`.
- Add support for `… is …` type guards.
closes#13715
## Test Plan
Moved existing `narrow_…` tests to Markdown-based tests and added new
ones (including a regression test for the bug described above). Note
that will create some conflicts with
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13719. I tried to establish the
correct organizational structure as proposed in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13719#discussion_r1800188105
Address a potential point of confusion that bit a contributor in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13719
Also remove a no-longer-accurate line about bare `error: ` assertions
(which are no longer allowed) and clarify another point about which
kinds of error assertions to use.
## Summary
Fixes#13708.
Silence `undefined-reveal` diagnostic on any line including a `#
revealed:` assertion.
Add more context to un-silenced `undefined-reveal` diagnostics in mdtest
test failures. This doesn't make the failure output less verbose, but it
hopefully clarifies the right fix for an `undefined-reveal` in mdtest,
while still making it clear what red-knot's normal diagnostic for this
looks like.
## Test Plan
Added and updated tests.
This adds documentation for the new test framework.
I also added documentation for the planned design of features we haven't
built yet (clearly marked as such), so that this doc can become the sole
source of truth for the test framework design (we don't need to refer
back to the original internal design document.)
Also fixes a few issues in the test framework implementation that were
discovered in writing up the docs.
---------
Co-authored-by: T-256 <132141463+T-256@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
Adds a markdown-based test framework for writing tests of type inference
and type checking. Fixes#11664.
Implements the basic required features. A markdown test file is a suite
of tests, each test can contain one or more Python files, with
optionally specified path/name. The test writes all files to an
in-memory file system, runs red-knot, and matches the resulting
diagnostics against `Type: ` and `Error: ` assertions embedded in the
Python source as comments.
We will want to add features like incremental tests, setting custom
configuration for tests, writing non-Python files, testing syntax
errors, capturing full diagnostic output, etc. There's also plenty of
room for improved UX (colored output?).
## Test Plan
Lots of tests!
Sample of the current output when a test fails:
```
Running tests/inference.rs (target/debug/deps/inference-7c96590aa84de2a4)
running 1 test
test inference::path_1_resources_inference_numbers_md ... FAILED
failures:
---- inference::path_1_resources_inference_numbers_md stdout ----
inference/numbers.md - Numbers - Floats
/src/test.py
line 2: unexpected error: [invalid-assignment] "Object of type `Literal["str"]` is not assignable to `int`"
thread 'inference::path_1_resources_inference_numbers_md' panicked at crates/red_knot_test/src/lib.rs:60:5:
Some tests failed.
note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace
failures:
inference::path_1_resources_inference_numbers_md
test result: FAILED. 0 passed; 1 failed; 0 ignored; 0 measured; 0 filtered out; finished in 0.19s
error: test failed, to rerun pass `-p red_knot_test --test inference`
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
Fixed a TODO by adding another TODO. It's the red-knot way!
## Summary
`builtins.type` can be subscripted at runtime on Python 3.9+, even
though it has no `__class_getitem__` method and its metaclass (which
is... itself) has no `__getitem__` method. The special case is
[hardcoded directly into `PyObject_GetItem` in
CPython](744caa8ef4/Objects/abstract.c (L181-L184)).
We just have to replicate the special case in our semantic model.
This will fail at runtime on Python <3.9. However, there's a bunch of
outstanding questions (detailed in the TODO comment I added) regarding
how we deal with subscriptions of other generic types on lower Python
versions. Since we want to avoid too many false positives for now, I
haven't tried to address this; I've just made `type` subscriptable on
all Python versions.
## Test Plan
`cargo test -p red_knot_python_semantic --lib`
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Treat async generators as "await" in ASYNC100.
Fixes#13637
## Test Plan
Updated snapshot
## Summary
Implements string literal comparisons and fallbacks to `str` instance
for `LiteralString`.
Completes an item in #13618
## Test Plan
- Adds a dedicated test with non exhaustive cases
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Implements the comparison operator for `[Type::IntLiteral]` and
`[Type::BooleanLiteral]` (as an artifact of special handling of `True` and
`False` in python).
Sets the framework to implement more comparison for types known at
static time (e.g. `BooleanLiteral`, `StringLiteral`), allowing us to only
implement cases of the triplet `<left> Type`, `<right> Type`, `CmpOp`.
Contributes to #12701 (without checking off an item yet).
## Test Plan
- Added a test for the comparison of literals that should include most
cases of note.
- Added a test for the comparison of int instances
Please note that the cases do not cover 100% of the branches as there
are many and the current testing strategy with variables make this
fairly confusing once we have too many in one test.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Resolves https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9962 by allowing a
configuration setting `allowed-unused-imports`
TODO:
- [x] Figure out the correct name and place for the setting; currently,
I have added it top level.
- [x] The comparison is pretty naive. I tried using `glob::Pattern` but
couldn't get it to work in the configuration.
- [x] Add tests
- [x] Update documentations
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13545
As described in the issue, we move comments before the inner `if`
statement to before the newly constructed `elif` statement (previously
`else`).
## Summary
fix#13602
Currently, `UP043` only applies to typing.Generator, but it should also
support collections.abc.Generator.
This update ensures `UP043` correctly handles both
`collections.abc.Generator` and `collections.abc.AsyncGenerator`
### UP043
> `UP043`
> Python 3.13 introduced the ability for type parameters to specify
default values. As such, the default type arguments for some types in
the standard library (e.g., Generator, AsyncGenerator) are now optional.
> Omitting type parameters that match the default values can make the
code more concise and easier to read.
```py
Generator[int, None, None] -> Generator[int]
```
## Summary
...and remove periods from messages that don't span more than a single
sentence.
This is more consistent with how we present user-facing messages in uv
(which has a defined style guide).
## Summary
You can now call `return_ty_result` to operate on a `Result` directly
thereby using your own diagnostics, as in:
```rust
return dunder_getitem_method
.call(self.db, &[slice_ty])
.return_ty_result(self.db, value.as_ref().into(), self)
.unwrap_or_else(|err| {
self.add_diagnostic(
(&**value).into(),
"call-non-callable",
format_args!(
"Method `__getitem__` is not callable on object of type '{}'.",
value_ty.display(self.db),
),
);
err.return_ty()
});
```
While looking into https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13545 I
noticed that we return `None` here if you pass a block of comments. This
is annoying because it causes `adjust_indentation` to fall back to
LibCST which panics when it cannot find a statement.
Adds a diagnostic for division by the integer zero in `//`, `/`, and
`%`.
Doesn't handle `<int> / 0.0` because we don't track the values of float
literals.
This variant shows inference that is not yet implemented..
## Summary
PR #13500 reopened the idea of adding a new type variant to keep track
of not-implemented features in Red Knot.
It was based off of #12986 with a more generic approach of keeping track
of different kind of unknowns. Discussion in #13500 agreed that keeping
track of different `Unknown` is complicated for now, and this feature is
better achieved through a new variant of `Type`.
### Requirements
Requirements for this implementation can be summed up with some extracts
of comment from @carljm on the previous PR
> So at the moment we are leaning towards simplifying this PR to just
use a new top-level variant, which behaves like Any and Unknown but
represents inference that is not yet implemented in red-knot.
> I think the general rule should be that Todo should propagate only
when the presence of the input Todo caused the output to be unknown.
>
> To take a specific example, the inferred result of addition must be
Unknown if either operand is Unknown. That is, Unknown + X will always
be Unknown regardless of what X is. (Same for X + Unknown.) In this
case, I believe that Unknown + Todo (or Todo + Unknown) should result in
Unknown, not result in Todo. If we fix the upstream source of the Todo,
the result would still be Unknown, so it's not useful to propagate the
Todo in this case: it wrongly suggests that the output is unknown
because of a todo item.
## Test Plan
This PR does not introduce new tests, but it did required to edit some
tests with the display of `[Type::Todo]` (currently `@Todo`), which
suggests that those test are placeholders requirements for features we
don't support yet.
While working on https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13576 I noticed
that it was really hard to tell which assertion failed in some of these
test cases. This could be expanded to elsewhere, but I've heard this
test suite format won't be around for long?
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
There was a typo in the links of the docs of PTH116, where Path.stat
used to link to Path.group.
Another rule, PTH202, does it correctly:
ec72e675d9/crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/flake8_use_pathlib/rules/os_path_getsize.rs (L33)
This PR only fixes a one word typo.
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
I did not test that the doc generation framework picked up these
changes, I assume it will do it successfully.
## Summary
Following #13449, this PR adds custom handling for the bool constructor,
so when the input type has statically known truthiness value, it will be
used as the return value of the bool function.
For example, in the following snippet x will now be resolved to
`Literal[True]` instead of `bool`.
```python
x = bool(1)
```
## Test Plan
Some cargo tests were added.
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Implement inference for `f-string`, contributes to #12701.
### First Implementation
When looking at the way `mypy` handles things, I noticed the following:
- No variables (e.g. `f"hello"`) ⇒ `LiteralString`
- Any variable (e.g. `f"number {1}"`) ⇒ `str`
My first commit (1ba5d0f13fdf70ed8b2b1a41433b32fc9085add2) implements
exactly this logic, except that we deal with string literals just like
`infer_string_literal_expression` (if below `MAX_STRING_LITERAL_SIZE`,
show `Literal["exact string"]`)
### Second Implementation
My second commit (90326ce9af5549af7b4efae89cd074ddf68ada14) pushes
things a bit further to handle cases where the expression within the
`f-string` are all literal values (string representation known at static
time).
Here's an example of when this could happen in code:
```python
BASE_URL = "https://httpbin.org"
VERSION = "v1"
endpoint = f"{BASE_URL}/{VERSION}/post" # Literal["https://httpbin.org/v1/post"]
```
As this can be sightly more costly (additional allocations), I don't
know if we want this feature.
## Test Plan
- Added a test `fstring_expression` covering all cases I can think of
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
Related to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13524
Doesn't offer a valid fix, opting to instead just not offer a fix at
all. If someone points me to a good way to handle parenthesis here I'm
down to try to fix the fix separately, but it looks quite hard.
## Summary
Building ruff on AIX breaks on `tiki-jemalloc-sys` due to OS header
incompatibility
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
Co-authored-by: Henry Jiang <henry.jiang1@ibm.com>
In https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13503, we added supported for
detecting variadic keyword arguments as dictionaries, here we use the
same strategy for detecting variadic positional arguments as tuples.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13266
Avoids false negatives for shadowed bindings that aren't actually
references to the loop variable. There are some shadowed bindings we
need to support still, e.g., `del` requires the loop variable to exist.
## Summary
I think we should also make the change that @BurntSushi recommended in
the linked issue, but this gets rid of the panic.
See: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13483
See: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/13442
## Test Plan
```
warning: `ruff analyze graph` is experimental and may change without warning
{
"/Users/crmarsh/workspace/django/django/__init__.py": [
"/Users/crmarsh/workspace/django/django/apps/__init__.py",
"/Users/crmarsh/workspace/django/django/conf/__init__.py",
"/Users/crmarsh/workspace/django/django/urls/__init__.py",
"/Users/crmarsh/workspace/django/django/utils/log.py",
"/Users/crmarsh/workspace/django/django/utils/version.py"
],
"/Users/crmarsh/workspace/django/django/__main__.py": [
"/Users/crmarsh/workspace/django/django/core/management/__init__.py"
ruff failed
Cause: Broken pipe (os error 32)
```
## Summary
This PR changes removes the typeshed stubs from the vendored file system
shipped with ruff
and instead ships an empty "typeshed".
Making the typeshed files optional required extracting the typshed files
into a new `ruff_vendored` crate. I do like this even if all our builds
always include typeshed because it means `red_knot_python_semantic`
contains less code that needs compiling.
This also allows us to use deflate because the compression algorithm
doesn't matter for an archive containing a single, empty file.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
I verified with ` cargo tree -f "{p} {f}" -p <package> ` that:
* red_knot_wasm: enables `deflate` compression
* red_knot: enables `zstd` compression
* `ruff`: uses stored
I'm not quiet sure how to build the binary that maturin builds but
comparing the release artifact size with `strip = true` shows a `1.5MB`
size reduction
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
For reasons I haven't investigated, this speeds up the resolver about 2x
(from 6.404s to 3.612s on an extremely large codebase).
## Test Plan
\cc @BurntSushi
```
[andrew@duff rippling]$ time ruff analyze graph --preview > /dev/null
real 3.274
user 16.039
sys 7.609
maxmem 11631 MB
faults 0
[andrew@duff rippling]$ time ruff-patch analyze graph --preview > /dev/null
real 1.841
user 14.625
sys 3.639
maxmem 7173 MB
faults 0
[andrew@duff rippling]$ time ruff-patch2 analyze graph --preview > /dev/null
real 2.087
user 15.333
sys 4.869
maxmem 8642 MB
faults 0
```
Where that's `main`, then (`ruff-patch`) using the version with no
`File`, no `SemanticModel`, then (`ruff-patch2`) using `File`.
Avoid quadratic time in subsumed elements when adding a super-type of
existing union elements.
Reserve space in advance when adding multiple elements (from another
union) to a union.
Make union elements a `Box<[Type]>` instead of an `FxOrderSet`; the set
doesn't buy much since the rules of union uniqueness are defined in
terms of supertype/subtype, not in terms of simple type identity.
Move sealed-boolean handling out of a separate `UnionBuilder::simplify`
method and into `UnionBuilder::add`; now that `add` is iterating
existing elements anyway, this is more efficient.
Remove `UnionType::contains`, since it's now `O(n)` and we shouldn't
really need it, generally we care about subtype/supertype, not type
identity. (Right now it's used for `Type::Unbound`, which shouldn't even
be a type.)
Add support for `is_subtype_of` for the `object` type.
Addresses comments on https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/13401
This was mentioned in an earlier review, and seemed easy enough to just
do it. No need to repeat all the types twice when it gives no additional
information.
## Summary
This PR adds an experimental Ruff subcommand to generate dependency
graphs based on module resolution.
A few highlights:
- You can generate either dependency or dependent graphs via the
`--direction` command-line argument.
- Like Pants, we also provide an option to identify imports from string
literals (`--detect-string-imports`).
- Users can also provide additional dependency data via the
`include-dependencies` key under `[tool.ruff.import-map]`. This map uses
file paths as keys, and lists of strings as values. Those strings can be
file paths or globs.
The dependency resolution uses the red-knot module resolver which is
intended to be fully spec compliant, so it's also a chance to expose the
module resolver in a real-world setting.
The CLI is, e.g., `ruff graph build ../autobot`, which will output a
JSON map from file to files it depends on for the `autobot` project.
This fixes the last panic on checking pandas.
(Match statement became an `if let` because clippy decided it wanted
that once I added the additional line in the else case?)
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
Support using `reveal_type` without importing it, as implied by the type
spec and supported by existing type checkers.
We use `typing_extensions.reveal_type` for the implicit built-in; this
way it exists on all Python versions. (It imports from `typing` on newer
Python versions.)
Emits an "undefined name" diagnostic whenever `reveal_type` is
referenced in this way (in addition to the revealed-type diagnostic when
it is called). This follows the mypy example (with `--enable-error-code
unimported-reveal`) and I think provides a good (and easily
understandable) balance for user experience. If you are using
`reveal_type` for quick temporary debugging, the additional
undefined-name diagnostic doesn't hinder that use case. If we make the
revealed-type diagnostic a non-failing one, the undefined-name
diagnostic can still be a failing diagnostic, helping prevent
accidentally leaving it in place. For any use cases where you want to
leave it in place, you can always import it to avoid the undefined-name
diagnostic.
In the future, we can easily provide configuration options to a) turn
off builtin-reveal_type altogether, and/or b) silence the undefined-name
diagnostic when using it, if we have users on either side (loving or
hating pseudo-builtin `reveal_type`) who are dissatisfied with this
compromise.
After looking at more cases (for example, the case in the added test in
this PR), I realized that our previous rule, "if a symbol has any
declarations, use only declarations for its public type" is not
adequate. Rather than using `Unknown` as fallback if the symbol is not
declared in some paths, we need to use the inferred type as fallback in
that case.
For the paths where the symbol _was_ declared, we know that any bindings
must be assignable to the declared type in that path, so this won't
change the overall declared type in those paths. But for paths where the
symbol wasn't declared, this will give us a better type in place of
`Unknown`.
Before `typing.reveal_type` existed, there was
`typing_extensions.reveal_type`. We should support both.
Also adds a test to verify that we can handle aliasing of `reveal_type`
to a different name.
Adds a bit of code to ensure that if we have a union of different
`reveal_type` functions (e.g. a union containing both
`typing_extensions.reveal_type` and `typing.reveal_type`) we still emit
the reveal-type diagnostic only once. This is probably unlikely in
practice, but it doesn't hurt to handle it smoothly. (It comes up now
because we don't support `version_info` checks yet, so
`typing_extensions.reveal_type` is actually that union.)
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
I noticed that this pattern sometimes occurs in typeshed:
```
if ...:
from foo import bar
else:
def bar(): ...
```
If we have the rule that symbols with declarations only use declarations
for the public type, then this ends up resolving as `Unknown |
Literal[bar]`, because we didn't consider the import to be a
declaration.
I think the most straightforward thing here is to also consider imports
as declarations. The same rationale applies as for function and class
definitions: if you shadow an import, you should have to explicitly
shadow with an annotation, rather than just doing it
implicitly/accidentally.
We may also ultimately need to re-evaluate the rule that public type
considers only declarations, if there are declarations.
Add support for the `typing.reveal_type` function, emitting a diagnostic
revealing the type of its single argument. This is a necessary piece for
the planned testing framework.
This puts the cart slightly in front of the horse, in that we don't yet
have proper support for validating call signatures / argument types. But
it's easy to do just enough to make `reveal_type` work.
This PR includes support for calling union types (this is necessary
because we don't yet support `sys.version_info` checks, so
`typing.reveal_type` itself is a union type), plus some nice
consolidated error messages for calls to unions where some elements are
not callable. This is mostly to demonstrate the flexibility in
diagnostics that we get from the `CallOutcome` enum.
Use declared types in inference and checking. This means several things:
* Imports prefer declarations over inference, when declarations are
available.
* When we encounter a binding, we check that the bound value's inferred
type is assignable to the live declarations of the bound symbol, if any.
* When we encounter a declaration, we check that the declared type is
assignable from the inferred type of the symbol from previous bindings,
if any.
* When we encounter a binding+declaration, we check that the inferred
type of the bound value is assignable to the declared type.
Add support for declared types to the semantic index. This involves a
lot of renaming to clarify the distinction between bindings and
declarations. The Definition (or more specifically, the DefinitionKind)
becomes responsible for determining which definitions are bindings,
which are declarations, and which are both, and the symbol table
building is refactored a bit so that the `IS_BOUND` (renamed from
`IS_DEFINED` for consistent terminology) flag is always set when a
binding is added, rather than being set separately (and requiring us to
ensure it is set properly).
The `SymbolState` is split into two parts, `SymbolBindings` and
`SymbolDeclarations`, because we need to store live bindings for every
declaration and live declarations for every binding; the split lets us
do this without storing more than we need.
The massive doc comment in `use_def.rs` is updated to reflect bindings
vs declarations.
The `UseDefMap` gains some new APIs which are allow-unused for now,
since this PR doesn't yet update type inference to take declarations
into account.
## Summary
Follow-up from #13268, this PR updates the test case to use
`assert_snapshot` now that the output is limited to only include the
rules with diagnostics.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
Add `::is_empty` and `::union` methods to the `BitSet` implementation.
Allowing unused for now, until these methods become used later with the
declared-types implementation.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
These are quite incomplete, but I needed to start stubbing them out in
order to build and test declared-types.
Allowing unused for now, until they are used later in the declared-types
PR.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR adds a new `Type` variant called `TupleType` which is used for
heterogeneous elements.
### Display notes
* For an empty tuple, I'm using `tuple[()]` as described in the docs:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html#annotating-tuples
* For nested elements, it'll use the literal type instead of builtin
type unlike Pyright which does `tuple[Literal[1], tuple[int, int]]`
instead of `tuple[Literal[1], tuple[Literal[2], Literal[3]]]`. Also,
mypy would give `tuple[builtins.int, builtins.int]` instead of
`tuple[Literal[1], Literal[2]]`
## Test Plan
Update test case to account for the display change and add cases for
multiple elements and nested tuple elements.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
This PR adds support for control flow for match statement.
It also adds the necessary infrastructure required for narrowing
constraints in case blocks and implements the logic for
`PatternMatchSingleton` which is either `None` / `True` / `False`. Even
after this the inferred type doesn't get simplified completely, there's
a TODO for that in the test code.
## Test Plan
Add test cases for control flow for (a) when there's a wildcard pattern
and (b) when there isn't. There's also a test case to verify the
narrowing logic.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
When a type of the form `Literal["..."]` would be constructed with too
large of a string, this PR converts it to `LiteralString` instead.
We also extend inference for binary operations to include the case where
one of the operands is `LiteralString`.
Closes#13224
Pull the tests from `types.rs` into `infer.rs`.
All of these are integration tests with the same basic form: create a
code sample, run type inference or check on it, and make some assertions
about types and/or diagnostics. These are the sort of tests we will want
to move into a test framework with a low-boilerplate custom textual
format. In the meantime, having them together (and more importantly,
their helper utilities together) means that it's easy to keep tests for
related language features together (iterable tests with other iterable
tests, callable tests with other callable tests), without an artificial
split based on tests which test diagnostics vs tests which test
inference. And it allows a single test to more easily test both
diagnostics and inference. (Ultimately in the test framework, they will
likely all test diagnostics, just in some cases the diagnostics will
come from `reveal_type()`.)
My plan for handling declared types is to introduce a `Declaration` in
addition to `Definition`. A `Declaration` is an annotation of a name
with a type; a `Definition` is an actual runtime assignment of a value
to a name. A few things (an annotated function parameter, an
annotated-assignment with an RHS) are both a `Definition` and a
`Declaration`.
This more cleanly separates type inference (only cares about
`Definition`) from declared types (only impacted by a `Declaration`),
and I think it will work out better than trying to squeeze everything
into `Definition`. One of the tests in this PR
(`annotation_only_assignment_transparent_to_local_inference`)
demonstrates one reason why. The statement `x: int` should have no
effect on local inference of the type of `x`; whatever the locally
inferred type of `x` was before `x: int` should still be the inferred
type after `x: int`. This is actually quite hard to do if `x: int` is
considered a `Definition`, because a core assumption of the use-def map
is that a `Definition` replaces the previous value. To achieve this
would require some hackery to effectively treat `x: int` sort of as if
it were `x: int = x`, but it's not really even equivalent to that, so
this approach gets quite ugly.
As a first step in this plan, this PR stops treating AnnAssign with no
RHS as a `Definition`, which fixes behavior in a couple added tests.
This actually makes things temporarily worse for the ellipsis-type test,
since it is defined in typeshed only using annotated assignments with no
RHS. This will be fixed properly by the upcoming addition of
declarations, which should also treat a declared type as sufficient to
import a name, at least from a stub.
Initially I had deferred annotation name lookups reuse the "public
symbol type", since that gives the correct "from end of scope" view of
reaching definitions that we want. But there is a key difference; public
symbol types are based only on definitions in the queried scope (or
"name in the given namespace" in runtime terms), they don't ever look up
a name in nonlocal/global/builtin scopes. Deferred annotation resolution
should do this lookup.
Add a test, and fix deferred name resolution to support
nonlocal/global/builtin names.
Fixes#13176
## Summary
Part of #13085, this PR updates the comprehension definition to handle
multiple targets.
## Test Plan
Update existing semantic index test case for comprehension with multiple
targets. Running corpus tests shouldn't panic.
Add support for non-local name lookups.
There's one TODO around annotated assignments without a RHS; these need
a fair amount of attention, which they'll get in an upcoming PR about
declared vs inferred types.
Fixes#11663
Test coverage for #13131 wasn't as good as I thought it was, because
although we infer a lot of types in stubs in typeshed, we don't check
typeshed, and therefore we don't do scope-level inference and pull all
types for a scope. So we didn't really have good test coverage for
scope-level inference in a stub. And because of this, I got the code for
supporting that wrong, meaning that if we did scope-level inference with
deferred types, we'd end up never populating the deferred types in the
scope's `TypeInference`, which causes panics like #13160.
Here I both add test coverage by running the corpus tests both as `.py`
and as `.pyi` (which reveals the panic), and I fix the code to support
deferred types in scope inference.
This also revealed a problem with deferred types in generic functions,
which effectively span two scopes. That problem will require a bit more
thought, and I don't want to block this PR on it, so for now I just
don't defer annotations on generic functions.
Fixes#13160.
## Summary
Follow-up to #13147, this PR implements the `AstNode` for `Identifier`.
This makes it easier to create the `NodeKey` in red knot because it uses
a generic method to construct the key from `AnyNodeRef` and is important
for definitions that are created only on identifiers instead of
`ExprName`.
## Test Plan
`cargo test` and `cargo clippy`
## Summary
This PR adds definition for match patterns.
## Test Plan
Update the existing test case for match statement symbols to verify that
the definitions are added as well.
This PR contains the following updates:
| Package | Type | Update | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| [quick-junit](https://redirect.github.com/nextest-rs/quick-junit) |
workspace.dependencies | minor | `0.4.0` -> `0.5.0` |
---
### Release Notes
<details>
<summary>nextest-rs/quick-junit (quick-junit)</summary>
###
[`v0.5.0`](https://redirect.github.com/nextest-rs/quick-junit/blob/HEAD/CHANGELOG.md#050---2024-09-01)
[Compare
Source](https://redirect.github.com/nextest-rs/quick-junit/compare/quick-junit-0.4.0...quick-junit-0.5.0)
##### Changed
- The `Output` type, which strips invalid XML characters from a string,
has been renamed to
`XmlString`.
- All internal storage now uses `XmlString` rather than `String`.
</details>
---
### Configuration
📅 **Schedule**: Branch creation - "before 4am on Monday" (UTC),
Automerge - At any time (no schedule defined).
🚦 **Automerge**: Disabled by config. Please merge this manually once you
are satisfied.
♻ **Rebasing**: Whenever PR becomes conflicted, or you tick the
rebase/retry checkbox.
🔕 **Ignore**: Close this PR and you won't be reminded about this update
again.
---
- [ ] <!-- rebase-check -->If you want to rebase/retry this PR, check
this box
---
This PR was generated by [Mend Renovate](https://mend.io/renovate/).
View the [repository job
log](https://developer.mend.io/github/astral-sh/ruff).
<!--renovate-debug:eyJjcmVhdGVkSW5WZXIiOiIzOC41Ni4wIiwidXBkYXRlZEluVmVyIjoiMzguNTkuMiIsInRhcmdldEJyYW5jaCI6Im1haW4iLCJsYWJlbHMiOlsiaW50ZXJuYWwiXX0=-->
---------
Co-authored-by: renovate[bot] <29139614+renovate[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
The `SequenceIndexVisitor` currently does not recurse into
subexpressions of subscripts when searching for subscript accesses that
would trigger this rule. That means that we don't currently detect
violations of the rule on snippets like this:
```py
data = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
column_names = ["a", "b"]
for index, column_name in enumerate(column_names):
_ = data[column_names[index]]
```
Fixes#13183
## Test Plan
`cargo test -p ruff_linter`
The `UnionBuilder` builds `builtins.bool` when handed `Literal[True]`
and `Literal[False]`.
Caveat: If the builtins module is unfindable somehow, the builder falls
back to the union type of these two literals.
First task from #12694
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
Adds basic support for inferring the type resulting from a call
expression. This only works for the *result* of call expressions; it
performs no inference on parameters. It also intentionally does nothing
with class instantiation, `__call__` implementors, or lambdas.
## Test Plan
Adds a test that it infers the right thing!
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
- Introduce methods for inferring annotation and type expressions.
- Correctly infer explicit return types from functions where they are
simple names that can be resolved in scope.
Contributes to #12701 by way of helping unlock call expressions (this
does not remotely finish that, as it stands, but it gets us moving that
direction).
## Test Plan
Added a test for function return types which use the name form of an
annotation expression, since this is aiming toward call expressions.
When we extend this to working for other annotation and type expression
positions, we should add explicit tests for those as well.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <alex.waygood@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
Extends deletions for RUF100, deleting trailing text from noqa
directives, while preserving upcoming comments on the same line if any.
In cases where it deletes a comment up to another comment on the same
line, the whitespace between them is now shown to be in the autofix in
the diagnostic as well. Leading whitespace before the removed comment is
not, though.
Fixes#12251
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
Prototype deferred evaluation of type expressions by deferring
evaluation of class bases in a stub file. This allows self-referential
class definitions, as occur with the definition of `str` in typeshed
(which inherits `Sequence[str]`).
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Just what it says on the tin: adds basic `EllipsisType` inference for
any time `...` appears in the AST.
## Test Plan
Test that `x = ...` produces exactly what we would expect.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@oddbird.net>
## Summary
The resulting type when multiplying a string literal by an integer
literal is one of two types:
- `StringLiteral`, in the case where it is a reasonably small resulting
string (arbitrarily bounded here to 4096 bytes, roughly a page on many
operating systems), including the fully expanded string.
- `LiteralString`, matching Pyright etc., for strings larger than that.
Additionally:
- Switch to using `Box<str>` instead of `String` for the internal value
of `StringLiteral`, saving some non-trivial byte overhead (and keeping
the total number of allocations the same).
- Be clearer and more accurate about which types we ought to defer to in
`StringLiteral` and `LiteralString` member lookup.
## Test Plan
Added a test case covering multiplication times integers: positive,
negative, zero, and in and out of bounds.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <alex.waygood@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
This fixes the outstanding TODO and make it easier to work with new
cases. (Tidy first, *then* implement, basically!)
## Test Plan
After making this change all the existing tests still pass. A classic
refactor win. 🎉
# Summary
Add support for the first unary operator: negating integer literals. The
resulting type is another integer literal, with the value being the
negated value of the literal. All other types continue to return
`Type::Unknown` for the present, but this is designed to make it easy to
extend easily with other combinations of operator and operand.
Contributes to #12701.
## Test Plan
Add tests with basic negation, including of very large integers and
double negation.
## Summary
Introduce a `StringLiteralType` with corresponding `Display` type and a
relatively basic test that the resulting representation is as expected.
Note: we currently always allocate for `StringLiteral` types. This may
end up being a perf issue later, at which point we may want to look at
other ways of representing `value` here, i.e. with some kind of smarter
string structure which can reuse types. That is most likely to show up
with e.g. concatenation.
Contributes to #12701.
## Test Plan
Added a test for individual strings with both single and double quotes
as well as concatenated strings with both forms.
## Summary
Now that Ruff provides a formatter, there is no need to rely on Black to
check that the docs are formatted correctly in
`check_docs_formatted.py`. This PR swaps out Black for the Ruff
formatter and updates inconsistencies between the two.
This PR will be a precursor to another PR
([branch](https://github.com/calumy/ruff/tree/format-pyi-in-docs)),
updating the `check_docs_formatted.py` script to check for pyi files,
fixing #11568.
## Test Plan
- CI to check that the docs are formatted correctly using the updated
script.
This PR has the `SemanticIndexBuilder` visit function definition
annotations before adding the function symbol/name to the builder.
For example, the following snippet no longer causes a panic:
```python
def bool(x) -> bool:
Return True
```
Note: This fix changes the ordering of the global symbol table.
Closes#13069
## Summary
This PR adds symbols introduced by `for` loops to red-knot:
- `x` in `for x in range(10): pass`
- `x` and `y` in `for x, y in d.items(): pass`
- `a`, `b`, `c` and `d` in `for [((a,), b), (c, d)] in foo: pass`
## Test Plan
Several tests added, and the assertion in the benchmarks has been
updated.
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
## Summary
This PR simplifies the virtual file support in the red knot core,
specifically:
* Update `File::add_virtual_file` method to `File::virtual_file` which
will always create a new virtual file and override the existing entry in
the lookup table
* Add `VirtualFile` which is a wrapper around `File` and provides
methods to increment the file revision / close the virtual file
* Add a new `File::try_virtual_file` to lookup the `VirtualFile` from
`Files`
* Add `File::sync_virtual_path` which takes in the `SystemVirtualPath`,
looks up the `VirtualFile` for it and calls the `sync` method to
increment the file revision
* Removes the `virtual_path_metadata` method on `System` trait
## Test Plan
- [x] Make sure the existing red knot tests pass
- [x] Updated code works well with the LSP
## Summary
This PR adds support for `textDocument/didChange` notification.
There seems to be a bug (probably in Salsa) where it panics with:
```
2024-08-22 15:33:38.802 [info] panicked at /Users/dhruv/.cargo/git/checkouts/salsa-61760caba2b17ca5/f608ff8/src/tracked_struct.rs:377:9:
two concurrent writers to Id(4800), should not be possible
```
## Test Plan
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/81055feb-ba8e-4acf-ad2f-94084a3efead
## Summary
This PR adds basic support for files outside of any workspace in the red
knot server.
This also limits the red knot server to only work in a single workspace.
The server will not start if there are multiple workspaces.
## Test Plan
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/de601387-0ad5-433c-9d2c-7b6ae5137654
## Summary
This PR adds the `bytes` type to red-knot:
- Added the `bytes` type
- Added support for bytes literals
- Support for the `+` operator
Improves on #12701
Big TODO on supporting and normalizing r-prefixed bytestrings
(`rb"hello\n"`)
## Test Plan
Added a test for a bytes literals, concatenation, and corner values
The `SemanticIndexBuilder` was causing a cycle in a salsa query by
attempting to resolve the target before the value in a named expression
(e.g. `x := x+1`). This PR swaps the order, avoiding a panic.
Closes#13012.
## Summary
This PR removes notebook sync support from server capabilities because
it isn't tested, it'll be added back once we actually add full support
for notebook.
## Summary
This PR adds symbols and definitions introduced by `with` statements.
The symbols and definitions are introduced for each with item. The type
inference is updated to call the definition region type inference
instead.
## Test Plan
Add test case to check for symbol table and definitions.
## Summary
This PR adds symbols introduced by `match` statements.
There are three patterns that introduces new symbols:
* `as` pattern
* Sequence pattern
* Mapping pattern
The recursive nature of the visitor makes sure that all symbols are
added.
## Test Plan
Add test case for all types of patterns that introduces a symbol.
## Summary
This PR adds definition for augmented assignment. This is similar to
annotated assignment in terms of implementation.
An augmented assignment should also record a use of the variable but
that's a TODO for now.
## Test Plan
Add test case to validate that a definition is added.
## Summary
As suggested by @MichaReiser in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/12886#pullrequestreview-2237679793,
this adds an exemption to `RUF027` for `fastAPI` paths, which require
template strings rather than eagerly evaluated f-strings.
## Test Plan
I added a fixture that causes Ruff to emit a false-positive error on
`main` but no longer does with this PR.
Extend the `UseDefMap` to also track which constraints (provided by e.g.
`if` tests) apply to each visible definition.
Uses a custom `BitSet` and `BitSetArray` to track which constraints
apply to which definitions, while keeping data inline as much as
possible.
## Summary
This PR is a pure refactor to simplify some of the logic for `RUF027`.
This will make it easier to file some followup PRs to help reduce the
false positives from this rule. I'm separating the refactor out into a
separate PR so it's easier to review, and so I can double-check from the
ecosystem report that this doesn't have any user-facing impact.
## Test Plan
`cargo test -p ruff_linter --lib`
## Summary
This PR adds support for adding symbols and definitions for function and
lambda parameters to the semantic index.
### Notes
* The default expression of a parameter is evaluated in the enclosing
scope (not the type parameter or function scope).
* The annotation expression of a parameter is evaluated in the type
parameter scope if they're present other in the enclosing scope.
* The symbols and definitions are added in the function parameter scope.
### Type Inference
There are two definitions `Parameter` and `ParameterWithDefault` and
their respective `*_definition` methods on the type inference builder.
These methods are preferred and are re-used when checking from a
different region.
## Test Plan
Add test case for validating that the parameters are defined in the
function / lambda scope.
### Benchmark update
Validated the difference in diagnostics for benchmark code between
`main` and this branch. All of them are either directly or indirectly
referencing one of the function parameters. The diff is in the PR description.
This adds the `fast-api-unused-path-parameter` lint rule, as described
in #12632.
I'm still pretty new to rust, so the code can probably be improved, feel
free to tell me if there's any changes i should make.
Also, i needed to add the `add_parameter` edit function, not sure if it
was in the scope of the PR or if i should've made another one.
If a builtin is conditionally shadowed by a global, we didn't correctly
fall back to builtins for the not-defined-in-globals path (see added
test for an example.)
List and set comprehensions using `async for` cannot be replaced with
underlying generators; this PR modifies C419 to skip such
comprehensions.
Closes#12891.
## Summary
Occasionally, we receive bug reports that imports in `src` directories
aren't correctly detected. The root of the problem is that we default to
`src = ["."]`, so users have to set `src = ["src"]` explicitly. This PR
extends the default to cover _both_ of them: `src = [".", "src"]`.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12454.
## Test Plan
I replicated the structure described in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12453, and verified that the
imports were considered sorted, but that adding `src = ["."]` showed an
error.
## Summary
This PR adds very basic support for using the line / column information
from the diagnostic message. This makes it easier to validate
diagnostics in an editor as oppose to going through the diff one
diagnostic at a time and confirming it at the location.
## Summary
This PR adds a fallback logic for `is_python_notebook` to check the
`kernelspec.language` field.
Reference implementation in VS Code:
1c31e75898/extensions/ipynb/src/deserializers.ts (L20-L22)
It's also required for the kernel to provide the `language` they're
implementing based on
https://jupyter-client.readthedocs.io/en/stable/kernels.html#kernel-specs
reference although that's for the `kernel.json` file but is also
included in the notebook metadata.
Closes: #12281
## Test Plan
Add a test case for `is_python_notebook` and include the test notebook
for round trip validation.
The test notebook contains two cells, one is JavaScript (denoted via the
`vscode.languageId` metadata) and the other is Python (no metadata). The
notebook metadata only contains `kernelspec` and the `language_info` is
absent.
I also verified that this is a valid notebook by opening it in Jupyter
Lab, VS Code and using `nbformat` validator.
## Summary
This PR adds support for VS Code specific cell metadata to consider when
collecting valid code cells.
For context, Ruff only runs on valid code cells. These are the code
cells that doesn't contain cell magics. Previously, Ruff only used the
notebook's metadata to determine whether it's a Python notebook. But, in
VS Code, a notebook's preferred language might be Python but it could
still contain code cells for other languages. This can be determined
with the `metadata.vscode.languageId` field.
### References:
* https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/languages/identifiers
* e6c009a3d4/extensions/ipynb/src/serializers.ts (L104-L107)
*
e6c009a3d4/extensions/ipynb/src/serializers.ts (L117-L122)
This brings us one step closer to fixing #12281.
## Test Plan
Add test cases for `is_valid_python_code_cell` and an integration test
case which showcase running it end to end. The test notebook contains a
JavaScript code cell and a Python code cell.
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug in the semantic model where it would evaluate the
default parameter value in the type parameter scope. For example,
```py
def foo[T1: int](a = T1):
pass
```
Here, the `T1` in `a = T1` is undefined but Ruff doesn't flag it
(https://play.ruff.rs/ba2f7c2f-4da6-417e-aa2a-104aa63e6d5e).
The fix here is to evaluate the default parameter value in the
_enclosing_ scope instead.
## Test Plan
Add a test case which includes the above code under `F821`
(`undefined-name`) and validate the snapshot.
## Summary
See #12703. This only addresses the first bullet point, adding a space
after the comma in the suggested fix from list/tuple to string.
## Test Plan
Updated the snapshots and compared.
## Summary
This PR adds scope and definition for comprehension nodes. This includes
the following nodes:
* List comprehension
* Dictionary comprehension
* Set comprehension
* Generator expression
### Scope
Each expression here adds it's own scope with one caveat - the `iter`
expression of the first generator is part of the parent scope. For
example, in the following code snippet the `iter1` variable is evaluated
in the outer scope.
```py
[x for x in iter1]
```
> The iterable expression in the leftmost for clause is evaluated
directly in the enclosing scope and then passed as an argument to the
implicitly nested scope.
>
> Reference:
https://docs.python.org/3/reference/expressions.html#displays-for-lists-sets-and-dictionaries
There's another special case for assignment expressions:
> There is one special case: an assignment expression occurring in a
list, set or dict comprehension or in a generator expression (below
collectively referred to as “comprehensions”) binds the target in the
containing scope, honoring a nonlocal or global declaration for the
target in that scope, if one exists.
>
> Reference: https://peps.python.org/pep-0572/#scope-of-the-target
For example, in the following code snippet, the variables `a` and `b`
are available after the comprehension while `x` isn't:
```py
[a := 1 for x in range(2) if (b := 2)]
```
### Definition
Each comprehension node adds a single definition, the "target" variable
(`[_ for target in iter]`). This has been accounted for and a new
variant has been added to `DefinitionKind`.
### Type Inference
Currently, type inference is limited to a single scope. It doesn't
_enter_ in another scope to infer the types of the remaining expressions
of a node. To accommodate this, the type inference for a **scope**
requires new methods which _doesn't_ infer the type of the `iter`
expression of the leftmost outer generator (that's defined in the
enclosing scope).
The type inference for the scope region is split into two parts:
* `infer_generator_expression` (similarly for comprehensions) infers the
type of the `iter` expression of the leftmost outer generator
* `infer_generator_expression_scope` (similarly for comprehension)
infers the type of the remaining expressions except for the one
mentioned in the previous point
The type inference for the **definition** also needs to account for this
special case of leftmost generator. This is done by defining a `first`
boolean parameter which indicates whether this comprehension definition
occurs first in the enclosing expression.
## Test Plan
New test cases were added to validate multiple scenarios. Refer to the
documentation for each test case which explains what is being tested.
Make `cargo doc -p red_knot_python_semantic --document-private-items`
run warning-free. I'd still like to do this for all of ruff and start
enforcing it in CI (https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12372) but
haven't gotten to it yet. But in the meantime I'm trying to maintain it
for at least `red_knot_python_semantic`, as it helps to ensure our doc
comments stay up to date.
A few of the comments I just removed or shortened, as their continued
relevance wasn't clear to me; please object in review if you think some
of them are important to keep!
Also remove a no-longer-needed `allow` attribute.
For type narrowing, we'll need intersections (since applying type
narrowing is just a type intersection.)
Add `IntersectionBuilder`, along with some tests for it and
`UnionBuilder` (renamed from `UnionTypeBuilder`).
We use smart builders to ensure that we always keep these types in
disjunctive normal form (DNF). That means that we never have deeply
nested trees of unions and intersections: unions flatten into unions,
intersections flatten into intersections, and intersections distribute
over unions, so the most complex tree we can ever have is a union of
intersections. We also never have a single-element union or a
single-positive-element intersection; these both just simplify to the
contained type.
Maintaining these invariants means that `UnionBuilder` doesn't
necessarily end up building a `Type::Union` (e.g. if you only add a
single type to the union, it'll just return that type instead), and
`IntersectionBuilder` doesn't necessarily build a `Type::Intersection`
(if you add a union to the intersection, we distribute the intersection
over that union, and `IntersectionBuilder` will end up returning a
`Type::Union` of intersections).
We also simplify intersections by ensuring that if a type and its
negation are both in an intersection, they simplify out. (In future this
should also respect subtyping, not just type identity, but we don't have
subtyping yet.) We do implement subtyping of `Never` as a special case
for now.
Most of this PR is unused for now until type narrowing lands; I'm just
breaking it out to reduce the review fatigue of a single massive PR.
## Summary
I'm not sure if this is useful but this is a hacky implementation to add
the filename and row / column numbers to the current Red Knot
diagnostics.
## Summary
Related to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/issues/571, this PR
updates the settings index builder to trace all the errors it
encountered. Without this, there's no way for user to know that
something failed and some of the capability might not work as expected.
For example, in the linked PR, the settings were invalid which means
notebooks weren't included and there were no log messages for it.
## Test Plan
Create an invalid `ruff.toml` file:
```toml
[tool.ruff]
extend-exclude = ["*.ipynb"]
```
Logs:
```
2024-08-12 18:33:09.873 [info] [Trace - 6:33:09 PM] 12.217043000s ERROR ruff:main ruff_server::session::index::ruff_settings: Failed to parse /Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/pyproject.toml
```
Notification Preview:
<img width="483" alt="Screenshot 2024-08-12 at 18 33 20"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/a4f303e5-f073-454f-bdcd-ba6af511e232">
Another way to trigger is to provide an invalid `cache-dir` value:
```toml
[tool.ruff]
cache-dir = "$UNKNOWN"
```
Same notification preview but different log message:
```
2024-08-12 18:41:37.571 [info] [Trace - 6:41:37 PM] 21.700112208s ERROR ThreadId(30) ruff_server::session::index::ruff_settings: Error while resolving settings from /Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/pyproject.toml: Invalid `cache-dir` value: error looking key 'UNKNOWN' up: environment variable not found
```
With multiple `pyproject.toml` file:
```
2024-08-12 18:41:15.887 [info] [Trace - 6:41:15 PM] 0.016636833s ERROR ThreadId(04) ruff_server::session::index::ruff_settings: Error while resolving settings from /Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/pyproject.toml: Invalid `cache-dir` value: error looking key 'UNKNOWN' up: environment variable not found
2024-08-12 18:41:15.888 [info] [Trace - 6:41:15 PM] 0.017378833s ERROR ThreadId(13) ruff_server::session::index::ruff_settings: Failed to parse /Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/tools/pyproject.toml
```
In most cases we should suggest a ternary operator, but there are three
edge cases where a binary operator is more appropriate.
Given an if-else block of the form
```python
if test:
target_var = body_value
else:
target_var = else_value
```
This PR updates the check for SIM108 to the following:
- If `test == body_value` and preview enabled, suggest to replace with
`target_var = test or else_value`
- If `test == not body_value` and preview enabled, suggest to replace
with `target_var = body_value and else_value`
- If `not test == body_value` and preview enabled, suggest to replace
with `target_var = body_value and else_value`
- Otherwise, suggest to replace with `target_var = body_value if test
else else_value`
Closes#12189.
## Summary
Adding parentheses to a tuple in a subscript with elements that include
slice expressions causes a syntax error. For example, `d[(1,2,:)]` is a
syntax error.
So, when `lint.ruff.parenthesize-tuple-in-subscript = true` and the
tuple includes a slice expression, we skip this check and fix.
Closes#12766.
> ~Builtins are also more efficient than `for` loops.~
Let's not promise performance because this code transformation does not
deliver.
Benchmark written by @dcbaker
> `any()` seems to be about 1/3 as fast (Python 3.11.9, NixOS):
```python
loop = 'abcdef'.split()
found = 'f'
nfound = 'g'
def test1():
for x in loop:
if x == found:
return True
return False
def test2():
return any(x == found for x in loop)
def test3():
for x in loop:
if x == nfound:
return True
return False
def test4():
return any(x == nfound for x in loop)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import timeit
print('for loop (found) :', timeit.timeit(test1))
print('for loop (not found):', timeit.timeit(test3))
print('any() (found) :', timeit.timeit(test2))
print('any() (not found) :', timeit.timeit(test4))
```
```
for loop (found) : 0.051076093994197436
for loop (not found): 0.04388196699437685
any() (found) : 0.15422860698890872
any() (not found) : 0.15568504799739458
```
I have retested with longer lists and on multiple Python versions with
similar results.
Implements the new fixable lint rule `RUF031` which checks for the use or omission of parentheses around tuples in subscripts, depending on the setting `lint.ruff.parenthesize-tuple-in-getitem`. By default, the use of parentheses is considered a violation.
## Summary
Follow-up from https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/12725, this is
just a small refactor to use a wrapper struct instead of type alias for
workspace settings index. This avoids the need to have the
`register_workspace_settings` as a static method on `Index` and instead
is a method on the new struct itself.
## Summary
This PR updates the server to ignore non-file workspace URL.
This is to avoid crashing the server if the URL scheme is not "file".
We'd still raise an error if the URL to file path conversion fails.
Also, as per the docs of
[`to_file_path`](https://docs.rs/url/2.5.2/url/struct.Url.html#method.to_file_path):
> Note: This does not actually check the URL’s scheme, and may give
nonsensical results for other schemes. It is the user’s responsibility
to check the URL’s scheme before calling this.
resolves: #12660
## Test Plan
I'm not sure how to test this locally but the change is small enough to
validate on its own.
## Summary
This PR updates the `red_knot` CLI to make the subcommand optional.
## Test Plan
Run the following commands:
* `cargo run --bin red_knot --
--current-directory=~/playground/ruff/type_inference` (no subcommand
requirement)
* `cargo run --bin red_knot -- server` (should start the server)
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Resolves#12636
Consider docstrings which begin with the word "Returns" as having
satisfactorily documented they're returns. For example
```python
def f():
"""Returns 1."""
return 1
```
is valid.
## Test Plan
Added example to test fixture.
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
Removes set comprehension as a violation for `sum` when checking `C419`,
because set comprehension may de-duplicate entries in a generator,
thereby modifying the value of the sum.
Closes#12690.
## Summary
Make it a violation of `C409` to call `tuple` with a list or set
comprehension, and
implement the (unsafe) fix of calling the `tuple` with the underlying
generator instead.
Closes#12648.
## Test Plan
Test fixture updated, cargo test, docs checked for updated description.
## Summary
Adds autofix for `RUF007`
## Test Plan
`cargo test`, however I get errors for `test resolver::tests::symlink
... FAILED` which seems to not be my fault
## Summary
Fixes#12630.
DOC501 and DOC502 now understand functions with constructs like this to
be explicitly raising `TypeError` (which should be documented in a
function's docstring):
```py
try:
foo():
except TypeError:
...
raise
```
I made an exception for `Exception` and `BaseException`, however.
Constructs like this are reasonably common, and I don't think anybody
would say that it's worth putting in the docstring that it raises "some
kind of generic exception":
```py
try:
foo()
except BaseException:
do_some_logging()
raise
```
## Test Plan
`cargo test -p ruff_linter --lib`
## Summary
Please see
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/12605#discussion_r1699957443 for
a description of the issue.
They way I fixed it is to get the *last* timeout item in the `with`, and
if it's an `async with` and there are items after it, then don't trigger
the lint.
## Test Plan
Updated the fixture with some more cases.
Changes the red-knot benchmark to run on the stdlib "tomllib" library
(which is self-contained, four files, uses type annotations) instead of
on very small bits of handwritten code.
Also remove the `without_parse` benchmark: now that we are running on
real code that uses typeshed, we'd either have to pre-parse all of
typeshed (slow) or find some way to determine which typeshed modules
will be used by the benchmark (not feasible with reasonable complexity.)
## Test Plan
`cargo bench -p ruff_benchmark --bench red_knot`
## Summary
This PR separates the current `red_knot` crate into two crates:
1. `red_knot` - This will be similar to the `ruff` crate, it'll act as
the CLI crate
2. `red_knot_workspace` - This includes everything except for the CLI
functionality from the existing `red_knot` crate
Note that the code related to the file watcher is in
`red_knot_workspace` for now but might be required to extract it out in
the future.
The main motivation for this change is so that we can have a `red_knot
server` command. This makes it easier to test the server out without
making any changes in the VS Code extension. All we need is to specify
the `red_knot` executable path in `ruff.path` extension setting.
## Test Plan
- `cargo build`
- `cargo clippy --workspace --all-targets --all-features`
- `cargo shear --fix`
## Summary
There's still a problem here. Given:
```python
class Class():
pass
# comment
# another comment
a = 1
```
We only add one newline before `a = 1` on the first pass, because
`max_precedling_blank_lines` is 1... We then add the second newline on
the second pass, so it ends up in the right state, but the logic is
clearly wonky.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11508.
I hit this `todo!` trying to run type inference over some real modules.
Since it's a one-liner to implement it, I just did that rather than
changing to `Type::Unknown`.
## Summary
@zanieb noticed while we were discussing #12595 that this flag is now
unnecessary, so remove it and the flags which reference it.
## Test Plan
Question for maintainers: is there a test to add *or* remove here? (I’ve
opened this as a draft PR with that in view!)
## Summary
This pull request adds support for logging via `$/logTrace` RPC
messages. It also enables that code path for when a client is Zed editor
or VS Code (as there's no way for us to generically tell whether a client prefers
`$/logTrace` over stderr.
Related to: #12523
## Test Plan
I've built Ruff from this branch and tested it manually with Zed.
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
Extend `flake8-builtins` to imports, lambda-arguments, and modules to be
consistent with original checker
[flake8_builtins](https://github.com/gforcada/flake8-builtins/blob/main/flake8_builtins.py).
closes#12540
## Details
- Implement builtin-import-shadowing (A004)
- Stop tracking imports shadowing in builtin-variable-shadowing (A001)
in preview mode.
- Implement builtin-lambda-argument-shadowing (A005)
- Implement builtin-module-shadowing (A006)
- Add new option `linter.flake8_builtins.builtins_allowed_modules`
## Test Plan
cargo test
## Summary
If an import is marked as "required", we should never flag it as unused.
In practice, this is rare, since required imports are typically used for
`__future__` annotations, which are always considered "used".
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12458.
Now that we have builtins available, resolve some simple cases to the
right builtin type.
We should also adjust the display for types to include their module
name; that's not done yet here.
## Summary
This PR adds support for untitled files in the Red Knot project.
Refer to the [design
discussion](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/discussions/12336) for
more details.
### Changes
* The `parsed_module` always assumes that the `SystemVirtual` path is of
`PySourceType::Python`.
* For the module resolver, as suggested, I went ahead by adding a new
`SystemOrVendoredPath` enum and renamed `FilePathRef` to
`SystemOrVendoredPathRef` (happy to consider better names here).
* The `file_to_module` query would return if it's a
`FilePath::SystemVirtual` variant because a virtual file doesn't belong
to any module.
* The sync implementation for the system virtual path is basically the
same as that of system path except that it uses the
`virtual_path_metadata`. The reason for this is that the system
(language server) would provide the metadata on whether it still exists
or not and if it exists, the corresponding metadata.
For point (1), VS Code would use `Untitled-1` for Python files and
`Untitled-1.ipynb` for Jupyter Notebooks. We could use this distinction
to determine whether the source type is `Python` or `Ipynb`.
## Test Plan
Added test cases in #12526
Extend red-knot type inference to cover all syntax, so that inferring
types for a scope gives all expressions a type. This means we can run
the red-knot semantic lint on all Python code without panics. It also
means we can infer types for `builtins.pyi` without panics.
To keep things simple, this PR intentionally doesn't add any new type
inference capabilities: the expanded coverage is all achieved with
`Type::Unknown`. But this puts the skeleton in place for adding better
inference of all these language features.
I also had to add basic Salsa cycle recovery (with just `Type::Unknown`
for now), because some `builtins.pyi` definitions are cyclic.
To test this, I added a comprehensive corpus of test snippets sourced
from Cinder under [MIT
license](https://github.com/facebookincubator/cinder/blob/cinder/3.10/cinderx/LICENSE),
which matches Ruff's license. I also added to this corpus some
additional snippets for newer language features: all the
`27_func_generic_*` and `73_class_generic_*` files, as well as
`20_lambda_default_arg.py`, and added a test which runs semantic-lint
over all these files. (The test doesn't assert the test-corpus files are
lint-free; just that they are able to lint without a panic.)
## Summary
Right now, in the isort comment model, there's nowhere for trailing
comments on the _statement_ to go, as in:
```python
from mylib import (
MyClient,
MyMgmtClient,
) # some comment
```
If the comment is on the _alias_, we do preserve it, because we attach
it to the alias, as in:
```python
from mylib import (
MyClient,
MyMgmtClient, # some comment
)
```
Similarly, if the comment is trailing on an import statement
(non-`from`), we again attach it to the alias, because it can't be
parenthesized, as in:
```python
import foo # some comment
```
This PR adds logic to track and preserve those trailing comments.
We also no longer drop several other comments, like:
```python
from mylib import (
# some comment
MyClient
)
```
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12487.
## Summary
When working on improving Ruff integration with Zed I noticed that it
errors out when we try to resolve a code action of a `QUICKFIX` kind;
apparently, per @dhruvmanila we shouldn't need to resolve it, as the
edit is provided in the initial response for the code action. However,
it's possible for the `resolve` call to fill out other fields (such as
`command`).
AFAICT Helix also tries to resolve the code actions unconditionally (as
in, when either `edit` or `command` is absent); so does VSC. They can
still apply the quickfixes though, as they do not error out on a failed
call to resolve code actions - Zed does. Following suit on Zed's side
does not cut it though, as we still get a log request from Ruff for that
failure (which is surfaced in the UI).
There are also other language servers (such as
[rust-analyzer](c1c9e10f72/crates/rust-analyzer/src/handlers/request.rs (L1257)))
that fill out both `command` and `edit` fields as a part of code action
resolution.
This PR makes the resolve calls for quickfix actions return the input
value.
## Test Plan
N/A
Add support for while-loop control flow.
This doesn't yet include general support for terminals and reachability;
that is wider than just while loops and belongs in its own PR.
This also doesn't yet add support for cyclic definitions in loops; that
comes with enough of its own complexity in Salsa that I want to handle
it separately.
Add a lint rule to detect if a name is definitely or possibly undefined
at a given usage.
If I create the file `undef/main.py` with contents:
```python
x = int
def foo():
z
return x
if flag:
y = x
y
```
And then run `cargo run --bin red_knot -- --current-directory
../ruff-examples/undef`, I get the output:
```
Name 'z' used when not defined.
Name 'flag' used when not defined.
Name 'y' used when possibly not defined.
```
If I modify the file to add `y = 0` at the top, red-knot re-checks it
and I get the new output:
```
Name 'z' used when not defined.
Name 'flag' used when not defined.
```
Note that `int` is not flagged, since it's a builtin, and `return x` in
the function scope is not flagged, since it refers to the global `x`.
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug to raise a syntax error when an unparenthesized
generator expression is used as an argument to a call when there are
more than one argument.
For reference, the grammar is:
```
primary:
| ...
| primary genexp
| primary '(' [arguments] ')'
| ...
genexp:
| '(' ( assignment_expression | expression !':=') for_if_clauses ')'
```
The `genexp` requires the parenthesis as mentioned in the grammar. So,
the grammar for a call expression is either a name followed by a
generator expression or a name followed by a list of argument. In the
former case, the parenthesis are excluded because the generator
expression provides them while in the later case, the parenthesis are
explicitly provided for a list of arguments which means that the
generator expression requires it's own parenthesis.
This was discovered in https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12420.
## Test Plan
Add test cases for valid and invalid syntax.
Make sure that the parser from CPython also raises this at the parsing
step:
```console
$ python3.13 -m ast parser/_.py
File "parser/_.py", line 1
total(1, 2, x for x in range(5), 6)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
SyntaxError: Generator expression must be parenthesized
$ python3.13 -m ast parser/_.py
File "parser/_.py", line 1
sum(x for x in range(10), 10)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
SyntaxError: Generator expression must be parenthesized
```
## Summary
Fix panic reported in #12428. Where a string would sometimes get split
within a character boundary. This bypasses the need to split the string.
This does not guarantee the correct formatting of the docstring, but
neither did the previous implementation.
Resolves#12428
## Test Plan
Test case added to fixture
## Summary
These are the first rules implemented as part of #458, but I plan to
implement more.
Specifically, this implements `docstring-missing-exception` which checks
for raised exceptions not documented in the docstring, and
`docstring-extraneous-exception` which checks for exceptions in the
docstring not present in the body.
## Test Plan
Test fixtures added for both google and numpy style.
When poring over traces, the ones that just include a definition or
symbol or expression ID aren't very useful, because you don't know which
file it comes from. This adds that information to the trace.
I guess the downside here is that if calling `.file(db)` on a
scope/definition/expression would execute other traced code, it would be
marked as outside the span? I don't think that's a concern, because I
don't think a simple field access on a tracked struct should ever
execute our code. If I'm wrong and this is a problem, it seems like the
tracing crate has this feature where you can record a field as
`tracing::field::Empty` and then fill in its value later with
`span.record(...)`, but when I tried this it wasn't working for me, not
sure why.
I think there's a lot more we can do to make our tracing output more
useful for debugging (e.g. record an event whenever a
definition/symbol/expression/use id is created with the details of that
definition/symbol/expression/use), this is just dipping my toes in the
water.
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
This PR updates D301 rule to allow inclduing escaped docstring, e.g.
`\"""Foo.\"""` or `\"\"\"Bar.\"\"\"`, within a docstring.
Related issue: #12152
## Test Plan
Add more test cases to D301.py and update the snapshot file.
<!-- How was it tested? -->
In preparation for supporting resolving builtins, simplify the benchmark
so it doesn't look up `str`, which is actually a complex builtin to deal
with because it inherits `Sequence[str]`.
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <alex.waygood@gmail.com>
Per comments in https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/12269, "module
global" is kind of long, and arguably redundant.
I tried just using "module" but there were too many cases where I felt
this was ambiguous. I like the way "global" works out better, though it
does require an understanding that in Python "global" generally means
"module global" not "globally global" (though in a sense module globals
are also globally global since modules are singletons).
Support falling back to a global name lookup if a name isn't defined in
the local scope, in the cases where that is correct according to Python
semantics.
In class scopes, a name lookup checks the local namespace first, and if
the name isn't found there, looks it up in globals.
In function scopes (and type parameter scopes, which are function-like),
if a name has any definitions in the local scope, it is a local, and
accessing it when none of those definitions have executed yet just
results in an `UnboundLocalError`, it does not fall back to a global. If
the name does not have any definitions in the local scope, then it is an
implicit global.
Public symbol type lookups never include such a fall back. For example,
if a name is not defined in a class scope, it is not available as a
member on that class, even if a name lookup within the class scope would
have fallen back to a global lookup.
This PR makes the `@override` lint rule work again.
Not yet included/supported in this PR:
* Support for free variables / closures: a free symbol in a nested
function-like scope referring to a symbol in an outer function-like
scope.
* Support for `global` and `nonlocal` statements, which force a symbol
to be treated as global or nonlocal even if it has definitions in the
local scope.
* Module-global lookups should fall back to builtins if the name isn't
found in the module scope.
I would like to expose nicer APIs for the various kinds of symbols
(explicit global, implicit global, free, etc), but this will also wait
for a later PR, when more kinds of symbols are supported.
Adds inference tests sufficient to give full test coverage of the
`UseDefMapBuilder::merge` method.
In the process I realized that we could implement visiting of if
statements in `SemanticBuilder` with fewer `snapshot`, `restore`, and
`merge` operations, so I restructured that visit a bit.
I also found one correctness bug in the `merge` method (it failed to
extend the given snapshot with "unbound" for any missing symbols,
meaning we would just lose the fact that the symbol could be unbound in
the merged-in path), and two efficiency bugs (if one of the ranges to
merge is empty, we can just use the other one, no need for copies, and
if the ranges are overlapping -- which can occur with nested branches --
we can still just merge them with no copies), and fixed all three.
## Summary
This PR allows us to fix both expressions in `foo == "a" or foo == "b"
or ("c" != bar and "d" != bar)`, but limits the rule to consecutive
comparisons, following https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/7797.
I think this logic was _probably_ added because of
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/12368 -- the intent being that
we'd replace the _entire_ expression.
## Summary
This PR adds documentation for the Ruff language server.
It mainly does the following:
1. Combines various READMEs containing instructions for different editor
setup in their respective section on the online docs
2. Provide an enumerated list of server settings. Additionally, it also
provides a section for VS Code specific options.
3. Adds a "Features" section which enumerates all the current
capabilities of the native server
For (2), the settings documentation is done manually but a future
improvement (easier after `ruff-lsp` is deprecated) is to move the docs
in to Rust struct and generate the documentation from the code itself.
And, the VS Code extension specific options can be generated by diffing
against the `package.json` in `ruff-vscode` repository.
### Structure
1. Setup: This section contains the configuration for setting up the
language server for different editors
2. Features: This section contains a list of capabilities provided by
the server along with short GIF to showcase it
3. Settings: This section contains an enumerated list of settings in a
similar format to the one for the linter / formatter
4. Migrating from `ruff-lsp`
> [!NOTE]
>
> The settings page is manually written but could possibly be
auto-generated via a macro similar to `OptionsMetadata` on the
`ClientSettings` struct
resolves: #11217
## Test Plan
Generate and open the documentation locally using:
1. `python scripts/generate_mkdocs.py`
2. `mkdocs serve -f mkdocs.insiders.yml`
## Summary
This PR removes the requirement of `--preview` flag to run the `ruff
server` and instead considers it to be an indicator to turn on preview
mode for the linter and the formatter.
resolves: #12161
## Test Plan
Add test cases to assert the `preview` value is updated accordingly.
In an editor context, I used the local `ruff` executable in Neovim with
the `--preview` flag and verified that the preview-only violations are
being highlighted.
Running with:
```lua
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup({
cmd = {
'/Users/dhruv/work/astral/ruff/target/debug/ruff',
'server',
'--preview',
},
})
```
The screenshot shows that `E502` is highlighted with the below config in
`pyproject.toml`:
<img width="877" alt="Screenshot 2024-07-17 at 16 43 09"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/c7016ef3-55b1-4a14-bbd3-a07b1bcdd323">
## Summary
This PR updates the settings index building logic in the language server
to consider the fallback settings for applying ignore filters in
`WalkBuilder` and the exclusion via `exclude` / `extend-exclude`.
This flow matches the one in the `ruff` CLI where the root settings is
built by (1) finding the workspace setting in the ancestor directory (2)
finding the user configuration if that's missing and (3) fallback to
using the default configuration.
Previously, the index building logic was being executed before (2) and
(3). This PR reverses the logic so that the exclusion /
`respect_gitignore` is being considered from the default settings if
there's no workspace / user settings. This has the benefit that the
server no longer enters the `.git` directory or any other excluded
directory when a user opens a file in the home directory.
Related to #11366
## Test plan
Opened a test file from the home directory and confirmed with the debug
trace (removed in #12360) that the server excludes the `.git` directory
when indexing.
## Summary
Add new rule and implement for `unnecessary default type arguments`
under the `UP` category (`UP043`).
```py
// < py313
Generator[int, None, None]
// >= py313
Generator[int]
```
I think that as Python 3.13 develops, there might be more default type
arguments added besides `Generator` and `AsyncGenerator`. So, I made
this more flexible to accommodate future changes.
related issue: #12286
## Test Plan
snapshot included..!
## Summary
Pretty sure this should still be an error, but also, I think I added
this because of ecosystem CI? So want to see what pops up.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12164.
## Summary
This is the _intended_ default that PEP 597 _wants_, but it's not
backwards compatible. The fix is already unsafe, so it's better for us
to recommend the desired and expected behavior.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12069.
Improve semantic index tests with better assertions than just `.len()`,
and re-add use-definition test that was commented out in the switch to
Salsa initially.
Implements definition-level type inference, with basic control flow
(only if statements and if expressions so far) in Salsa.
There are a couple key ideas here:
1) We can do type inference queries at any of three region
granularities: an entire scope, a single definition, or a single
expression. These are represented by the `InferenceRegion` enum, and the
entry points are the salsa queries `infer_scope_types`,
`infer_definition_types`, and `infer_expression_types`. Generally
per-scope will be used for scopes that we are directly checking and
per-definition will be used anytime we are looking up symbol types from
another module/scope. Per-expression should be uncommon: used only for
the RHS of an unpacking or multi-target assignment (to avoid
re-inferring the RHS once per symbol defined in the assignment) and for
test nodes in type narrowing (e.g. the `test` of an `If` node). All
three queries return a `TypeInference` with a map of types for all
definitions and expressions within their region. If you do e.g.
scope-level inference, when it hits a definition, or an
independently-inferable expression, it should use the relevant query
(which may already be cached) to get all types within the smaller
region. This avoids double-inferring smaller regions, even though larger
regions encompass smaller ones.
2) Instead of building a control-flow graph and lazily traversing it to
find definitions which reach a use of a name (which is O(n^2) in the
worst case), instead semantic indexing builds a use-def map, where every
use of a name knows which definitions can reach that use. We also no
longer track all definitions of a symbol in the symbol itself; instead
the use-def map also records which defs remain visible at the end of the
scope, and considers these the publicly-visible definitions of the
symbol (see below).
Major items left as TODOs in this PR, to be done in follow-up PRs:
1) Free/global references aren't supported yet (only lookup based on
definitions in current scope), which means the override-check example
doesn't currently work. This is the first thing I'll fix as follow-up to
this PR.
2) Control flow outside of if statements and expressions.
3) Type narrowing.
There are also some smaller relevant changes here:
1) Eliminate `Option` in the return type of member lookups; instead
always return `Type::Unbound` for a name we can't find. Also use
`Type::Unbound` for modules we can't resolve (not 100% sure about this
one yet.)
2) Eliminate the use of the terms "public" and "root" to refer to
module-global scope or symbols. Instead consistently use the term
"module-global". It's longer, but it's the clearest, and the most
consistent with typical Python terminology. In particular I don't like
"public" for this use because it has other implications around author
intent (is an underscore-prefixed module-global symbol "public"?). And
"root" is just not commonly used for this in Python.
3) Eliminate the `PublicSymbol` Salsa ingredient. Many non-module-global
symbols can also be seen from other scopes (e.g. by a free var in a
nested scope, or by class attribute access), and thus need to have a
"public type" (that is, the type not as seen from a particular use in
the control flow of the same scope, but the type as seen from some other
scope.) So all symbols need to have a "public type" (here I want to keep
the use of the term "public", unless someone has a better term to
suggest -- since it's "public type of a symbol" and not "public symbol"
the confusion with e.g. initial underscores is less of an issue.) At
least initially, I would like to try not having special handling for
module-global symbols vs other symbols.
4) Switch to using "definitions that reach end of scope" rather than
"all definitions" in determining the public type of a symbol. I'm
convinced that in general this is the right way to go. We may want to
refine this further in future for some free-variable cases, but it can
be changed purely by making changes to the building of the use-def map
(the `public_definitions` index in it), without affecting any other
code. One consequence of combining this with no control-flow support
(just last-definition-wins) is that some inference tests now give more
wrong-looking results; I left TODO comments on these tests to fix them
when control flow is added.
And some potential areas for consideration in the future:
1) Should `symbol_ty` be a Salsa query? This would require making all
symbols a Salsa ingredient, and tracking even more dependencies. But it
would save some repeated reconstruction of unions, for symbols with
multiple public definitions. For now I'm not making it a query, but open
to changing this in future with actual perf evidence that it's better.
## Summary
I believe these should always bind more tightly -- e.g., in:
```python
for _ in bar(baz for foo in [1]):
pass
```
The inner `baz` and `foo` should be considered comprehension variables,
not for loop bindings.
We need to revisit this more holistically. In some of these cases,
`BindingKind` should probably be a flag, not an enum, since the values
aren't mutually exclusive. Separately, we should probably be more
precise in how we set it (e.g., by passing down from the parent rather
than sniffing in `handle_node_store`).
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12339
When there is a function or class definition at the end of a suite
followed by the beginning of an alternative block, we have to insert a
single empty line between them.
In the if-else-statement example below, we insert an empty line after
the `foo` in the if-block, but none after the else-block `foo`, since in
the latter case the enclosing suite already adds empty lines.
```python
if sys.version_info >= (3, 10):
def foo():
return "new"
else:
def foo():
return "old"
class Bar:
pass
```
To do so, we track whether the current suite is the last one in the
current statement with a new option on the suite kind.
Fixes#12199
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
## Summary
This PR updates the server to build the settings index in parallel using
similar logic as `python_files_in_path`.
This should help with https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11366 but
ideally we would want to build it lazily.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
I don't know that there's more to do here. We could consider not raising
the violation at all for arguments, but that would have some false
negatives and could also be surprising to users.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12267.
## Summary
Ensures that, e.g., the following is not considered a
redefinition-without-use:
```python
import contextlib
foo = None
with contextlib.suppress(ImportError):
from some_module import foo
```
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12309.
## Summary
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12291.
## Test Plan
```shell
❯ cargo run check ../uv/foo --select INP
/Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/foo/bar/baz.py:1:1: INP001 File `/Users/crmarsh/workspace/uv/foo/bar/baz.py` is part of an implicit namespace package. Add an `__init__.py`.
Found 1 error.
```
## Summary
I don't fully understand the purpose of this. In #7905, it was just
copied over from the previous non-preview implementation. But it means
that (e.g.) we don't treat `type(self.foo)` as a type -- which is wrong.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12290.
## Summary
Update the name of `ASYNC109` to match
[upstream](https://flake8-async.readthedocs.io/en/latest/rules.html).
Also update to the functionality to match upstream by supporting
additional context managers from `asyncio` and `anyio`. This doesn't
change any of the detection functionality, but recommends additional
context managers from `asyncio` and `anyio` depending on context.
Part of https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12039.
## Test Plan
Added fixture for asyncio recommendation
## Summary
S113 exists because `requests` doesn't have a default timeout, so
request without timeout may hang indefinitely
> B113: Test for missing requests timeout
This plugin test checks for requests or httpx calls without a timeout
specified.
>
> Nearly all production code should use this parameter in nearly all
requests, **Failure to do so can cause your program to hang
indefinitely.**
But httpx has default timeout 5s, so S113 for httpx request without
`timeout` argument is a false positive, only valid case would be
`timeout=None`.
https://www.python-httpx.org/advanced/timeouts/
> HTTPX is careful to enforce timeouts everywhere by default.
>
> The default behavior is to raise a TimeoutException after 5 seconds of
network inactivity.
## Test Plan
snap updated
Intern types using Salsa interning instead of in the `TypeInference`
result.
This eliminates the need for `TypingContext`, and also paves the way for
finer-grained type inference queries.
## Summary
This PR fixes the bug where the server was not considering the
`cells.structure.didOpen` field to sync up the new content of the newly
added cells.
The parameters corresponding to this request provides two fields to get
the newly added cells:
1. `cells.structure.array.cells`: This is a list of `NotebookCell` which
doesn't contain any cell content. The only useful information from this
array is the cell kind and the cell document URI which we use to
initialize the new cell in the index.
2. `cells.structure.didOpen`: This is a list of `TextDocumentItem` which
corresponds to the newly added cells. This actually contains the text
content and the version.
This wasn't a problem before because we initialize the cell with an
empty string and this isn't a problem when someone just creates an empty
cell. But, when someone copy-pastes a cell, the cell needs to be
initialized with the content.
fixes: #12201
## Test Plan
First, let's see the panic in action:
1. Press <kbd>Esc</kbd> to allow using the keyboard to perform cell
actions (move around, copy, paste, etc.)
2. Copy the second cell with <kbd>c</kbd> key
3. Delete the second cell with <kbd>dd</kbd> key
4. Paste the copied cell with <kbd>p</kbd> key
You can see that the content isn't synced up because the `unused-import`
for `sys` is still being highlighted but it's being used in the second
cell. And, the hover isn't working either. Then, as I start editing the
second cell, it panics.
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/67177269/fc58364c-c8fc-4c11-a917-71b6dd90c1ef
Now, here's the preview of the fixed version:
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/67177269/207872dd-dca6-49ee-8b6e-80435c7ef22e
This reverts commit b28dc9ac14.
We're not ready to stabilize the server yet. There's some pending work
for the VS Code extension and documentation improvements.
This change is to unblock Ruff release.
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
This is the implementation for the new rule of `pycodestyle (E204)`. It
follows the guidlines described in the contributing site, and as such it
has a new file named `whitespace_after_decorator.rs`, a new test file
called `E204.py`, and as such invokes the `function` in the `AST
statement checker` for functions and functions in classes. Linking #2402
because it has all the pycodestyle rules.
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
The file E204.py, has a `decorator` defined called wrapper, and this
decorator is used for 2 cases. The first one is when a `function` which
has a `decorator` is called in the file, and the second one is when
there is a `class` and 2 `methods` are defined for the `class` with a
`decorator` attached it.
Test file:
``` python
def foo(fun):
def wrapper():
print('before')
fun()
print('after')
return wrapper
# No error
@foo
def bar():
print('bar')
# E204
@ foo
def baz():
print('baz')
class Test:
# No error
@foo
def bar(self):
print('bar')
# E204
@ foo
def baz(self):
print('baz')
```
I am still new to rust and any suggestion is appreciated. Specially with
the way im using native ruff utilities.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
Fixes a few typos and consistency issues in the "Settings"
documentation:
- use "Ruff" consistently in the few places where "ruff" is used
- use double quotes in the few places where single quotes are used
- add backticks around rule codes where they are currently missing
- update a few example values where they are the same as the defaults,
for consistency
2nd commit might be controversial, as there are many options mentioned
where we don't currently link to the documentation sections, so maybe
it's done on purpose, as this will also appear in the JSON schema where
it's not desirable? If that's the case, I can easily drop it.
## Test Plan
Local testing.
## Summary
This PR fixes various bugs for computing the replacement range between
the original and modified source for the language server.
1. When finding the end offset of the source and modified range, we
should apply `zip` on the reversed iterator. The bug was that it was
reversing the already zipped iterator. The problem here is that the
length of both slices aren't going to be the same unless the source
wasn't modified at all. Refer to the [Rust
playground](https://play.rust-lang.org/?version=stable&mode=debug&edition=2021&gist=44f860d31bd26456f3586b6ab530c22f)
where you can see this in action.
2. Skip the first line when computing the start offset because the first
line start value will always be 0 and the default value of the source /
modified range start is also 0. So, comparing 0 and 0 is not useful
which means we can skip the first value.
3. While iterating in the reverse direction, we should only stop if the
line start is strictly less than the source start i.e., we should use
`<` instead of `<=`.
fixes: #12128
## Test Plan
Add test cases where the text is being inserted, deleted, and replaced
between the original and new source code, validate the replacement
ranges.
## Summary
Bandit now also reports `B113` on `httpx`
(https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit/pull/1060). This PR implements the same
logic, to detect missing or `None` timeouts for `httpx` alongside
`requests`.
## Test Plan
Snapshot tests.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12158
Hashing `Path` does not take into account path separators so `foo/bar`
is the same as `foobar` which is no good for our case. I'm guessing this
is an upstream bug, perhaps introduced by
45082b077b?
I'm investigating that further.
## Summary
This PR updates the linter, specifically the token-based rules, to work
on the tokens that come after a syntax error.
For context, the token-based rules only diagnose the tokens up to the
first lexical error. This PR builds up an error resilience by
introducing a `TokenIterWithContext` which updates the `nesting` level
and tries to reflect it with what the lexer is seeing. This isn't 100%
accurate because if the parser recovered from an unclosed parenthesis in
the middle of the line, the context won't reduce the nesting level until
it sees the newline token at the end of the line.
resolves: #11915
## Test Plan
* Add test cases for a bunch of rules that are affected by this change.
* Run the fuzzer for a long time, making sure to fix any other bugs.
## Summary
This PR updates Ruff to **not** generate auto-fixes if the source code
contains syntax errors as determined by the parser.
The main motivation behind this is to avoid infinite autofix loop when
the token-based rules are run over any source with syntax errors in
#11950.
Although even after this, it's not certain that there won't be an
infinite autofix loop because the logic might be incorrect. For example,
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12094 and
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/12136.
This requires updating the test infrastructure to not validate for fix
availability status when the source contained syntax errors. This is
required because otherwise the fuzzer might fail as it uses the test
function to run the linter and validate the source code.
resolves: #11455
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
This PR updates various references in the linter to compute the
line-width for summing the width of each `char` in a `str` instead of
computing the width of the `str` itself.
Refer to #12133 for more details.
fixes: #12130
## Test Plan
Add a file with null (`\0`) character which is zero-width. Run this test
case on `main` to make sure it panics and switch over to this branch to
make sure it doesn't panic now.
## Summary
Use the following to reproduce this:
```console
$ cargo run -- check --select=E275,E203 --preview --no-cache ~/playground/ruff/src/play.py --fix
debug error: Failed to converge after 100 iterations in `/Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/src/play.py` with rule codes E275:---
yield,x
---
/Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/src/play.py:1:1: E275 Missing whitespace after keyword
|
1 | yield,x
| ^^^^^ E275
|
= help: Added missing whitespace after keyword
Found 101 errors (100 fixed, 1 remaining).
[*] 1 fixable with the `--fix` option.
```
## Test Plan
Add a test case and run `cargo insta test`.
## Summary
This patch inverts the defaults for
[pytest-fixture-incorrect-parentheses-style
(PT001)](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/pytest-fixture-incorrect-parentheses-style/)
and [pytest-incorrect-mark-parentheses-style
(PT003)](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/pytest-incorrect-mark-parentheses-style/)
to prefer dropping superfluous parentheses.
Presently, Ruff defaults to adding superfluous parentheses on pytest
mark and fixture decorators for documented purpose of consistency; for
example,
```diff
import pytest
-@pytest.mark.foo
+@pytest.mark.foo()
def test_bar(): ...
```
This behaviour is counter to the official pytest recommendation and
diverges from the flake8-pytest-style plugin as of version 2.0.0 (see
https://github.com/m-burst/flake8-pytest-style/issues/272). Seeing as
either default satisfies the documented benefit of consistency across a
codebase, it makes sense to change the behaviour to be consistent with
pytest and the flake8 plugin as well.
This change is breaking, so is gated behind preview (at least under my
understanding of Ruff versioning). The implementation of this gating
feature is a bit hacky, but seemed to be the least disruptive solution
without performing invasive surgery on the `#[option()]` macro.
Related to #8796.
### Caveat
Whilst updating the documentation, I sought to reference the pytest
recommendation to drop superfluous parentheses, but couldn't find any
official instruction beyond it being a revealed preference within the
pytest documentation code examples (as well as the linked issues from a
core pytest developer). Thus, the wording of the preference is
deliberately timid; it's to cohere with pytest rather than follow an
explicit guidance.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run`
I also ran
```sh
cargo run -p ruff -- check crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/flake8_pytest_style/PT001.py --no-cache --diff --select PT001
```
and compared against it with `--preview` to verify that the default does
change under preview (I also repeated this with `echo
'[tool.ruff]\npreview = true' > pyproject.toml` to verify that it works
with a configuration file).
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
Implement mutable-contextvar-default (B039) which was added to
flake8-bugbear in https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8-bugbear/pull/476.
This rule is similar to [mutable-argument-default
(B006)](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/mutable-argument-default) and
[function-call-in-default-argument
(B008)](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/function-call-in-default-argument),
except that it checks the `default` keyword argument to
`contextvars.ContextVar`.
```
B039.py:19:26: B039 Do not use mutable data structures for ContextVar defaults
|
18 | # Bad
19 | ContextVar("cv", default=[])
| ^^ B039
20 | ContextVar("cv", default={})
21 | ContextVar("cv", default=list())
|
= help: Replace with `None`; initialize with `.set()` after checking for `None`
```
In the upstream flake8-plugin, this rule is written expressly as a
corollary to B008 and shares much of its logic. Likewise, this
implementation reuses the logic of the Ruff implementation of B008,
namely
f765d19402/crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/flake8_bugbear/rules/function_call_in_argument_default.rs (L104-L106)
and
f765d19402/crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/flake8_bugbear/rules/mutable_argument_default.rs (L106)
Thus, this rule deliberately replicates B006's and B008's heuristics.
For example, this rule assumes that all functions are mutable unless
otherwise qualified. If improvements are to be made to B039 heuristics,
they should probably be made to B006 and B008 as well (whilst trying to
match the upstream implementation).
This rule does not have an autofix as it is unknown where the ContextVar
next used (and it might not be within the same file).
Closes#12054
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run`
## Summary
This adds a fix for the `duplicate-bases` rule that removes the
duplicate base from the class definition.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run duplicate_bases`, `cargo insta review`.
## Summary
`ruff server` has reached a point of stabilization, and `--preview` is
no longer required as a flag.
`--preview` is still supported as a flag, since future features may be
need to gated behind it initially.
## Test Plan
A simple way to test this is to run `ruff server` from the command line.
No error about a missing `--preview` argument should be reported.
## Summary
Follow-up to #11902
This PR simplifies the `LinterResult` struct by avoiding the generic and
not store the `ParseError`.
This is possible because the callers already have access to the
`ParseError` via the `Parsed` output. This also means that we can
simplify the return type of `check_path` and avoid the generic `T` on
`LinterResult`.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
Follow-up to #11901
This PR avoids displaying the syntax errors as log message now that the
`E999` diagnostic cannot be disabled.
For context on why this was added, refer to
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/2505. Basically, we would allow
ignoring the syntax error diagnostic because certain syntax feature
weren't supported back then like `match` statement. And, if a user
ignored `E999`, Ruff would give no feedback if the source code contained
any syntax error. So, this log message was a way to indicate to the user
even if `E999` was disabled.
The current state of the parser is such that (a) it matches with the
latest grammar and (b) it's easy to add support for any new syntax.
**Note:** This PR doesn't remove the `DisplayParseError` struct because
it's still being used by the formatter.
## Test Plan
Update existing snapshots from the integration tests.
## Summary
This PR updates the way syntax errors are handled throughout the linter.
The main change is that it's now not considered as a rule which involves
the following changes:
* Update `Message` to be an enum with two variants - one for diagnostic
message and the other for syntax error message
* Provide methods on the new message enum to query information required
by downstream usages
This means that the syntax errors cannot be hidden / disabled via any
disablement methods. These are:
1. Configuration via `select`, `ignore`, `per-file-ignores`, and their
`extend-*` variants
```console
$ cargo run -- check ~/playground/ruff/src/lsp.py --extend-select=E999
--no-preview --no-cache
Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.10s
Running `target/debug/ruff check /Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/src/lsp.py
--extend-select=E999 --no-preview --no-cache`
warning: Rule `E999` is deprecated and will be removed in a future
release. Syntax errors will always be shown regardless of whether this
rule is selected or not.
/Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/src/lsp.py:1:8: F401 [*] `abc` imported but
unused
|
1 | import abc
| ^^^ F401
2 | from pathlib import Path
3 | import os
|
= help: Remove unused import: `abc`
```
3. Command-line flags via `--select`, `--ignore`, `--per-file-ignores`,
and their `--extend-*` variants
```console
$ cargo run -- check ~/playground/ruff/src/lsp.py --no-cache
--config=~/playground/ruff/pyproject.toml
Finished `dev` profile [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.11s
Running `target/debug/ruff check /Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/src/lsp.py
--no-cache --config=/Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/pyproject.toml`
warning: Rule `E999` is deprecated and will be removed in a future
release. Syntax errors will always be shown regardless of whether this
rule is selected or not.
/Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/src/lsp.py:1:8: F401 [*] `abc` imported but
unused
|
1 | import abc
| ^^^ F401
2 | from pathlib import Path
3 | import os
|
= help: Remove unused import: `abc`
```
This also means that the **output format** needs to be updated:
1. The `code`, `noqa_row`, `url` fields in the JSON output is optional
(`null` for syntax errors)
2. Other formats are changed accordingly
For each format, a new test case specific to syntax errors have been
added. Please refer to the snapshot output for the exact format for
syntax error message.
The output of the `--statistics` flag will have a blank entry for syntax
errors:
```
315 F821 [ ] undefined-name
119 [ ] syntax-error
103 F811 [ ] redefined-while-unused
```
The **language server** is updated to consider the syntax errors by
convert them into LSP diagnostic format separately.
### Preview
There are no quick fixes provided to disable syntax errors. This will
automatically work for `ruff-lsp` because the `noqa_row` field will be
`null` in that case.
<img width="772" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-26 at 14 57 08"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/67177269/aaac827e-4777-4ac8-8c68-eaf9f2c36774">
Even with `noqa` comment, the syntax error is displayed:
<img width="763" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-26 at 14 59 51"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/67177269/ba1afb68-7eaf-4b44-91af-6d93246475e2">
Rule documentation page:
<img width="1371" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-26 at 16 48 07"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/67177269/524f01df-d91f-4ac0-86cc-40e76b318b24">
## Test Plan
- [x] Disablement methods via config shows a warning
- [x] `select`, `extend-select`
- [ ] ~`ignore`~ _doesn't show any message_
- [ ] ~`per-file-ignores`, `extend-per-file-ignores`~ _doesn't show any
message_
- [x] Disablement methods via command-line flag shows a warning
- [x] `--select`, `--extend-select`
- [ ] ~`--ignore`~ _doesn't show any message_
- [ ] ~`--per-file-ignores`, `--extend-per-file-ignores`~ _doesn't show
any message_
- [x] File with syntax errors should exit with code 1
- [x] Language server
- [x] Should show diagnostics for syntax errors
- [x] Should not recommend a quick fix edit for adding `noqa` comment
- [x] Same for `ruff-lsp`
resolves: #8447
The motivation for this rule is solid; it's been in preview for a long
time; the implementation and tests seem sound; there are no open issues
regarding it, and as far as I can tell there never have been any.
The only issue I see is that the docs don't really describe the rule
accurately right now; I fix that in this PR.
## Summary
This PR migrates our release workflow to
[`cargo-dist`](https://github.com/axodotdev/cargo-dist). The primary
motivation here is that we want to ship dedicated installers for Ruff
that work across platforms, and `cargo-dist` gives us those installers
out-of-the-box. The secondary motivation is that `cargo-dist` formalizes
some of the patterns that we've built up over time in our own release
process.
At a high level:
- The `release.yml` file is generated by `cargo-dist` with `cargo dist
generate`. It doesn't contain any modifications vis-a-vis the generated
file. (If it's edited out of band from generation, the release fails.)
- Our customizations are inserted as custom steps within the
`cargo-dist` workflow. Specifically, `build-binaries` builds the wheels
and packages them into binaries (as on `main`), while `build-docker.yml`
builds the Docker image. `publish-pypi.yml` publishes the wheels to
PyPI. This is effectively our `release.yaml` (on `main`), broken down
into individual workflows rather than steps within a single workflow.
### Changes from `main`
The workflow is _nearly_ unchanged. We kick off a release manually via
the GitHub Action by providing a tag. If the tag doesn't match the
`Cargo.toml`, the release fails. If the tag matches an already-existing
release, the release fails.
The release proceeds by (in order):
0. Doing some upfront validation via `cargo-dist`.
1. Creating the wheels and archives.
2. Building and pushing the Docker image.
3. Publishing to PyPI (if it's not a "dry run").
4. Creating the GitHub Release (if it's not a "dry run").
5. Notifying `ruff-pre-commit` (if it's not a "dry run").
There are a few changes in the workflow as compared to `main`:
- **We no longer validate the SHA** (just the tag). It's not an input to
the job. The Axo team is considering whether / how to support this.
- **Releases are now published directly** (rather than as draft). Again,
the Axo team is considering whether / how to support this. The downside
of drafts is that the URLs aren't stable, so the installers don't work
_as long as the release is in draft_. This is fine for our workflow. It
seems like the Axo team will add it.
- Releases already contain the latest entry from the changelog (we don't
need to copy it over). This "Just Works", which is nice, though we'll
still want to edit them to add contributors.
There are also a few **breaking changes** for consumers of the binaries:
- **We no longer include the version tag in the file name**. This
enables users to install via `/latest` URLs on GitHub, and is part of
the cargo-dist paradigm.
- **Archives now include an extra level of nesting,** which you can
remove with `--strip-components=1` when untarring.
Here's an example release that I created -- I omitted all the artifacts
since I was just testing a workflow, so none of the installers or links
work, but it gives you a sense for what the release looks like:
https://github.com/charliermarsh/cargodisttest/releases/tag/0.1.13.
### Test Plan
I ran a successful release to completion last night, and installed Ruff
via the installer:


The piece I'm least confident about is the Docker push. We build the
image, but the push fails in my test repo since I haven't wired up the
credentials.
## Summary
This rule removes `PLR1701` and redirects it to `SIM101`.
In addition to that, the `SIM101` autofix has been fixed to add padding
if required.
### `PLR1701` has bugs
It also seems that the implementation of `PLR1701` is incorrect in
multiple scenarios. For example, the following code snippet:
```py
# There are two _different_ variables `a` and `b`
if isinstance(a, int) or isinstance(b, bool) or isinstance(a, float):
pass
# There's another condition `or 1`
if isinstance(self.k, int) or isinstance(self.k, float) or 1:
pass
```
is fixed to:
```py
# Fixed to only considering variable `a`
if isinstance(a, (float, int)):
pass
# The additional condition is not present in the fix
if isinstance(self.k, (float, int)):
pass
```
Playground: https://play.ruff.rs/6cfbdfb7-f183-43b0-b59e-31e728b34190
## Documentation Preview
### `PLR1701`
<img width="1397" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-25 at 11 14 40"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/67177269/779ee84d-7c4d-4bb8-a3a4-c2b23a313eba">
## Test Plan
Remove the test cases for `PLR1701`, port the padding test case to
`SIM101` and update the snapshot.
## Summary
This PR splits the re-lexing logic into two parts:
1. `TokenSource`: The token source will be responsible to find the
position the lexer needs to be moved to
2. `Lexer`: The lexer will be responsible to reduce the nesting level
and move itself to the new position if recovered from a parenthesized
context
This split makes it easy to find the new lexer position without needing
to implement the backwards lexing logic again which would need to handle
cases involving:
* Different kinds of newlines
* Line continuation character(s)
* Comments
* Whitespaces
### F-strings
This change did reveal one thing about re-lexing f-strings. Consider the
following example:
```py
f'{'
# ^
f'foo'
```
Here, the quote as highlighted by the caret (`^`) is the start of a
string inside an f-string expression. This is unterminated string which
means the token emitted is actually `Unknown`. The parser tries to
recover from it but there's no newline token in the vector so the new
logic doesn't recover from it. The previous logic does recover because
it's looking at the raw characters instead.
The parser would be at `FStringStart` (the one for the second line) when
it calls into the re-lexing logic to recover from an unterminated
f-string on the first line. So, moving backwards the first character
encountered is a newline character but the first token encountered is an
`Unknown` token.
This is improved with #12067fixes: #12046fixes: #12036
## Test Plan
Update the snapshot and validate the changes.
## Summary
This PR fixes the lexer logic to **not** consume the newline character
for an unterminated string literal.
Currently, the lexer would consume it to be part of the string itself
but that would be bad for recovery because then the lexer wouldn't emit
the newline token ever. This PR fixes that to avoid consuming the
newline character in that case.
This was discovered during https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/12060.
## Test Plan
Update the snapshots and validate them.
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug introduced in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/12008 which didn't consider the
two character newline after the line continuation character.
For example, consider the following code highlighted with whitespaces:
```py
call(foo # comment \\r\n
\r\n
def bar():\r\n
....pass\r\n
```
The lexer is at `def` when it's running the re-lexing logic and trying
to move back to a newline character. It encounters `\n` and it's being
escaped (incorrect) but `\r` is being escaped, so it moves the lexer to
`\n` character. This creates an overlap in token ranges which causes the
panic.
```
Name 0..4
Lpar 4..5
Name 5..8
Comment 9..20
NonLogicalNewline 20..22 <-- overlap between
Newline 21..22 <-- these two tokens
NonLogicalNewline 22..23
Def 23..26
...
```
fixes: #12028
## Test Plan
Add a test case with line continuation and windows style newline
character.
## Summary
(I'm pretty sure I added this in the parser re-write but must've got
lost in the rebase?)
This PR raises a syntax error if the type parameter list is empty.
As per the grammar, there should be at least one type parameter:
```
type_params:
| invalid_type_params
| '[' type_param_seq ']'
type_param_seq: ','.type_param+ [',']
```
Verified via the builtin `ast` module as well:
```console
$ python3.13 -m ast parser/_.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
[..]
File "parser/_.py", line 1
def foo[]():
^
SyntaxError: Type parameter list cannot be empty
```
## Test Plan
Add inline test cases and update the snapshots.
## Summary
Right now, it's inconsistent... We sometimes match against the name, and
sometimes against the alias (`asname`). I could see a case for always
matching against the name, but matching against both seems fine too,
since the rule is really about the combination of the two?
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/12031.
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug where Ruff would raise `E203` for f-string debug
expression. This isn't valid because whitespaces are important for debug
expressions.
fixes: #12023
## Test Plan
Add test case and make sure there are no snapshot changes.
## Summary
This PR updates the parser test infrastructure to validate the token
ranges.
From the code documentation:
```
/// Verifies that:
/// * the ranges are strictly increasing when loop the tokens in insertion order
/// * all ranges are within the length of the source code
```
Follow-up from #12016 and #12017resolves: #11938
## Test Plan
Make sure that there are no failures.
## Summary
This PR updates the unterminated string error range to not include the
final newline character.
This is a follow-up to #12016 and required for #12019
This is not done for when the unterminated string goes till the end of
file (not a newline character). The unterminated f-string range is
correct.
### Why is this required for #12019 ?
Because otherwise the token ranges will overlap. For example:
```py
f"{"
f"{foo!r"
```
Here, the re-lexing logic recovers from an unterminated f-string and
thus emitting a `Newline` token for the one at the end of the first
line. But, currently the `Unknown` and the `Newline` token would overlap
because the `Unknown` token (unterminated string literal) range would
include the newline character.
## Test Plan
Update and validate the snapshot.
## Summary
This PR fixes the range highlighted for the line continuation error.
Previously, it would highlight an incorrect range:
```
1 | call(a, b, \\\
| ^^ Syntax Error: unexpected character after line continuation character
2 |
3 | def bar():
|
```
And now:
```
|
1 | call(a, b, \\\
| ^ Syntax Error: unexpected character after line continuation character
2 |
3 | def bar():
|
```
This is implemented by avoiding to update the token range for the
`Unknown` token which is emitted when there's a lexical error. Instead,
the `push_error` helper method will be responsible to update the range
to the error location.
This actually becomes a requirement which can be seen in follow-up PRs.
## Test Plan
Update and validate the snapshot.
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug where the re-lexing logic didn't consider the line
continuation character being present before the newline character. This
meant that the lexer was being moved back to the newline character which
is actually ignored via `\`.
Considering the following code:
```py
f'middle {'string':\
'format spec'}
```
The old token stream is:
```
...
Colon 18..19
FStringMiddle 19..29 (flags = F_STRING)
Newline 20..21
Indent 21..29
String 29..42
Rbrace 42..43
...
```
Notice how the ranges are overlapping between the `FStringMiddle` token
and the tokens emitted after moving the lexer backwards.
After this fix, the new token stream which is without moving the lexer
backwards in this scenario:
```
FStringStart 0..2 (flags = F_STRING)
FStringMiddle 2..9 (flags = F_STRING)
Lbrace 9..10
String 10..18
Colon 18..19
FStringMiddle 19..29 (flags = F_STRING)
FStringEnd 29..30 (flags = F_STRING)
Name 30..36
Name 37..41
Unknown 41..44
Newline 44..45
```
fixes: #12004
## Test Plan
Add test cases and update the snapshots.
## Summary
This PR updates `F811` rule to include assignment as possible shadowed
binding. This will fix issue: #11828 .
## Test Plan
Add a test file, F811_30.py, which includes a redefinition after an
assignment and a verified snapshot file.
## Summary
Addresses #11974 to add a `RUF` rule to replace `print` expressions in
`assert` statements with the inner message.
An autofix is available, but is considered unsafe as it changes
behaviour of the execution, notably:
- removal of the printout in `stdout`, and
- `AssertionError` instance containing a different message.
While the detection of the condition is a straightforward matter,
deciding how to resolve the print arguments into a string literal can be
a relatively subjective matter. The implementation of this PR chooses to
be as tolerant as possible, and will attempt to reformat any number of
`print` arguments containing single or concatenated strings or variables
into either a string literal, or a f-string if any variables or
placeholders are detected.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`.
## Examples
For ease of discussion, this is the diff for the tests:
```diff
# Standard Case
# Expects:
# - single StringLiteral
-assert True, print("This print is not intentional.")
+assert True, "This print is not intentional."
# Concatenated string literals
# Expects:
# - single StringLiteral
-assert True, print("This print" " is not intentional.")
+assert True, "This print is not intentional."
# Positional arguments, string literals
# Expects:
# - single StringLiteral concatenated with " "
-assert True, print("This print", "is not intentional")
+assert True, "This print is not intentional"
# Concatenated string literals combined with Positional arguments
# Expects:
# - single stringliteral concatenated with " " only between `print` and `is`
-assert True, print("This " "print", "is not intentional.")
+assert True, "This print is not intentional."
# Positional arguments, string literals with a variable
# Expects:
# - single FString concatenated with " "
-assert True, print("This", print.__name__, "is not intentional.")
+assert True, f"This {print.__name__} is not intentional."
# Mixed brackets string literals
# Expects:
# - single StringLiteral concatenated with " "
-assert True, print("This print", 'is not intentional', """and should be removed""")
+assert True, "This print is not intentional and should be removed"
# Mixed brackets with other brackets inside
# Expects:
# - single StringLiteral concatenated with " " and escaped brackets
-assert True, print("This print", 'is not "intentional"', """and "should" be 'removed'""")
+assert True, "This print is not \"intentional\" and \"should\" be 'removed'"
# Positional arguments, string literals with a separator
# Expects:
# - single StringLiteral concatenated with "|"
-assert True, print("This print", "is not intentional", sep="|")
+assert True, "This print|is not intentional"
# Positional arguments, string literals with None as separator
# Expects:
# - single StringLiteral concatenated with " "
-assert True, print("This print", "is not intentional", sep=None)
+assert True, "This print is not intentional"
# Positional arguments, string literals with variable as separator, needs f-string
# Expects:
# - single FString concatenated with "{U00A0}"
-assert True, print("This print", "is not intentional", sep=U00A0)
+assert True, f"This print{U00A0}is not intentional"
# Unnecessary f-string
# Expects:
# - single StringLiteral
-assert True, print(f"This f-string is just a literal.")
+assert True, "This f-string is just a literal."
# Positional arguments, string literals and f-strings
# Expects:
# - single FString concatenated with " "
-assert True, print("This print", f"is not {'intentional':s}")
+assert True, f"This print is not {'intentional':s}"
# Positional arguments, string literals and f-strings with a separator
# Expects:
# - single FString concatenated with "|"
-assert True, print("This print", f"is not {'intentional':s}", sep="|")
+assert True, f"This print|is not {'intentional':s}"
# A single f-string
# Expects:
# - single FString
-assert True, print(f"This print is not {'intentional':s}")
+assert True, f"This print is not {'intentional':s}"
# A single f-string with a redundant separator
# Expects:
# - single FString
-assert True, print(f"This print is not {'intentional':s}", sep="|")
+assert True, f"This print is not {'intentional':s}"
# Complex f-string with variable as separator
# Expects:
# - single FString concatenated with "{U00A0}", all placeholders preserved
condition = "True is True"
maintainer = "John Doe"
-assert True, print("Unreachable due to", condition, f", ask {maintainer} for advice", sep=U00A0)
+assert True, f"Unreachable due to{U00A0}{condition}{U00A0}, ask {maintainer} for advice"
# Empty print
# Expects:
# - `msg` entirely removed from assertion
-assert True, print()
+assert True
# Empty print with separator
# Expects:
# - `msg` entirely removed from assertion
-assert True, print(sep=" ")
+assert True
# Custom print function that actually returns a string
# Expects:
@@ -100,4 +100,4 @@
# Use of `builtins.print`
# Expects:
# - single StringLiteral
-assert True, builtins.print("This print should be removed.")
+assert True, "This print should be removed."
```
## Known Issues
The current implementation resolves all arguments and separators of the
`print` expression into a single string, be it
`StringLiteralValue::single` or a `FStringValue::single`. This:
- potentially joins together strings well beyond the ideal character
limit for each line, and
- does not preserve multi-line strings in their original format, in
favour of a single line `"...\n...\n..."` format.
These are purely formatting issues only occurring in unusual scenarios.
Additionally, the autofix will tolerate `print` calls that were
previously invalid:
```python
assert True, print("this", "should not be allowed", sep=42)
```
This will be transformed into
```python
assert True, f"this{42}should not be allowed"
```
which some could argue is an alteration of behaviour.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Documentation mentions:
> PEP 563 enabled the use of a number of convenient type annotations,
such as `list[str]` instead of `List[str]`
but it meant [PEP 585](https://peps.python.org/pep-0585/) instead.
[PEP 563](https://peps.python.org/pep-0563/) is the one defining `from
__future__ import annotations`.
## Test Plan
No automated test required, just verify that
https://peps.python.org/pep-0585/ is the correct reference.
## Summary
I look at the token stream a lot, not specifically in the playground but
in the terminal output and it's annoying to scroll a lot to find
specific location. Most of the information is also redundant.
The final format we end up with is: `<kind> <range> (flags = ...)` e.g.,
`String 0..4 (flags = BYTE_STRING)` where the flags part is only
populated if there are any flags set.
## Summary
Fixes#11651.
Fixes#11851.
We were double-closing a notebook document from the index, once in
`textDocument/didClose` and then in the `notebookDocument/didClose`
handler. The second time this happens, taking a snapshot fails.
I've rewritten how we handle snapshots for closing notebooks / notebook
cells so that any failure is simply logged instead of propagating
upwards. This implementation works consistently even if we don't receive
`textDocument/didClose` notifications for each specific cell, since they
get closed (and the diagnostics get cleared) in the notebook document
removal process.
## Test Plan
1. Open an untitled, unsaved notebook with the `Create: New Jupyter
Notebook` command from the VS Code command palette (`Ctrl/Cmd + Shift +
P`)
2. Without saving the document, close it.
3. No error popup should appear.
4. Run the debug command (`Ruff: print debug information`) to confirm
that there are no open documents
## Summary
This PR does some housekeeping into moving certain structs into related
modules. Specifically,
1. Move `LexicalError` from `lexer.rs` to `error.rs` which also contains
the `ParseError`
2. Move `Token`, `TokenFlags` and `TokenValue` from `lexer.rs` to
`token.rs`
## Summary
This PR removes the duplication around `is_trivia` functions.
There are two of them in the codebase:
1. In `pycodestyle`, it's for newline, indent, dedent, non-logical
newline and comment
2. In the parser, it's for non-logical newline and comment
The `TokenKind::is_trivia` method used (1) but that's not correct in
that context. So, this PR introduces a new `is_non_logical_token` helper
method for the `pycodestyle` crate and updates the
`TokenKind::is_trivia` implementation with (2).
This also means we can remove `Token::is_trivia` method and the
standalone `token_source::is_trivia` function and use the one on
`TokenKind`.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
Closes#11914.
This PR introduces a snapshot test that replays the LSP requests made
during a document formatting request, and confirms that the notebook
document is updated in the expected way.
## Summary
Fixes#11911.
`shellexpand` is now used on `logFile` to expand the file path, allowing
the usage of `~` and environment variables.
## Test Plan
1. Set `logFile` in either Neovim or Helix to a file path that needs
expansion, like `~/.config/helix/ruff_logs.txt`.
2. Ensure that `RUFF_TRACE` is set to `messages` or `verbose`
3. Open a Python file in Neovim/Helix
4. Confirm that a file at the path specified was created, with the
expected logs.
## Summary
This PR updates the logical line rules entry-point function to only run
the logic if any of the rules within that group is enabled.
Although this shouldn't really give any performance improvements, it's
better not to do additional work if we can. This is also consistent with
how other rules are run.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
This PR avoids moving back the lexer for a triple-quoted f-string during
the re-lexing phase.
The reason this is a problem is that for a triple-quoted f-string the
newlines are part of the f-string itself, specifically they'll be part
of the `FStringMiddle` token. So, if we moved the lexer back, there
would be a `Newline` token whose range would be in between an
`FStringMiddle` token. This creates a panic in downstream usage.
fixes: #11937
## Test Plan
Add test cases and validate the snapshots.
## Summary
This PR avoids the `depth` counter when detecting indentation from
non-logical lines because it seems to never be used. It might have been
a leftover when the logic was added originally in #11608.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
This PR updates the linter to show all the parse errors as diagnostics
instead of just the first one.
Note that this doesn't affect the parse error displayed as error log
message. This will be removed in a follow-up PR.
### Breaking?
I don't think this is a breaking change even though this might give more
diagnostics. The main reason is that this shouldn't affect any users
because it'll only give additional diagnostics in the case of multiple
syntax errors.
## Test Plan
Add an integration test case which would raise more than one parse
error.
## Summary
This PR updates the re-lexing logic to avoid consuming the trailing
whitespace and move the lexer explicitly to the last newline character
encountered while moving backwards.
Consider the following code snippet as taken from the test case
highlighted with whitespace (`.`) and newline (`\n`) characters:
```py
# There are trailing whitespace before the newline character but those whitespaces are
# part of the comment token
f"""hello {x # comment....\n
# ^
y = 1\n
```
The parser is at `y` when it's trying to recover from an unclosed `{`,
so it calls into the re-lexing logic which tries to move the lexer back
to the end of the previous line. But, as it consumed all whitespaces it
moved the lexer to the location marked by `^` in the above code snippet.
But, those whitespaces are part of the comment token. This means that
the range for the two tokens were overlapping which introduced the
panic.
Note that this is only a bug when there's a comment with a trailing
whitespace otherwise it's fine to move the lexer to the whitespace
character. This is because the lexer would just skip the whitespace
otherwise. Nevertheless, this PR updates the logic to move it explicitly
to the newline character in all cases.
fixes: #11929
## Test Plan
Add test cases and update the snapshot. Make sure that it doesn't panic
on the code snippet in the linked issue.
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
related to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/5306
The check right now only checks in the first 1024 bytes, and that's
really not enough when there's a docstring at the beginning of a file.
A more proper fix might be needed, which might be more complex (and I
don't have the `rust` skills to implement that). But this temporary
"fix" might enable more users to use this.
Context: We want to use this rule in
https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/ and we got blocked because
of this hardcoded rule (which TBH took us quite a while to figure out
why it was failing since it's not documented).
## Test Plan
This is already kinda tested, modified the test for the new byte number.
<!-- How was it tested? -->
## Summary
This PR removes most of the syntax errors from the test cases. This
would create noise when https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11901 is
complete. These syntax errors are also just noise for the test itself.
## Test Plan
Update the snapshots and verify that they're still the same.
## Summary
This PR is a follow-up on #11845 to add the re-lexing logic for normal
list parsing.
A normal list parsing is basically parsing elements without any
separator in between i.e., there can only be trivia tokens in between
the two elements. Currently, this is only being used for parsing
**assignment statement** and **f-string elements**. Assignment
statements cannot be in a parenthesized context, but f-string can have
curly braces so this PR is specifically for them.
I don't think this is an ideal recovery but the problem is that both
lexer and parser could add an error for f-strings. If the lexer adds an
error it'll emit an `Unknown` token instead while the parser adds the
error directly. I think we'd need to move all f-string errors to be
emitted by the parser instead. This way the parser can correctly inform
the lexer that it's out of an f-string and then the lexer can pop the
current f-string context out of the stack.
## Test Plan
Add test cases, update the snapshots, and run the fuzzer.
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/issues/496.
Cells are no longer removed from the notebook index when a notebook gets
updated, but rather when `textDocument/didClose` is called for them.
This solves an issue where their premature removal from the notebook
cell index would cause their URL to be un-queryable in the
`textDocument/didClose` handler.
## Test Plan
Create and then delete a notebook cell in VS Code. No error should
appear.
## Summary
This PR implements the re-lexing logic in the parser.
This logic is only applied when recovering from an error during list
parsing. The logic is as follows:
1. During list parsing, if an unexpected token is encountered and it
detects that an outer context can understand it and thus recover from
it, it invokes the re-lexing logic in the lexer
2. This logic first checks if the lexer is in a parenthesized context
and returns if it's not. Thus, the logic is a no-op if the lexer isn't
in a parenthesized context
3. It then reduces the nesting level by 1. It shouldn't reset it to 0
because otherwise the recovery from nested list parsing will be
incorrect
4. Then, it tries to find last newline character going backwards from
the current position of the lexer. This avoids any whitespaces but if it
encounters any character other than newline or whitespace, it aborts.
5. Now, if there's a newline character, then it needs to be re-lexed in
a logical context which means that the lexer needs to emit it as a
`Newline` token instead of `NonLogicalNewline`.
6. If the re-lexing gives a different token than the current one, the
token source needs to update it's token collection to remove all the
tokens which comes after the new current position.
It turns out that the list parsing isn't that happy with the results so
it requires some re-arranging such that the following two errors are
raised correctly:
1. Expected comma
2. Recovery context error
For (1), the following scenarios needs to be considered:
* Missing comma between two elements
* Half parsed element because the grammar doesn't allow it (for example,
named expressions)
For (2), the following scenarios needs to be considered:
1. If the parser is at a comma which means that there's a missing
element otherwise the comma would've been consumed by the first `eat`
call above. And, the parser doesn't take the re-lexing route on a comma
token.
2. If it's the first element and the current token is not a comma which
means that it's an invalid element.
resolves: #11640
## Test Plan
- [x] Update existing test snapshots and validate them
- [x] Add additional test cases specific to the re-lexing logic and
validate the snapshots
- [x] Run the fuzzer on 3000+ valid inputs
- [x] Run the fuzzer on invalid inputs
- [x] Run the parser on various open source projects
- [x] Make sure the ecosystem changes are none
## Summary
This PR updates the server capabilities to include the commands that
Ruff supports. This is similar to how there's a list of possible code
actions supported by the server.
I noticed this when I was trying to find whether Helix supported
workspace commands or not based on Jane's comment
(https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11831#discussion_r1634984921)
and I found the `:lsp-workspace-command` in the editor but it didn't
show up anything in the picker.
So, I looked at the implementation in Helix
(9c479e6d2d/helix-term/src/commands/typed.rs (L1372-L1384))
which made me realize that Ruff doesn't provide this in its
capabilities. Currently, this does require `ruff` to be first in the
list of language servers in the user config but that should be resolved
by https://github.com/helix-editor/helix/pull/10176. So, the following
config should work:
```toml
[[language]]
name = "python"
# Ruff should come first until https://github.com/helix-editor/helix/pull/10176 is released
language-servers = ["ruff", "pyright"]
```
## Test Plan
1. Neovim's server capabilities output should include the supported
commands:
```
executeCommandProvider = {
commands = { "ruff.applyFormat", "ruff.applyAutofix", "ruff.applyOrganizeImports", "ruff.printDebugInformation" },
workDoneProgress = false
},
```
2. Helix should now display the commands to pick from when
`:lsp-workspace-command` is invoked:
<img width="832" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-13 at 08 47 14"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/67177269/09048ecd-c974-4e09-ab56-9482ff3d780b">
## Summary
This PR adds a new enum to determine the kind of terminator token i.e.,
is it actually terminates the list or is it used for error recovery.
This is important because the parser should take the error recovery
route in case the terminator token is used for better error recovery.
This will then try to re-lex the token if it's the case.
I haven't updated any reference to use this new enum as otherwise it'll
update the snapshots. I plan to do that in a follow-up PR so that it's
easier to reason about.
## Test plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
This PR separates the terminator token for f-string elements depending
on the context. A list of f-string element can occur either in a regular
f-string or a format spec of an f-string. The terminator token is
different depending on that context.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test` and verify the updated snapshots.
## Summary
This PR re-uses the `ruff_python_trivia::is_python_whitespace` in the
lexer instead of defining its own. This was mainly to avoid circular
dependency which was resolved in #11261.
## Summary
Add Constraint nodes to flow graph, and narrow types based on that (only
`is None` and `is not None` narrowing supported for now, to prototype
the structure.)
Also add simplification of zero- and one-element unions and
intersections, and flattening of intersections.
There's a lot more normalization logic needed for unions and
intersections (as is obvious from the inferred type in the added
`narrow_none` test), but this will be non-trivial and I'd rather do it
in a separate PR.
Here's a flowchart diagram for the code in the added `narrow_none` test:

The top branch is for the `if` expression in the initial assignment to
`x`; that `Constraint` node would only affect the type of `flag`, which
we don't care about in this test.
The second branch is for the `if` statement, with `Constraint` node
affecting the type of `x`.
## Test Plan
Added tests.
## Summary
Fixes#11744.
We now show a distinct popup message when we fail to get a document
snapshot during command execution. This message more clearly
communicates the issue to the user, instead of a generic "ruff
encountered an error" message.
## Test Plan
Try running `Fix all auto-fixable problems` on an incompatible file (for
example: `settings.json`). You should see the following popup message:
<img width="456" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-11 at 11 47 16 AM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/3a28e3d7-3896-4dd0-b117-f87300dd3b68">
## Summary
Closes#11715.
Introduces a new command, `ruff.printDebugInformation`. This will print
useful information about the status of the server to `stderr`.
Right now, the information shown by this command includes:
* The path to the server executable
* The version of the executable
* The text encoding being used
* The number of open documents and workspaces
* A list of registered configuration files
* The capabilities of the client
## Test Plan
First, checkout and use [the corresponding `ruff-vscode`
PR](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/pull/495).
Running the `Print debug information` command in VS Code should show
something like the following in the Output channel:
<img width="991" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-11 at 11 41 46 AM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/ab93c009-bb7b-4291-b057-d44fdc6f9f86">
## Summary
Fixes#10968.
Fixes#11545.
The server's tracing system has been rewritten from the ground up. The
server now has trace level and log level settings which restrict the
tracing events and spans that get logged.
* A `logLevel` setting has been added, which lets a user set the log
level. By default, it is set to `"info"`.
* A `logFile` setting has also been added, which lets the user supply an
optional file to send tracing output (it does not have to exist as a
file yet). By default, if this is unset, tracing output will be sent to
`stderr`.
* A `$/setTrace` handler has also been added, and we also set the trace
level from the initialization options. For editors without direct
support for tracing, the environment variable `RUFF_TRACE` can override
the trace level.
* Small changes have been made to how we display tracing output. We no
longer use `tracing-tree`, and instead use
`tracing_subscriber::fmt::Layer` to format output. Thread names are now
included in traces, and I've made some adjustment to thread worker names
to be more useful.
## Test Plan
In VS Code, with `ruff.trace.server` set to its default value, no logs
from Ruff should appear.
After changing `ruff.trace.server` to either `messages` or `verbose`,
you should see log messages at `info` level or higher appear in Ruff's
output:
<img width="1005" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-10 at 10 35 04 AM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/6050d107-9815-4bd2-96d0-e86f096a57f5">
In Helix, by default, no logs from Ruff should appear.
To set the trace level in Helix, you'll need to modify your language
configuration as follows:
```toml
[language-server.ruff]
command = "/Users/jane/astral/ruff/target/debug/ruff"
args = ["server", "--preview"]
environment = { "RUFF_TRACE" = "messages" }
```
After doing this, logs of `info` level or higher should be visible in
Helix:
<img width="1216" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-10 at 10 39 26 AM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/8ff88692-d3f7-4fd1-941e-86fb338fcdcc">
You can use `:log-open` to quickly open the Helix log file.
In Neovim, by default, no logs from Ruff should appear.
To set the trace level in Neovim, you'll need to modify your
configuration as follows:
```lua
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup {
cmd = {"/path/to/debug/executable", "server", "--preview"},
cmd_env = { RUFF_TRACE = "messages" }
}
```
You should see logs appear in `:LspLog` that look like the following:
<img width="1490" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-11 at 11 24 01 AM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/576cd5fa-03cf-477a-b879-b29a9a1200ff">
You can adjust `logLevel` and `logFile` in `settings`:
```lua
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup {
cmd = {"/path/to/debug/executable", "server", "--preview"},
cmd_env = { RUFF_TRACE = "messages" },
settings = {
logLevel = "debug",
logFile = "your/log/file/path/log.txt"
}
}
```
The `logLevel` and `logFile` can also be set in Helix like so:
```toml
[language-server.ruff.config.settings]
logLevel = "debug"
logFile = "your/log/file/path/log.txt"
```
Even if this log file does not exist, it should now be created and
written to after running the server:
<img width="1148" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-10 at 10 43 44 AM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/ab533cf7-d5ac-4178-97f1-e56da17450dd">
## Summary
This PR updates the parser to remove building the `CommentRanges` and
instead it'll be built by the linter and the formatter when it's
required.
For the linter, it'll be built and owned by the `Indexer` while for the
formatter it'll be built from the `Tokens` struct and passed as an
argument.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
The fix for E203 now produces the same result as ruff format in cases
where a slice ends on a colon and the closing square bracket is on the
following line.
Refers to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10973
## Test Plan
The minimal reproduction case in the ticket was added as test case
producing no error. Additional cases with multiple spaces or a tab
before the colon where added to make sure that the rule still finds
these.
## Summary
As-is, we're using the URL path for all files, leading us to use paths
like:
```
/c%3A/Users/crmar/workspace/fastapi/tests/main.py
```
This doesn't match against per-file ignores and other patterns in Ruff
configuration.
This PR modifies the LSP to use the real file path if available, and the
virtual file path if not.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11751.
## Test Plan
Ran the LSP on Windows. In the FastAPI repo, added:
```toml
[tool.ruff.lint.per-file-ignores]
"tests/**/*.py" = ["F401"]
```
And verified that an unused import was ignored in `tests` after this
change, but not before.
## Summary
This PR removes the `result-like` dependency and instead implement the
required functionality. The motivation being that `noqa.is_enabled()` is
easier to read than `noqa.into()`.
For context, I was just trying to understand the syntax error workflow
and I saw these flags which were being converted via `into`. I always
find `into` confusing because you never know what's it being converted
into unless you know the type. Later realized that it's just a boolean
flag. After removing the usages from these two flags, it turns out that
the dependency is only being used in one rule so I thought to remove
that as well.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
This PR implements the [consider dict
items](https://pylint.pycqa.org/en/latest/user_guide/messages/convention/consider-using-dict-items.html)
rule from Pylint. Enabling this rule flags:
```python
ORCHESTRA = {
"violin": "strings",
"oboe": "woodwind",
"tuba": "brass",
"gong": "percussion",
}
for instrument in ORCHESTRA:
print(f"{instrument}: {ORCHESTRA[instrument]}")
for instrument in ORCHESTRA.keys():
print(f"{instrument}: {ORCHESTRA[instrument]}")
for instrument in (inline_dict := {"foo": "bar"}):
print(f"{instrument}: {inline_dict[instrument]}")
```
For not using `items()` to extract the value out of the dict. We ignore
the case of an assignment, as you can't modify the underlying
representation with the value in the list of tuples returned.
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
`cargo test`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
Definitions are used in symbol table and in flow graph, and aren't
inherently owned by one or the other; move them into their own
submodule.
## Test Plan
Existing tests.
## Summary
Add support for inferring int literal types from basic arithmetic on int
literals. Just to begin showing examples of resolving more complex
expression types, and because this will be useful in testing walrus
expressions.
## Test Plan
Added test.
## Summary
After looking at this a bit, I think it does make sense to have
`Unbound` as part of the `Definition` enum; if we are modeling `Unbound`
as a type (which currently we are), then every symbol implicitly starts
each scope with a "definition" as unbound, and the cleanest way to model
that is as a real `Definition`. We should be able to handle a definition
of "unbound" anywhere we handle definitions.
But the name `None` wasn't clear enough; changing the name to `Unbound`
and adding a doc comment.
Also change `[first].into_iter()` to `std::iter::once(first)`, from
post-land code review on a prior PR.
## Test Plan
Existing tests.
## Summary
This PR is a follow-up to #11740 to restrict access to the `Parsed`
output by replacing the `parsed` API function with a more specific one.
Currently, that is `comment_ranges` but the linked PR exposes a `tokens`
method.
The main motivation is so that there's no way to get an incorrect
information from the checker. And, it also encapsulates the source of
the comment ranges and the tokens itself. This way it would become
easier to just update the checker if the source for these information
changes in the future.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug where the checker would require the tokens for an
invalid offset w.r.t. the source code.
Taking the source code from the linked issue as an example:
```py
relese_version :"0.0is 64"
```
Now, this isn't really a valid type annotation but that's what this PR
is fixing. Regardless of whether it's valid or not, Ruff shouldn't
panic.
The checker would visit the parsed type annotation (`0.0is 64`) and try
to detect any violations. Certain rule logic requests the tokens for the
same but it would fail because the lexer would only have the `String`
token considering original source code. This worked before because the
lexer was invoked again for each rule logic.
The solution is to store the parsed type annotation on the checker if
it's in a typing context and use the tokens from that instead if it's
available. This is enforced by creating a new API on the checker to get
the tokens.
But, this means that there are two ways to get the tokens via the
checker API. I want to restrict this in a follow-up PR (#11741) to only
expose `tokens` and `comment_ranges` as methods and restrict access to
the parsed source code.
fixes: #11736
## Test Plan
- [x] Add a test case for `F632` rule and update the snapshot
- [x] Check all affected rules
- [x] No ecosystem changes
## Summary
This PR updates the return type of `parse_type_annotation` from `Expr`
to `Parsed<ModExpression>`. This is to allow accessing the tokens for
the parsed sub-expression in the follow-up PR.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/issues/482.
I've made adjustments to `format` and `format_range` that handle parsing
errors before they become server errors. We'll still log this as a
problem, but there will no longer be a visible popup.
## Test Plan
Instead of seeing a visible error when formatting a document with syntax
issues, you should see this warning in the LSP logs:
<img width="991" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-04 at 3 38 23 PM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/9d68947d-6462-4ca6-ab5a-65e573c91db6">
Similarly, if you try to format a range with syntax issues, you should
see this warning in the LSP logs instead of a visible error popup:
<img width="1010" alt="Screenshot 2024-06-04 at 3 39 10 PM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/99fff098-798d-406a-976e-81ead0da0352">
---------
Co-authored-by: Zanie Blue <contact@zanie.dev>
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug where the lexer didn't consider the BOM into the
start offset.
fixes: #11731
## Test Plan
Add multiple test cases which involves BOM character in the source for
the lexer and verify the snapshot.
## Summary
This PR updates the lexer checkpoint to store the cursor offset instead
of cloning the cursor itself. This reduces the size of `LexerCheckpoint`
from 136 to 112 bytes and also removes the need for lifetime.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
Ensures that we respect per-file ignores and exemptions for these rules.
Specifically, we allow:
```python
# ruff: noqa: PGH004
```
...to ignore `PGH004`.
## Summary
Should resolve https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11454.
This is my first PR to `ruff`, so I may have missed something.
If I understood the suggestion in the issue correctly, rule `PGH004`
should be set to `Preview` again.
## Test Plan
Created two fixtures derived from the issue.
## Summary
Switch name resolution in `infer_expression_type` from resolving the
public type of a symbol, to resolving the reachable definitions of that
symbol from the reference point, using the flow graph.
This surfaced a bug in the flow graph implementation and a bug in symbol
table building, both of which are also fixed here.
The bug in flow graph implementation was that when we pushed and popped
scopes, we didn't maintain a stack of "current flow nodes" in all
stacked scopes, to be restored when we returned to that scope. Now we
do.
The bug in symbol table building that we didn't visit the parts of
functions and class definitions in the correct scopes. E.g. decorators
should be visited in the outer scope, arguments should be visited inside
the type-params scope (if any) but not inside the function body scope,
and only the body itself should actually be visited inside the body
scope. Fixing this requires that we no longer use `walk_stmt` here,
instead we have to visit each individual component.
## Test Plan
Added test.
## Summary
Rename `infer_symbol_type` to `infer_symbol_public_type`, and allow it
to work on symbols with more than one definition. For now, use the most
cautious/sound inference, which is the union of all definitions. We can
prune this union more in future by eliminating definitions if we can
show that they can't be visible (this requires both that the symbol is
definitely later reassigned, and that there is no intervening
call/import that might be able to see the over-written definition).
## Test Plan
Added a test showing inference of union from multiple definitions.
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug where the `Generator` wouldn't add a newline before
a type alias statement. This is because it wasn't using the `statement`
macro which takes care of the newline.
Without this fix, a code like:
```py
type X = int
type Y = str
```
The generator would produce:
```py
type X = inttype Y = str
```
## Test Plan
Add a test case.
## Summary
This PR removes the following dependencies from the `ruff_python_parser`
crate:
* `anyhow` (moved to dev dependencies)
* `is-macro`
* `itertools`
The main motivation is that they aren't used much.
Additionally, it updates the return type of `parse_type_annotation` to
use a more specific `ParseError` instead of the generic `anyhow::Error`.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
This PR updates the logic for parsing type annotation to accept a
`ExprStringLiteral` node instead of the string value and the range.
The main motivation of this change is to simplify the implementation of
`parse_type_annotation` function with:
* Use the `opener_len` and `closer_len` from the string flags to get the
raw contents range instead of extracting it via
* `str::leading_quote(expression).unwrap().text_len()`
* `str::trailing_quote(expression).unwrap().text_len()`
* Avoid comparing the string content if we already know that it's
implicitly concatenated
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
This PR re-orders the lexer methods in the following order:
1. `next_token`
2. `lex_token`
3. `eat_indentation`
4. `handle_indentation`
5. `skip_whitespace`
6. `consume_ascii_character`
7. `try_single_char_prefix`
8. `try_double_char_prefix`
9. `lex_identifier`
10. `lex_fstring_start`
11. `lex_fstring_middle_or_end`
12. `lex_string`
13. `lex_number`
14. `lex_number_radix`
15. `lex_decimal_number`
16. `radix_run`
17. `lex_comment`
18. `lex_ipython_escape_command`
19. `consume_end`
Following was considered for the ordering:
* 1 is the main entry point which delegates to 2
* 3, 4, 5 are all related to whitespace which is done first
* 6 is the entrypoint for an ascii character which delegates to 9, 12,
13, 17, 18, 19
* Others are grouped around similar kind of methods
## Summary
This PR updates the entire parser stack in multiple ways:
### Make the lexer lazy
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11244
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11473
Previously, Ruff's lexer would act as an iterator. The parser would
collect all the tokens in a vector first and then process the tokens to
create the syntax tree.
The first task in this project is to update the entire parsing flow to
make the lexer lazy. This includes the `Lexer`, `TokenSource`, and
`Parser`. For context, the `TokenSource` is a wrapper around the `Lexer`
to filter out the trivia tokens[^1]. Now, the parser will ask the token
source to get the next token and only then the lexer will continue and
emit the token. This means that the lexer needs to be aware of the
"current" token. When the `next_token` is called, the current token will
be updated with the newly lexed token.
The main motivation to make the lexer lazy is to allow re-lexing a token
in a different context. This is going to be really useful to make the
parser error resilience. For example, currently the emitted tokens
remains the same even if the parser can recover from an unclosed
parenthesis. This is important because the lexer emits a
`NonLogicalNewline` in parenthesized context while a normal `Newline` in
non-parenthesized context. This different kinds of newline is also used
to emit the indentation tokens which is important for the parser as it's
used to determine the start and end of a block.
Additionally, this allows us to implement the following functionalities:
1. Checkpoint - rewind infrastructure: The idea here is to create a
checkpoint and continue lexing. At a later point, this checkpoint can be
used to rewind the lexer back to the provided checkpoint.
2. Remove the `SoftKeywordTransformer` and instead use lookahead or
speculative parsing to determine whether a soft keyword is a keyword or
an identifier
3. Remove the `Tok` enum. The `Tok` enum represents the tokens emitted
by the lexer but it contains owned data which makes it expensive to
clone. The new `TokenKind` enum just represents the type of token which
is very cheap.
This brings up a question as to how will the parser get the owned value
which was stored on `Tok`. This will be solved by introducing a new
`TokenValue` enum which only contains a subset of token kinds which has
the owned value. This is stored on the lexer and is requested by the
parser when it wants to process the data. For example:
8196720f80/crates/ruff_python_parser/src/parser/expression.rs (L1260-L1262)
[^1]: Trivia tokens are `NonLogicalNewline` and `Comment`
### Remove `SoftKeywordTransformer`
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11441
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11459
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11442
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11443
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11474
For context,
https://github.com/RustPython/RustPython/pull/4519/files#diff-5de40045e78e794aa5ab0b8aacf531aa477daf826d31ca129467703855408220
added support for soft keywords in the parser which uses infinite
lookahead to classify a soft keyword as a keyword or an identifier. This
is a brilliant idea as it basically wraps the existing Lexer and works
on top of it which means that the logic for lexing and re-lexing a soft
keyword remains separate. The change here is to remove
`SoftKeywordTransformer` and let the parser determine this based on
context, lookahead and speculative parsing.
* **Context:** The transformer needs to know the position of the lexer
between it being at a statement position or a simple statement position.
This is because a `match` token starts a compound statement while a
`type` token starts a simple statement. **The parser already knows
this.**
* **Lookahead:** Now that the parser knows the context it can perform
lookahead of up to two tokens to classify the soft keyword. The logic
for this is mentioned in the PR implementing it for `type` and `match
soft keyword.
* **Speculative parsing:** This is where the checkpoint - rewind
infrastructure helps. For `match` soft keyword, there are certain cases
for which we can't classify based on lookahead. The idea here is to
create a checkpoint and keep parsing. Based on whether the parsing was
successful and what tokens are ahead we can classify the remaining
cases. Refer to #11443 for more details.
If the soft keyword is being parsed in an identifier context, it'll be
converted to an identifier and the emitted token will be updated as
well. Refer
8196720f80/crates/ruff_python_parser/src/parser/expression.rs (L487-L491).
The `case` soft keyword doesn't require any special handling because
it'll be a keyword only in the context of a match statement.
### Update the parser API
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11494
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11505
Now that the lexer is in sync with the parser, and the parser helps to
determine whether a soft keyword is a keyword or an identifier, the
lexer cannot be used on its own. The reason being that it's not
sensitive to the context (which is correct). This means that the parser
API needs to be updated to not allow any access to the lexer.
Previously, there were multiple ways to parse the source code:
1. Passing the source code itself
2. Or, passing the tokens
Now that the lexer and parser are working together, the API
corresponding to (2) cannot exists. The final API is mentioned in this
PR description: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11494.
### Refactor the downstream tools (linter and formatter)
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11511
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11515
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11529
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11562
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11592
And, the final set of changes involves updating all references of the
lexer and `Tok` enum. This was done in two-parts:
1. Update all the references in a way that doesn't require any changes
from this PR i.e., it can be done independently
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11402
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11406
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11418
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11419
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11420
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11424
2. Update all the remaining references to use the changes made in this
PR
For (2), there were various strategies used:
1. Introduce a new `Tokens` struct which wraps the token vector and add
methods to query a certain subset of tokens. These includes:
1. `up_to_first_unknown` which replaces the `tokenize` function
2. `in_range` and `after` which replaces the `lex_starts_at` function
where the former returns the tokens within the given range while the
latter returns all the tokens after the given offset
2. Introduce a new `TokenFlags` which is a set of flags to query certain
information from a token. Currently, this information is only limited to
any string type token but can be expanded to include other information
in the future as needed. https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11578
3. Move the `CommentRanges` to the parsed output because this
information is common to both the linter and the formatter. This removes
the need for `tokens_and_ranges` function.
## Test Plan
- [x] Update and verify the test snapshots
- [x] Make sure the entire test suite is passing
- [x] Make sure there are no changes in the ecosystem checks
- [x] Run the fuzzer on the parser
- [x] Run this change on dozens of open-source projects
### Running this change on dozens of open-source projects
Refer to the PR description to get the list of open source projects used
for testing.
Now, the following tests were done between `main` and this branch:
1. Compare the output of `--select=E999` (syntax errors)
2. Compare the output of default rule selection
3. Compare the output of `--select=ALL`
**Conclusion: all output were same**
## What's next?
The next step is to introduce re-lexing logic and update the parser to
feed the recovery information to the lexer so that it can emit the
correct token. This moves us one step closer to having error resilience
in the parser and provides Ruff the possibility to lint even if the
source code contains syntax errors.
## Summary
Implement support for RDJson output for `ruff check`, as requested in
#8655.
## Test Plan
Tested using a snapshot test. Same approach as for e.g. the JSON output
formatter.
## Additional info
I tried to keep the implementation close to the JSON implementation.
I had to deviate a bit to make the `suggestions` key work: If there are
no suggestions, then setting `suggestions` to `null` is invalid
according to the JSONSchema. Therefore, I opted for a slightly more
complex implementation, that skips the `suggestions` key entirely if
there are no fixes available for the given diagnostic. Maybe it would
have been easier to set `"suggestions": []`, but I ended up doing it
this way.
I didn't consider notebooks, as I _think_ that RDJson doesn't work with
notebooks. This should be confirmed, and if so, there should be some
form of warning or error emitted when trying to output diagnostics for a
notebook.
I also didn't consider `ruff format`, as this comment:
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/8655#issuecomment-1811446160
suggests that that wouldn't be compatible.
I'm new to Rust, any feedback is appreciated. 🙂 I
implemented this in order to have a productive rainy saturday afternoon,
I'm not knowledgeable about RDJson beyond the sources linked in the
issue.
## Summary
This PR implements the rule B901, which is part of the opinionated rules
of `flake8-bugbear`.
This rule seems to be desired in `ruff` as per
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/3758 and
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/2954#issuecomment-1441162976.
## Test Plan
As this PR was made closely following the
[CONTRIBUTING.md](8a25531a71/CONTRIBUTING.md),
it tests using the snapshot approach, that is described there.
## Sources
The implementation is inspired by [the original implementation in the
`flake8-bugbear`
repository](d1aec4cbef/bugbear.py (L1092)).
The error message and [test
file](d1aec4cbef/tests/b901.py)
where also copied from there.
The documentation I came up with on my own and needs improvement. Maybe
the example given in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/2954#issuecomment-1441162976
could be used, but maybe they are too complex, I'm not sure.
## Open Questions
- [ ] Documentation. (See above.)
- [x] Can I access the parent in a visitor?
The [original
implementation](d1aec4cbef/bugbear.py (L1100))
references the `yield` statement's parent to check if it is an
expression statement. I didn't find a way to do this in `ruff` and used
the `is_expresssion_statement` field on the visitor instead. What are
your thoughts on this? Is it possible and / or desired to access the
parent node here?
- [x] Is `Option::is_some(...)` -> `...unwrap()` the right thing to do?
Referring to [this piece of
code](9d5a280f71/crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/flake8_bugbear/rules/return_x_in_generator.rs?plain=1#L91-L96).
From my understanding, the `.unwrap()` is safe, because it is checked
that `return_` is not `None`. However, I feel like I missed a more
elegant solution that does both in one.
## Other
I don't know a lot about this rule, I just implemented it because I
found it in a
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/labels/good%20first%20issue.
I'm new to Rust, so any constructive critisism is appreciated.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Introduces the skeleton of the flow graph. So far it doesn't actually
handle any non-linear control flow :) But it does show how we can go
from an expression that references a symbol, backward through the flow
graph, to find reachable definitions of that symbol.
Adding non-linear control flow will mean adding flow nodes with multiple
predecessors, which will introduce more complexity into
`ReachableDefinitionsIterator.next()`. But one step at a time.
## Test Plan
Added a (very basic) test.
## Summary
Give red-knot the ability to infer int literal types. This is quick and
easy, mostly because these types are a convenient way to observe
control-flow handling with simple assignments.
## Test Plan
Added test.
## Summary
In the [roadmap for `ruff
server`](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/discussions/10581) support
for vim and kate is listed. Therefore I added setup guides for them
based on the neovim guide. As I don't use pyright I wasn't able to
translate the corresponding part from the neovim guide.
## Test Plan
Doesn't apply.
* Potentially resolves#11619 (nondeterministic hashmap order across
different architectures) in F401 by replacing a hashmap with
nondeterministic traversal order with an ordered mapping.
I'm not sure how to test this with our CI/CD. I don't have an s390x
machine at home. Should I try it in Qemu?
## Summary
In an `__init__.py` file, it's not uncommon to lack a logical indent
(since it may just contain imports). In such cases, we were always
falling back to four-space indent. This PR adds detection for indents
within import groups.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11606.
## Summary
This PR aims to close#10095 by adding an option
`init-allow-undef-export` to the `pyflakes` settings. This option is
currently set to `true` such that behavior is kept identical.
But setting this option to `false` will lead to `F822` warnings to be
shown in all files, **including** `__init__.py` files.
As I've mentioned on #10095, I think `init-allow-undef-export=false`
would be the more user-friendly default option, as it creates fewer
surprises. @charliermarsh what do you think about making that the
default?
With this option in place, it's a single line fix for people that rely
on the old behavior.
And thinking longer term, for future major releases, one could probably
consider deprecating the option and eventually having people just `noqa`
these warnings if they are not wanted.
## Test Plan
I've added a `test_init_f822_enabled` test which repeats the test that
is done in the `init` test but this time with
`init-allow-undef-export=false` and the snap file correctly shows that
ruff will then trigger the otherwise suppressed F822 warning.
closes#10095
## Summary
Removed stray space in sample code snippet that is against ruff's own
default formatting rules.
This documentation appears on
https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/unused-import/
## Test Plan
This is a trivially obvious change, verifiable with `ruff format
--check`
## Summary
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11587.
## Test Plan
- Added a lint error to `test_server.py` in `vscode-ruff`.
- Validated that, prior to this change, diagnostics appeared in the
file.
- Validated that, with this change, no diagnostics were shown.
- Validated that, with this change, no diagnostics were fixed on-save.
## Summary
- Implements `Y066` from `flake8-pyi` as `PYI066`
- Fixes `PYI006` not being raised for `elif` clauses. This would have
conflicted with PYI006's implementation, so decided to do it in the same
PR.
## Test Plan
`cargo test` / `cargo insta review`
* Add a module type, `ModuleTypeId`
* Add an attribute lookup method `get_member` for `Type`
* Only implemented for `ModuleTypeId` and `ClassTypeId`
* [x] Should this be a trait?
*Answer: no*
* [x] Uses `unwrap`, but we should remove that. Maybe add a new variant
to `QueryError`?
*Answer: Return `Option<Type>` as is done elsewhere*
* Add `infer_definition_type` case for `Import`
* Add `infer_expr_type` case for `Attribute`
* Add a test to exercise these
* [x] remove all NOTE/FIXME/TODO after discussing with reviewers
## Summary
This PR ensures that if a variable is bound via `global`, and then the
`global` is read, the originating variable is also marked as read. It's
not perfect, in that it won't detect _rebindings_, like:
```python
from app import redis_connection
def func():
global redis_connection
redis_connection = 1
redis_connection()
```
So, above, `redis_connection` is still marked as unused.
But it does avoid flagging `redis_connection` as unused in:
```python
from app import redis_connection
def func():
global redis_connection
redis_connection()
```
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11518.
## Summary
Follow up to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11521
Removes the extra added complexity for catch all match cases. This
matches the implementation of plain `else` statements.
## Test Plan
Added new test cases.
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR fixes the bug to avoid flattening the global-only settings for
the new server.
This was added in https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11497, possibly
to correctly de-serialize an empty value (`{}`). But, this lead to a bug
where the configuration under the `settings` key was not being read for
global-only variant.
By using #[serde(default)], we ensure that the settings field in the
`GlobalOnly` variant is optional and that an empty JSON object `{}` is
correctly deserialized into `GlobalOnly` with a default `ClientSettings`
instance.
fixes: #11507
## Test Plan
Update the snapshot and existing test case. Also, verify the following
settings in Neovim:
1. Nothing
```lua
ruff = {
cmd = {
'/Users/dhruv/work/astral/ruff/target/debug/ruff',
'server',
'--preview',
},
}
```
2. Empty dictionary
```lua
ruff = {
cmd = {
'/Users/dhruv/work/astral/ruff/target/debug/ruff',
'server',
'--preview',
},
init_options = vim.empty_dict(),
}
```
3. Empty `settings`
```lua
ruff = {
cmd = {
'/Users/dhruv/work/astral/ruff/target/debug/ruff',
'server',
'--preview',
},
init_options = {
settings = vim.empty_dict(),
},
}
```
4. With some configuration:
```lua
ruff = {
cmd = {
'/Users/dhruv/work/astral/ruff/target/debug/ruff',
'server',
'--preview',
},
init_options = {
settings = {
configuration = '/tmp/ruff-repro/pyproject.toml',
},
},
}
```
## Summary
This PR brings back the functionality to remove empty strings when
converting to an f-string in `UP032`.
For context, https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/8712 added this
functionality to remove _trailing_ empty strings but it got removed in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/8697 possibly unexpectedly so.
There's one difference which is that this PR will remove _any_ empty
strings and not just trailing ones. For example,
```diff
--- /Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/src/UP032.py
+++ /Users/dhruv/playground/ruff/src/UP032.py
@@ -1,7 +1,5 @@
(
- "{a}"
- ""
- "{b}"
- ""
-).format(a=1, b=1)
+ f"{1}"
+ f"{1}"
+)
```
## Test Plan
Run `cargo insta test` and update the snapshots.
## Summary
This PR updates the sequence sorting (`RUF022` and `RUF023`) to avoid
using the owned data from the string token. Instead, we will directly
use the reference to the data on the AST. This does introduce a lot of
lifetimes but that's required.
The main motivation for this is to allow removing the `lex_starts_at`
usage easily.
### Alternatives
1. Extract the raw string content (stripping the prefix and quotes)
using the `Locator` and use that for comparison
2. Build up an
[`IndexVec`](3e30962077/crates/ruff_index/src/vec.rs)
and use the newtype index in place of the string value itself. This also
does require lifetimes so we might as well just use the method in this
PR.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test` and no ecosystem changes
## Summary
Fixes#11506.
`RuffSettingsIndex::new` now searches for configuration files in parent
directories.
## Test Plan
I confirmed that the original test case described in the issue worked as
expected.
## Summary
Concurrent GitLab runners clone projects into separate directories, e.g.
`{builds_dir}/$RUNNER_TOKEN_KEY/$CONCURRENT_ID/$NAMESPACE/$PROJECT_NAME`.
Since the fingerprint uses the full path to the file, the fingerprints
calculated by Ruff are different depending on which concurrent runner it
executes on, so often an MR will appear to remove all existing issues
and add them with new fingerprints.
I've adjusted the fingerprint function to use the project relative path,
which fixes this. Unfortunately this will have a breaking change for any
current users of this output - the fingerprints will change and appear
in GitLab as all linting messages having been fixed and then created.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run`
Running `ruff check --output-format gitlab` in a git repo, moving the
repo and running again, verifying no diffs between the outputs
## Summary
Fixes#11534.
`DocumentQuery::source_type` now returns `PySourceType::Stub` when the
document is a `.pyi` file.
## Test Plan
I confirmed that stub-specific rule violations appeared with a build
from this PR (they were not visible from a `main` build).
<img width="1066" alt="Screenshot 2024-05-24 at 2 15 38 PM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/cd519b7e-21e4-41c8-bc30-43eb6d4d438e">
Hi!
I left out some of the functions in the migration rule which became
removed in NumPy 2.0:
- `np.alltrue`
- `np.anytrue`
- `np.cumproduct`
- `np.product`
Addressing: https://github.com/numpy/numpy/issues/26493
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
Current doc says `sys.version[0]` will select the first digit of a major
version number (correct) then as an example says
> e.g., `"3.10"` would evaluate to `"1"`
(would actually evaluate to `"3"`). Changed the example version to a
two-digit number to make the problem more clear.
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
ran the following:
- `cargo run -p ruff -- check
crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/flake8_2020/YTT301.py
--no-cache`
- `cargo insta review`
- `cargo test`
which all passed.
## Summary
Rule `logging-warn` (`G010`) prescribes a change from `warn` to
`warning` and has a corresponding autofix, but the autofix is mistakenly
titled ```"Convert to `warn`"``` instead of ```"Convert to `warning`"```
(the latter is what the autofix actually does). Seems to be a plain
typo.
## Summary
Fixes#11516
`ruff server` was sending both regular source actions and notebook
source actions back when passed an empty action filter. This PR makes a
few small changes so that notebook source actions are not sent when
regular source actions are sent, which means that an empty filter will
only return regular source actions.
## Test Plan
I confirmed that duplicate code actions no longer appeared in Neovim,
using a configuration similar to the one from the original issue.
<img width="509" alt="Screenshot 2024-05-23 at 11 48 48 PM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/9a5d6907-dd41-48bd-b015-8a344c5e0b3f">
## Summary
It turns out that `singledispatch` does end up evaluating all arguments,
even though only the first is used to dispatch.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11520.
## Summary
Addresses #8451 by implementing rule 116 to add an unsafe fix when sleep
is used with a >24 hour interval to instead consider sleeping forever.
This rule is added as async instead as I my understanding was that these
trio rules would be moved to async anyway.
There are a couple of TODOs, which address further extending the rule by
adding support for lookups and evaluations, and also supporting `anyio`.
## Summary
This PR updates the `FA102` rule logic to use the `Importer` which is
available on the `Checker`.
The main motivation is that this would make updating the `Importer` to
use the `Tokens` struct which will be required to remove the
`lex_starts_at` usage in `Insertion::start_of_block` method.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11236.
This PR fixes several issues, most of which relate to non-VS Code
editors (Helix and Neovim).
1. Global-only initialization options are now correctly deserialized
from Neovim and Helix
2. Empty diagnostics are now published correctly for Neovim and Helix.
3. A workspace folder is created at the current working directory if the
initialization parameters send an empty list of workspace folders.
4. The server now gracefully handles opening files outside of any known
workspace, and will use global fallback settings taken from client
editor settings and a user settings TOML, if it exists.
## Test Plan
I've tested to confirm that each issue has been fixed.
* Global-only initialization options are now correctly deserialized from
Neovim and Helix + the server gracefully handles opening files outside
of any known workspace
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/4f33477f-20c8-4e50-8214-6608b1a1ea6b
* Empty diagnostics are now published correctly for Neovim and Helix
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/c93f56a0-f75d-466f-9f40-d77f99cf0637
* A workspace folder is created at the current working directory if the
initialization parameters send an empty list of workspace folders.
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/b4b2e818-4b0d-40ce-961d-5831478cc726
## Summary
Similar to #11414, this PR extends `UP037` to flag quoted annotations
that are located in positions that won't be evaluated at runtime.
For example, the quotes on `Tuple` are unnecessary in:
```python
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
if TYPE_CHECKING:
from typing import Tuple
def foo():
x: "Tuple[int, int]" = (0, 0)
foo()
```
## Summary
Recent changes made in the [Jupyter Notebook feature
PR](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11206) caused automatic
configuration reloading to stop working. This was because we would check
for paths to reload using the changed path, when we should have been
using the parent path of the changed path (to get the directory it was
changed in).
Additionally, this PR fixes an issue where `ruff.toml` and `.ruff.toml`
files were not being automatically reloaded.
Finally, this PR improves configuration reloading by actively publishing
diagnostics for notebook documents (which won't be affected by the
workspace refresh since they don't use pull diagnostics). It will also
publish diagnostics for text documents if pull diagnostics aren't
supported.
## Test Plan
To test this, open an existing configuration file in a codebase, and
make modifications that will affect one or more open Python / Jupyter
Notebook files. You should observe that the diagnostics for both kinds
of files update automatically when the file changes are saved.
Here's a test video showing what a successful test should look like:
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/7172b598-d6de-4965-b33c-6cb8b911ef6c
## Summary
Previously, `ruff.applyFormat`, seen in VS Code as the command `Ruff:
Format Document`, would only format the currently active notebook cell
inside a notebook document. This PR makes `ruff.applyFormat` format the
entire notebook document at once, operating on each code cell in order.
## Test Plan
1. Open a notebook document that has multiple unformatted code cells.
2. Run `Ruff: Format Document` through the Command Palette
(`Ctrl/Cmd+Shift+P` by default)
3. Observe that all code cells in the notebook have been formatted.
## Summary
This PR moves the `has_comments` function from `Indexer` to
`CommentRanges`. The main motivation is that the `CommentRanges` will
now be built by the parser which is shared between the linter and the
formatter. Thus, the `CommentRanges` will be removed from the `Indexer`.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Matching Pylint, we now omit the `try` body itself from branch counting.
Each `except` counts as a branch, as does the `else` and the `finally`.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11205.
## Summary
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10858.
`ruff server` now supports `*.ipynb` (aka Jupyter Notebook) files.
Extensive internal changes have been made to facilitate this, which I've
done some work to contextualize with documentation and an pre-review
that highlights notable sections of the code.
`*.ipynb` cells should behave similarly to `*.py` documents, with one
major exception. The format command `ruff.applyFormat` will only apply
to the currently selected notebook cell - if you want to format an
entire notebook document, use `Format Notebook` from the VS Code context
menu.
## Test Plan
The VS Code extension does not yet have Jupyter Notebook support
enabled, so you'll first need to enable it manually. To do this,
checkout the `pre-release` branch and modify `src/common/server.ts` as
follows:
Before:

After:

I recommend testing this PR with large, complicated notebook files. I
used notebook files from [this popular
repository](https://github.com/jakevdp/PythonDataScienceHandbook/tree/master/notebooks)
in my preliminary testing.
The main thing to test is ensuring that notebook cells behave the same
as Python documents, besides the aforementioned issue with
`ruff.applyFormat`. You should also test adding and deleting cells (in
particular, deleting all the code cells and ensure that doesn't break
anything), changing the kind of a cell (i.e. from markup -> code or vice
versa), and creating a new notebook file from scratch. Finally, you
should also test that source actions work as expected (and across the
entire notebook).
Note: `ruff.applyAutofix` and `ruff.applyOrganizeImports` are currently
broken for notebook files, and I suspect it has something to do with
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11248. Once this is fixed, I
will update the test plan accordingly.
---------
Co-authored-by: nolan <nolan.king90@gmail.com>
The wording 'negative comparison' is a rather vague description of the
'is not' operation and does not describe what the 'not in' operation
does (potentially copied from 'is not'). This was replaced with more
precise language to describe the operators taken from the official
python docs[1].
Both rules didn't have a strong reasoning besides 'it's bad, use the
other'. The origin of these rules seems to be PEP8[2] which prefers 'is
not' over 'not ... is' for readability. This is now reflected in the
description.
[1]:
https://docs.python.org/3/reference/expressions.html#membership-test-operations
[2]: https://peps.python.org/pep-0008/#programming-recommendations
## Summary
If an annotation won't be evaluated at runtime, we don't need to flag
`from __future__ import annotations` as required. This applies both to
quoted annotations and annotations outside of runtime-evaluated
positions, like:
```python
def main() -> None:
a_list: list[str] | None = []
a_list.append("hello")
```
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11397.
## Summary
* Update documentation for F401 following recent PRs
* #11168
* #11314
* Deprecate `ignore_init_module_imports`
* Add a deprecation pragma to the option and a "warn user once" message
when the option is used.
* Restore the old behavior for stable (non-preview) mode:
* When `ignore_init_module_imports` is set to `true` (default) there are
no `__init_.py` fixes (but we get nice fix titles!).
* When `ignore_init_module_imports` is set to `false` there are unsafe
`__init__.py` fixes to remove unused imports.
* When preview mode is enabled, it overrides
`ignore_init_module_imports`.
* Fixed a bug in fix titles where `import foo as bar` would recommend
reexporting `bar as bar`. It now says to reexport `foo as foo`. (In this
case we don't issue a fix, fwiw; it was just a fix title bug.)
## Test plan
Added new fixture tests that reuse the existing fixtures for
`__init__.py` files. Each of the three situations listed above has
fixture tests. The F401 "stable" tests cover:
> * When `ignore_init_module_imports` is set to `true` (default) there
are no `__init_.py` fixes (but we get nice fix titles!).
The F401 "deprecated option" tests cover:
> * When `ignore_init_module_imports` is set to `false` there are unsafe
`__init__.py` fixes to remove unused imports.
These complement existing "preview" tests that show the new behavior
which recommends fixes in `__init__.py` according to whether the import
is 1st party and other circumstances (for more on that behavior see:
#11314).
## Summary
This is a follow-up PR to #11445 update the `E27` rules to consider soft
keywords as well.
## Test Plan
Add test cases consisting of soft keywords and update the snapshot.
## Summary
We weren't treating the escaped newline as a valid condition to trigger
the safer fix (add an extra backslash before each invalid escape
sequence).
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11461.
## Summary
This PR updates the `TokenKind::is_keyword` check to include soft
keywords. To account for this change, it adds a new
`is_non_soft_keyword` method.
The usage in logical line rules were updated to use the
`is_non_soft_keyword` method but it'll be updated to use `is_keyword` in
a follow-up PR (#11446).
While, the parser usages were kept as is. And because of that, the
snapshots for two test cases were updated in a better direction.
## Test Plan
`cargo insta test`
## Summary
We already have handling for "references that get quoted within our
quoted references", but we were assuming a specific ordering in the way
edits were generated.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11449.
This is useful for extracting the defaults in order to construct
equivalent configs by external scripts. This is my first non-hello-world
rust code, comments and suggested tests appreciated.
## Summary
We already have `ruff linter --output-format json`, this provides `ruff
config x --output-format json` as well. I plan to use this to construct
an equivalent config snippet to include in some managed repos, so when
we update their version of ruff and it adds new lints, they get a PR
that includes the commented-out new lints.
Note that the no-args form of `ruff config` ignores output-format
currently, but probably should obey it (although array-of-strings
doesn't seem that useful, looking for input on format).
## Test Plan
I could use a hand coming up with a typical way to write automated tests
for this.
```sh-session
(.venv) [timhatch:ruff ]$ ./target/debug/ruff config lint.select
A list of rule codes or prefixes to enable. Prefixes can specify exact
rules (like `F841`), entire categories (like `F`), or anything in
between.
When breaking ties between enabled and disabled rules (via `select` and
`ignore`, respectively), more specific prefixes override less
specific prefixes.
Default value: ["E4", "E7", "E9", "F"]
Type: list[RuleSelector]
Example usage:
``toml
# On top of the defaults (`E4`, E7`, `E9`, and `F`), enable flake8-bugbear (`B`) and flake8-quotes (`Q`).
select = ["E4", "E7", "E9", "F", "B", "Q"]
``
(.venv) [timhatch:ruff ]$ ./target/debug/ruff config lint.select --output-format json
{
"Field": {
"doc": "A list of rule codes or prefixes to enable. Prefixes can specify exact\nrules (like `F841`), entire categories (like `F`), or anything in\nbetween.\n\nWhen breaking ties between enabled and disabled rules (via `select` and\n`ignore`, respectively), more specific prefixes override less\nspecific prefixes.",
"default": "[\"E4\", \"E7\", \"E9\", \"F\"]",
"value_type": "list[RuleSelector]",
"scope": null,
"example": "# On top of the defaults (`E4`, E7`, `E9`, and `F`), enable flake8-bugbear (`B`) and flake8-quotes (`Q`).\nselect = [\"E4\", \"E7\", \"E9\", \"F\", \"B\", \"Q\"]",
"deprecated": null
}
}
```
## Summary
As discussed in issue #11408, PLR0912 has a broader definition of
"branches" than I expected. This updates the documentation to include
this definition.
I also updated the example to include several different types of
branches, while still maintaining dictionary lookup as an alternative
solution. (Crafting a realistic example was quite a challenge 😅).
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11408.
## Summary
This moves the string-prefix enumerations in `ruff_python_ast` to a
separate submodule. I think this helps clarify that these prefixes are
purely abstract: they only depend on each other, and do not depend on
any of the other code in `nodes.rs` in any way. Moreover, while various
AST nodes _use_ them, they're not really nodes themselves, so they feel
slightly out of place in `nodes.rs`.
I considered moving all of them to `str.rs`, but it felt like enough
code that it could be a separate submodule.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
Followup on #11168 and resolve#10391
# User facing changes
* F401 now recommends a fix to add unused import bindings to to
`__all__` if a single `__all__` list or tuple is found in `__init__.py`.
* If there are no `__all__` found in the file, fall back to recommending
redundant-aliases.
* If there are multiple `__all__` or only one but of the wrong type (non
list or tuple) then diagnostics are generated without fixes.
* `fix_title` is updated to reflect what the fix/recommendation is.
Subtlety: For a renamed import such as `import foo as bees`, we can
generate a fix to add `bees` to `__all__` but cannot generate a fix to
produce a redundant import (because that would break uses of the binding
`bees`).
# Implementation changes
* Add `name` field to `ImportBinding` to contain the name of the
_binding_ we want to add to `__all__` (important for the `import foo as
bees` case). It previously only contained the `AnyImport` which can give
us information about the import but not the binding.
* Add `binding` field to `UnusedImport` to contain the same. (Naming
note: the field `name` field already existed on `UnusedImport` and
contains the qualified name of the imported symbol/module)
* Change `fix_by_reexporting` to branch on the size of `dunder_all:
Vec<&Expr>`
* For length 0 call the edit-producing function `make_redundant_alias`.
* For length 1 call edit-producing function `add_to_dunder_all`.
* Otherwise, produce no fix.
* Implement the edit-producing function `add_to_dunder_all` and add unit
tests.
* Implement several fixture tests: empty `__all__ = []`, nonempty
`__all__ = ["foo"]`, mis-typed `__all__ = None`, plus-eq `__all__ +=
["foo"]`
* `UnusedImportContext::Init` variant now has two fields: whether the
fix is in `__init__.py` and how many `__all__` were found.
# Other changes
* Remove a spurious pattern match and instead use field lookups b/c the
addition of a field would have required changing the unrelated pattern.
* Tweak input type of `make_redundant_alias`
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR follows up from #11420 to move `UP034` to use `TokenKind`
instead of `Tok`.
The main reason to have a separate PR is so that the reviewing is easy.
This required a lot more updates because the rule used an index (`i`) to
keep track of the current position in the token vector. Now, as it's
just an iterator, we just use `next` to move the iterator forward and
extract the relevant information.
This is part of https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11401
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
This PR moves the following rules to use `TokenKind` instead of `Tok`:
* `PLE2510`, `PLE2512`, `PLE2513`, `PLE2514`, `PLE2515`
* `E701`, `E702`, `E703`
* `ISC001`, `ISC002`
* `COM812`, `COM818`, `COM819`
* `W391`
I've paused here because the next set of rules
(`pyupgrade::rules::extraneous_parentheses`) indexes into the token
slice but we only have an iterator implementation. So, I want to isolate
that change to make sure the logic is still the same when I move to
using the iterator approach.
This is part of #11401
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Alternative to #11237
This PR adds a new `Tokens` struct which is a newtype wrapper around a
vector of lexer output. This allows us to add a `kinds` method which
returns an iterator over the corresponding `TokenKind`. This iterator is
implemented as a separate `TokenKindIter` struct to allow using the type
and provide additional methods like `peek` directly on the iterator.
This exposes the linter to access the stream of `TokenKind` instead of
`Tok`.
Edit: I've made the necessary downstream changes and plan to merge the
entire stack at once.
## Summary
This PR updates the linter benchmark to use the `tokenize` function
instead of the lexer.
The linter expects the token list to be up to and including the first
error which is what the `ruff_python_parser::tokenize` function returns.
This was not a problem before because the benchmarks only uses valid
Python code.
## Summary
This PR adds a newtype wrapper around `Vec<FStringElement>` that derefs
to a `&Vec<FStringElement>`.
Both f-string and format specifier are made up of `Vec<FStringElement>`.
By creating a newtype wrapper around it, we can share the methods for
both parent types.
## Summary
This PR adds support to iterate over each part of a string-like
expression.
This similar to the one in the formatter:
128414cd95/crates/ruff_python_formatter/src/string/any.rs (L121-L125)
Although I don't think it's a 1-1 replacement in the formatter because
the one implemented in the formatter has another information for certain
variants (as can be seen for `FString`).
The main motivation for this is to avoid duplication for rules which
work only on the parts of the string and doesn't require any information
from the parent node. Here, the parent node being the expression node
which could be an implicitly concatenated string.
This PR also updates certain rule implementation to make use of this and
avoids logic duplication.
## Summary
This PR renames `AnyStringKind` to `AnyStringFlags` and `AnyStringFlags`
to `AnyStringFlagsInner`.
The main motivation is to have consistent usage of "kind" and "flags".
For each string kind, it's "flags" like `StringLiteralFlags`,
`BytesLiteralFlags`, and `FStringFlags` but it was `AnyStringKind` for
the "any" variant.
## Summary
Changes `future-rewritable-type-annotation` (`FA100`) message to be less
confusing. Uses phrasing from the rule documentation to be consistent.
For example,
```
from_typing_import.py:5:13: FA100 Add `from __future__ import annotations` to rewrite `typing.List` more succinctly
```
Closes#10573.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run`
## Summary
Should this consider the decorator only if the name is actually a
property or is the logic in this PR correct?
fixes: #11358
## Test Plan
Add test case.
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug where the auto-fix for `TCH005` would delete the
entire `if` statement.
The fix in this PR is to not consider it a violation if there are any
`elif`/`else` blocks. This also matches the behavior of the original
plugin.
fixes: #11368
## Test plan
Add test cases.
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10594.
Code actions to disable a diagnostic via `noqa` comment are now
available.
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/6d3bcf11-a9d9-499b-8c7f-a10cd39cfbba
`DiagnosticFix` has been changed so that `noqa` code actions appear even
for diagnostics with no available quick fix. It can contain quick fix
edits, `noqa` comment edits, or both.
## Test Plan
The scenarios that need to be tested are as follows:
* A code action to disable a diagnostic should be available for every
diagnostic.
* Using this code action should append to the appropriate line with the
diagnostic, or modify an existing `noqa` comment.
* Adding a `noqa` comment manually should make a diagnostic disappear
* `Fix all auto-fixable problems` should not add `noqa` comments
* Removing a code from a `noqa` comment should make the diagnostic
re-appear
## Summary
`--add-noqa` now runs in two stages: first, the linter finds all
diagnostics that need noqa comments and generate edits on a per-line
basis. Second, these edits are applied, in order, to the document.
A public-facing function, `generate_noqa_edits`, has also been
introduced, which returns noqa edits generated on a per-diagnostic
basis. This will be used by `ruff server` for noqa comment quick-fixes.
## Test Plan
Unit tests have been updated.
## Summary
This PR adds updates the semantic model to detect attribute docstring.
Refer to [PEP 258](https://peps.python.org/pep-0258/#attribute-docstrings)
for the definition of an attribute docstring.
This PR doesn't add full support for it but only considers string
literals as attribute docstring for the following cases:
1. A string literal following an assignment statement in the **global
scope**.
2. A global class attribute
For an assignment statement, it's considered an attribute docstring only
if the target expression is a name expression (`x = 1`). So, chained
assignment, multiple assignment or unpacking, and starred expression,
which are all valid in the target position, aren't considered here.
In `__init__` method, an assignment to the `self` variable like `self.x = 1`
is also a candidate for an attribute docstring. **This PR does not
support this position.**
## Test Plan
I used the following source code along with a print statement to verify
that the attribute docstring detection is correct.
Refer to the PR description for the code snippet.
I'll add this in the follow-up PR
(https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11302) which uses this method.
## Summary
Lots of TODOs and things to clean up here, but it demonstrates the
working lint rule.
## Test Plan
```
➜ cat main.py
from typing import override
from base import B
class C(B):
@override
def method(self): pass
➜ cat base.py
class B: pass
➜ cat typing.py
def override(func):
return func
```
(We provide our own `typing.py` since we don't have typeshed vendored or
type stub support yet.)
```
➜ ./target/debug/red_knot main.py
...
1 0.012086s TRACE red_knot Main Loop: Tick
[crates/red_knot/src/main.rs:157:21] diagnostics = [
"Method C.method is decorated with `typing.override` but does not override any base class method",
]
```
If we add `def method(self): pass` to class `B` in `base.py` and run
red_knot again, there is no lint error.
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Resolves#11263
Detect `pathlib.Path.open` calls which do not specify a file encoding.
## Test Plan
Test cases added to fixture.
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
This PR vendors typeshed!
- The first commit vendors the stdlib directory from typeshed into a new crates/red_knot/vendored_typeshed directory.
- The second commit adjusts various linting config files to make sure that the vendored code is excluded from typo checks, formatting checks, etc.
- The LICENSE and README.md files are also vendored, but all other directories and files (stubs, scripts, tests, test_cases, etc.) are excluded. We should have no need for them (except possibly stubs/, discussed in more depth below).
- Similar to the way pyright has a commit.txt file in its vendored copy of typeshed, to indicate which typeshed commit the vendored code corresponds to, I've also added a crates/red_knot/vendored_typeshed/source_commit.txt file in the third commit of this PR.
One open question is: should we vendor the stdlib and stubs directories, or just the stdlib directory? The stubs/ directory contains stubs for 162 third-party packages outside the stdlib. Mypy and typeshed_client1 only vendor the stdlib directory; pyright and pyre vendor both the stdlib and stubs directories; pytype vendors the entire typeshed repo (scripts/, tests/ and all).
In this PR, I've chosen to copy mypy and typeshed_client. Unlike vendoring the stdlib, which is unavoidable if we want to do typechecking of the stdlib, it's not strictly necessary to vendor the stubs directory: each subdirectory in stubs is published to PyPI as a standalone stubs distribution that can be (uv)-pip-installed into a virtual environment. It might be useful for our users if we vendored those stubs anyway, but there are costs as well as benefits to doing so (apart from just the sheer amount of vendored code in the ruff repository), so I'd rather consider it separately.
Resolves https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11313
## Summary
PLR0912(too-many-branches) did not count branches inside with: blocks.
With this fix, the branches inside with statements are also counted.
## Test Plan
Added a new test case.
## Summary
This PR removes the cyclic dev dependency some of the crates had with
the parser crate.
The cyclic dependencies are:
* `ruff_python_ast` has a **dev dependency** on `ruff_python_parser` and
`ruff_python_parser` directly depends on `ruff_python_ast`
* `ruff_python_trivia` has a **dev dependency** on `ruff_python_parser`
and `ruff_python_parser` has an indirect dependency on
`ruff_python_trivia` (`ruff_python_parser` - `ruff_python_ast` -
`ruff_python_trivia`)
Specifically, this PR does the following:
* Introduce two new crates
* `ruff_python_ast_integration_tests` and move the tests from the
`ruff_python_ast` crate which uses the parser in this crate
* `ruff_python_trivia_integration_tests` and move the tests from the
`ruff_python_trivia` crate which uses the parser in this crate
### Motivation
The main motivation for this PR is to help development. Before this PR,
`rust-analyzer` wouldn't provide any intellisense in the
`ruff_python_parser` crate regarding the symbols in `ruff_python_ast`
crate.
```
[ERROR][2024-05-03 13:47:06] .../vim/lsp/rpc.lua:770 "rpc" "/Users/dhruv/.cargo/bin/rust-analyzer" "stderr" "[ERROR project_model::workspace] cyclic deps: ruff_python_parser(Idx::<CrateData>(50)) -> ruff_python_ast(Idx::<CrateData>(37)), alternative path: ruff_python_ast(Idx::<CrateData>(37)) -> ruff_python_parser(Idx::<CrateData>(50))\n"
```
## Test Plan
Check the logs of `rust-analyzer` to not see any signs of cyclic
dependency.
## Summary
While I was here, I also updated the rule to use
`function_type::classify` rather than hard-coding `staticmethod` and
friends.
Per Carl:
> Enum instances are already referred to by the class, forming a cycle
that won't get collected until the class itself does. At which point the
`lru_cache` itself would be collected, too.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9912.
## Summary
Historically, we only ignored `flake8-blind-except` if you re-raised or
logged the exception as a _direct_ child statement; but it could be
nested somewhere. This was just a known limitation at the time of adding
the previous logic.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11289.
## Summary
A follow-up to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11222. `ruff
server` stalls during shutdown with Neovim because after it receives an
exit notification and closes the I/O thread, it attempts to log a
success message to `stderr`. Removing this log statement fixes this
issue.
## Test Plan
Track the instances of `ruff` in the OS task manager as you open and
close Neovim. A new instance should appear when Neovim starts and it
should disappear once Neovim is closed.
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11258.
This PR fixes the settings resolver to match the expected behavior when
file-based configuration is not available.
## Test Plan
In a workspace with no file-based configuration, set a setting in your
editor and confirm that this setting is used instead of the default.
## Summary
Users can now include tildes and environment variables in the provided
path, just like with `--config`.
Closes#11277.
## Test Plan
Set the configuration path to `"ruff.configuration": "~/x.toml"`;
verified that the server attempted to read from `/Users/crmarsh/x.toml`.
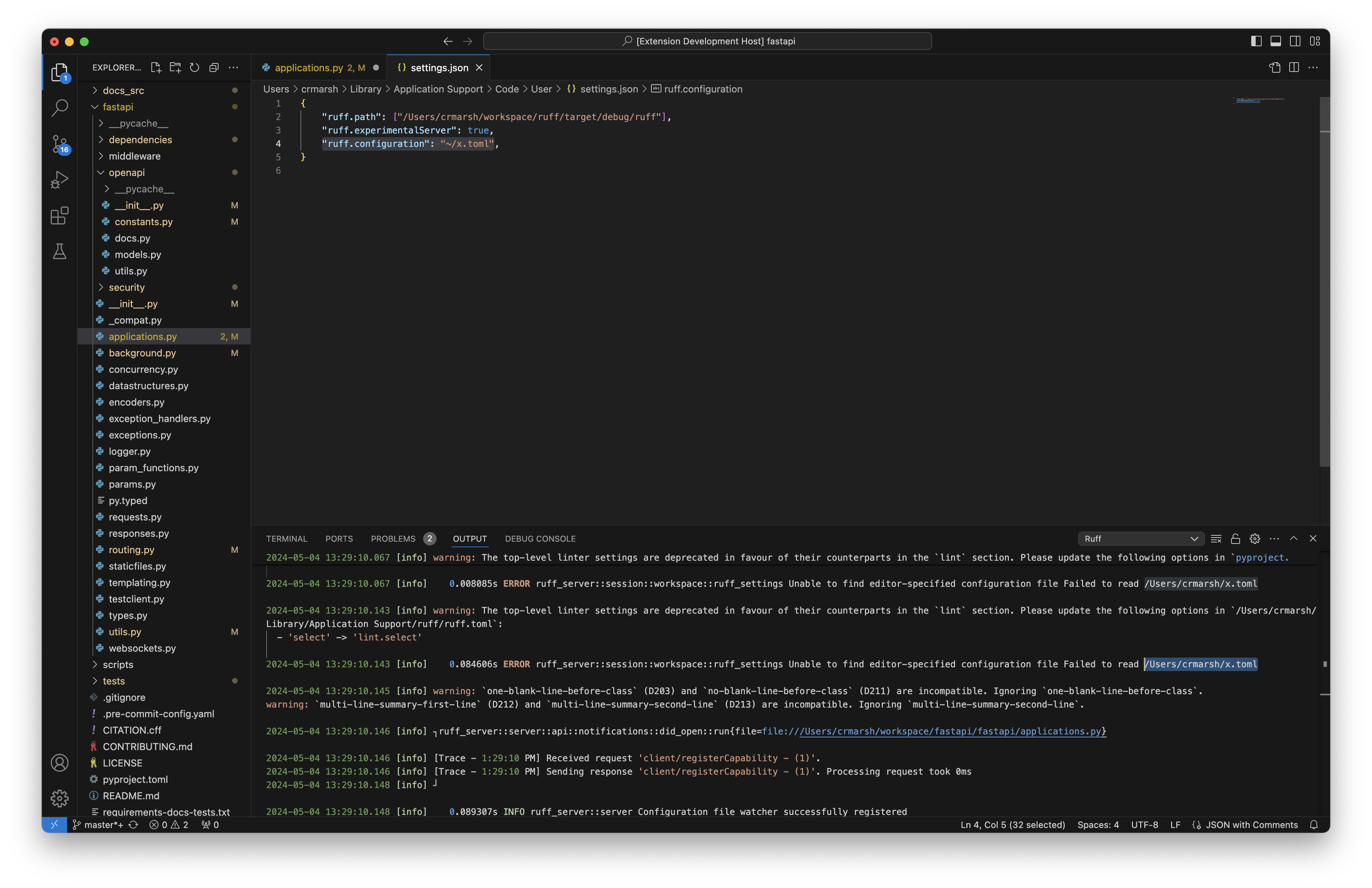
## Summary
Change `hardcoded-tmp-directory-extend` example to follow the schema:
1e91a09918/ruff.schema.json (L896-L901)
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
## Summary
In #9218 `Rule::NeverUnion` was partially removed from a
`checker.any_enabled` call. This makes the change consistent.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11207.
The server would hang after handling a shutdown request on
`IoThreads::join()` because a global sender (`MESSENGER`, used to send
`window/showMessage` notifications) would remain allocated even after
the event loop finished, which kept the writer I/O thread channel open.
To fix this, I've made a few structural changes to `ruff server`. I've
wrapped the send/receive channels and thread join handle behind a new
struct, `Connection`, which facilitates message sending and receiving,
and also runs `IoThreads::join()` after the event loop finishes. To
control the number of sender channels, the `Connection` wraps the sender
channel in an `Arc` and only allows the creation of a wrapper type,
`ClientSender`, which hold a weak reference to this `Arc` instead of
direct channel access. The wrapper type implements the channel methods
directly to prevent access to the inner channel (which would allow the
channel to be cloned). ClientSender's function is analogous to
[`WeakSender` in
`tokio`](https://docs.rs/tokio/latest/tokio/sync/mpsc/struct.WeakSender.html).
Additionally, the receiver channel cannot be accessed directly - the
`Connection` only exposes an iterator over it.
These changes will guarantee that all channels are closed before the I/O
threads are joined.
## Test Plan
Repeatedly open and close an editor utilizing `ruff server` while
observing the task monitor. The net total amount of open `ruff`
instances should be zero once all editor windows have closed.
The following logs should also appear after the server is shut down:
<img width="835" alt="Screenshot 2024-04-30 at 3 56 22 PM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/404b74f5-ef08-4bb4-9fa2-72e72b946695">
This can be tested on VS Code by changing the settings and then checking
`Output`.
* Add `decorators: Vec<Type>` to `FunctionType` struct
* Thread decorators through two `add_function` definitions
* Populate decorators at the callsite in `infer_symbol_type`
* Small test
Resolves#10390 and starts to address #10391
# Changes to behavior
* In `__init__.py` we now offer some fixes for unused imports.
* If the import binding is first-party this PR suggests a fix to turn it
into a redundant alias.
* If the import binding is not first-party, this PR suggests a fix to
remove it from the `__init__.py`.
* The fix-titles are specific to these new suggested fixes.
* `checker.settings.ignore_init_module_imports` setting is
deprecated/ignored. There is probably a documentation change to make
that complete which I haven't done.
---
<details><summary>Old description of implementation changes</summary>
# Changes to the implementation
* In the body of the loop over import statements that contain unused
bindings, the bindings are partitioned into `to_reexport` and
`to_remove` (according to how we want to resolve the fact they're
unused) with the following predicate:
```rust
in_init && is_first_party(checker, &import.qualified_name().to_string())
// true means make it a reexport
```
* Instead of generating a single fix per import statement, we now
generate up to two fixes per import statement:
```rust
(fix_by_removing_imports(checker, node_id, &to_remove, in_init).ok(),
fix_by_reexporting(checker, node_id, &to_reexport, dunder_all).ok())
```
* The `to_remove` fixes are unsafe when `in_init`.
* The `to_explicit` fixes are safe. Currently, until a future PR, we
make them redundant aliases (e.g. `import a` would become `import a as
a`).
## Other changes
* `checker.settings.ignore_init_module_imports` is deprecated/ignored.
Instead, all fixes are gated on `checker.settings.preview.is_enabled()`.
* Got rid of the pattern match on the import-binding bound by the inner
loop because it seemed less readable than referencing fields on the
binding.
* [x] `// FIXME: rename "imports" to "bindings"` if reviewer agrees (see
code)
* [x] `// FIXME: rename "node_id" to "import_statement"` if reviewer
agrees (see code)
<details>
<summary><h2>Scope cut until a future PR</h2></summary>
* (Not implemented) The `to_explicit` fixes will be added to `__all__`
unless it doesn't exist. When `__all__` doesn't exist they're resolved
by converting to redundant aliases (e.g. `import a` would become `import
a as a`).
---
</details>
# Test plan
* [x] `crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pyflakes/F401_24`
contains an `__init__.py` with*out* `__all__` that exercises the
features in this PR, but it doesn't pass.
* [x]
`crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pyflakes/F401_25_dunder_all`
contains an `__init__.py` *with* `__all__` that exercises the features
in this PR, but it doesn't pass.
* [x] Write unit tests for the new edit functions in
`fix::edits::make_redundant_alias`.
</details>
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
## Summary
This PR removes the `ImportMap` implementation and all its routing
through ruff.
The import map was added in https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/3243
but we then never ended up using it to do cross file analysis.
We are now working on adding multifile analysis to ruff, and revisit
import resolution as part of it.
```
hyperfine --warmup 10 --runs 20 --setup "./target/release/ruff clean" \
"./target/release/ruff check crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/cpython -e -s --extend-select=I" \
"./target/release/ruff-import check crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/cpython -e -s --extend-select=I"
Benchmark 1: ./target/release/ruff check crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/cpython -e -s --extend-select=I
Time (mean ± σ): 37.6 ms ± 0.9 ms [User: 52.2 ms, System: 63.7 ms]
Range (min … max): 35.8 ms … 39.8 ms 20 runs
Benchmark 2: ./target/release/ruff-import check crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/cpython -e -s --extend-select=I
Time (mean ± σ): 36.0 ms ± 0.7 ms [User: 50.3 ms, System: 58.4 ms]
Range (min … max): 34.5 ms … 37.6 ms 20 runs
Summary
./target/release/ruff-import check crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/cpython -e -s --extend-select=I ran
1.04 ± 0.03 times faster than ./target/release/ruff check crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/cpython -e -s --extend-select=I
```
I suspect that the performance improvement should even be more
significant for users that otherwise don't have any diagnostics.
```
hyperfine --warmup 10 --runs 20 --setup "cd ../ecosystem/airflow && ../../ruff/target/release/ruff clean" \
"./target/release/ruff check ../ecosystem/airflow -e -s --extend-select=I" \
"./target/release/ruff-import check ../ecosystem/airflow -e -s --extend-select=I"
Benchmark 1: ./target/release/ruff check ../ecosystem/airflow -e -s --extend-select=I
Time (mean ± σ): 53.7 ms ± 1.8 ms [User: 68.4 ms, System: 63.0 ms]
Range (min … max): 51.1 ms … 58.7 ms 20 runs
Benchmark 2: ./target/release/ruff-import check ../ecosystem/airflow -e -s --extend-select=I
Time (mean ± σ): 50.8 ms ± 1.4 ms [User: 50.7 ms, System: 60.9 ms]
Range (min … max): 48.5 ms … 55.3 ms 20 runs
Summary
./target/release/ruff-import check ../ecosystem/airflow -e -s --extend-select=I ran
1.06 ± 0.05 times faster than ./target/release/ruff check ../ecosystem/airflow -e -s --extend-select=I
```
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Fixes#11185Fixes#11214
Document path and package information is now forwarded to the Ruff
linter, which allows `per-file-ignores` to correctly match against the
file name. This also fixes an issue where the import sorting rule didn't
distinguish between third-party and first-party packages since we didn't
pass in the package root.
## Test Plan
`per-file-ignores` should ignore files as expected. One quick way to
check is by adding this to your `pyproject.toml`:
```toml
[tool.ruff.lint.per-file-ignores]
"__init__.py" = ["ALL"]
```
Then, confirm that no diagnostics appear when you add code to an
`__init__.py` file (besides syntax errors).
The import sorting fix can be verified by failing to reproduce the
original issue - an `I001` diagnostic should not appear in
`other_module.py`.
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11158.
A settings file in the ruff user configuration directory will be used as
a configuration fallback, if it exists.
## Test Plan
Create a `pyproject.toml` or `ruff.toml` configuration file in the ruff
user configuration directory.
* On Linux, that will be `$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/ruff/` or `$HOME/.config`
* On macOS, that will be `$HOME/Library/Application Support`
* On Windows, that will be `{FOLDERID_LocalAppData}`
Then, open a file inside of a workspace with no configuration. The
settings in the user configuration file should be used.
## Summary
I think the check included here does make sense, but I don't see why we
would allow it if a value is provided for the attribute -- since, in
that case, isn't it _not_ abstract?
Closes: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11208.
## Summary
This PR changes the `DebugStatistics` and `ReleaseStatistics` structs so
that they implement a common `StatisticsRecorder` trait, and makes the
`KeyValueCache` struct generic over a type parameter bound to that
trait. The advantage of this approach is that it's much harder for the
`DebugStatistics` and `ReleaseStatistics` structs to accidentally grow
out of sync in the methods that they implement, which was the cause of
the release-build failure recently fixed in #11177.
## Test Plan
`cargo test -p red_knot` and `cargo build --release` both continue to
pass for me locally
* Adds `Symbol.flag` bitfield. Populates it from (the three renamed)
`add_or_update_symbol*` methods.
* Currently there are these flags supported:
* `IS_DEFINED` is set in a scope where a variable is defined.
* `IS_USED` is set in a scope where a variable is referenced. (To have
both this and `IS_DEFINED` would require two separate appearances of a
variable in the same scope-- one def and one use.)
* `MARKED_GLOBAL` and `MARKED_NONLOCAL` are **not yet implemented**.
(*TODO: While traversing, if you find these declarations, add these
flags to the variable.*)
* Adds `Symbol.kind` field (commented) and the data structure which will
populate it: `Kind` which is an enum of freevar, cellvar,
implicit_global, and implicit_local. **Not yet populated**. (*TODO: a
second pass over the scope (or the ast?) will observe the
`MARKED_GLOBAL` and `MARKED_NONLOCAL` flags to populate this field. When
that's added, we'll uncomment the field.*)
* Adds a few tests that the `IS_DEFINED` and `IS_USED` fields are
correctly set and/or merged:
* Unit test that subsequent calls to `add_or_update_symbol` will merge
the flag arguments.
* Unit test that in the statement `x = foo`, the variable `foo` is
considered used but not defined.
* Unit test that in the statement `from bar import foo`, the variable
`foo` is considered defined but not used.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carl Meyer <carl@astral.sh>
## Summary
This PR adds a basic README for the `ruff_python_parser` crate and
updates the CONTRIBUTING docs with the fuzzer and benchmark section.
Additionally, it also updates some inline documentation within the
parser crate and splits the `parse_program` function into
`parse_single_expression` and `parse_module` which will be called by
matching against the `Mode`.
This PR doesn't go into too much internal detail around the parser logic
due to the following reasons:
1. Where should the docs go? Should it be as a module docs in `lib.rs`
or in README?
2. The parser is still evolving and could include a lot of refactors
with the future work (feedback loop and improved error recovery and
resilience)
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
`cargo build --release` currently fails to compile on `main`:
<details>
```
error[E0599]: no method named `hit` found for struct `ReleaseStatistics` in the current scope
--> crates/red_knot/src/cache.rs:22:29
|
22 | self.statistics.hit();
| ^^^ method not found in `ReleaseStatistics`
...
145 | pub struct ReleaseStatistics;
| ---------------------------- method `hit` not found for this struct
error[E0599]: no method named `miss` found for struct `ReleaseStatistics` in the current scope
--> crates/red_knot/src/cache.rs:25:29
|
25 | self.statistics.miss();
| ^^^^ method not found in `ReleaseStatistics`
...
145 | pub struct ReleaseStatistics;
| ---------------------------- method `miss` not found for this struct
error[E0599]: no method named `hit` found for struct `ReleaseStatistics` in the current scope
--> crates/red_knot/src/cache.rs:36:33
|
36 | self.statistics.hit();
| ^^^ method not found in `ReleaseStatistics`
...
145 | pub struct ReleaseStatistics;
| ---------------------------- method `hit` not found for this struct
error[E0599]: no method named `miss` found for struct `ReleaseStatistics` in the current scope
--> crates/red_knot/src/cache.rs:41:33
|
41 | self.statistics.miss();
| ^^^^ method not found in `ReleaseStatistics`
...
145 | pub struct ReleaseStatistics;
| ---------------------------- method `miss` not found for this struct
```
</details>
This is because in a release build, `CacheStatistics` is a type alias
for `ReleaseStatistics`, and `ReleaseStatistics` doesn't have `hit()` or
`miss()` methods. (In a debug build, `CacheStatistics` is a type alias
for `DebugStatistics`, which _does_ have those methods.)
Possibly we could make this less likely to happen in the future by
making both structs implement a common trait instead of using type
aliases that vary depending on whether it's a debug build or not? For
now, though, this PR just brings the two structs in sync w.r.t. the
methods they expose.
## Test Plan
`cargo build --release` now once again compiles for me locally
## Summary
This PR adds an override to the fixer to ensure that we apply any
`redefined-while-unused` fixes prior to `unused-import`.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10905.
## Summary
Implement duplicate code detection as part of `RUF100`, mirroring the
behavior of `flake8-noqa` (`NQA005`) mentioned in #850. The idea to
merge the rule into `RUF100` was suggested by @MichaReiser
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10325#issuecomment-2025535444.
## Test Plan
Test cases were added to the fixture.
This syntax wasn't "deprecated" in Python 3; it was removed.
I started looking at this rule because I was curious how Ruff could even
detect this without a Python 2 parser. Then I realized that
"print >> f, x" is actually valid Python 3 syntax: it creates a tuple
containing a right-shifted version of the print function.
## Summary
Based on discussion in #10850.
As it stands today `RUF100` will attempt to replace code redirects with
their target codes even though this is not the "goal" of `RUF100`. This
behavior is confusing and inconsistent, since code redirects which don't
otherwise violate `RUF100` will not be updated. The behavior is also
undocumented. Additionally, users who want to use `RUF100` but do not
want to update redirects have no way to opt out.
This PR explicitly detects redirects with a new rule `RUF101` and
patches `RUF100` to keep original codes in fixes and reporting.
## Test Plan
Added fixture.
## Summary
Closes#10985.
The server now supports a custom TOML configuration file as a client
setting. The setting must be an absolute path to a file. If the file is
called `pyproject.toml`, the server will attempt to parse it as a
pyproject file - otherwise, it will attempt to parse it as a `ruff.toml`
file, even if the file has a name besides `ruff.toml`.
If an option is set in both the custom TOML configuration file and in
the client settings directly, the latter will be used.
## Test Plan
1. Create a `ruff.toml` file outside of the workspace you are testing.
Set an option that is different from the one in the configuration for
your test workspace.
2. Set the path to the configuration in NeoVim:
```lua
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup {
init_options = {
settings = {
configuration = "absolute/path/to/your/configuration"
}
}
}
```
3. Confirm that the option in the configuration file is used, regardless
of what the option is set to in the workspace configuration.
4. Add the same option, with a different value, to the NeoVim
configuration directly. For example:
```lua
require('lspconfig').ruff.setup {
init_options = {
settings = {
configuration = "absolute/path/to/your/configuration",
lint = {
select = []
}
}
}
}
```
5. Confirm that the option set in client settings is used, regardless of
the value in either the custom configuration file or in the workspace
configuration.
## Summary
This PR fixes the bug where the formatter would format an f-string and
could potentially change the AST.
For a triple-quoted f-string, the element can't be formatted into
multiline if it has a format specifier because otherwise the newline
would be treated as part of the format specifier.
Given the following f-string:
```python
f"""aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb ccccccccccc {
variable:.3f} ddddddddddddddd eeeeeeee"""
```
The formatter sees that the f-string is already multiline so it assumes
that it can contain line breaks i.e., broken into multiple lines. But,
in this specific case we can't format it as:
```python
f"""aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb ccccccccccc {
variable:.3f
} ddddddddddddddd eeeeeeee"""
```
Because the format specifier string would become ".3f\n", which is not
the original string (`.3f`).
If the original source code already contained a newline, they'll be
preserved. For example:
```python
f"""aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb ccccccccccc {
variable:.3f
} ddddddddddddddd eeeeeeee"""
```
The above will be formatted as:
```py
f"""aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb ccccccccccc {variable:.3f
} ddddddddddddddd eeeeeeee"""
```
Note that the newline after `.3f` is part of the format specifier which
needs to be preserved.
The Python version is irrelevant in this case.
fixes: #10040
## Test Plan
Add some test cases to verify this behavior.
## Summary
This is intended to address
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/issues/425, and is a follow-up
to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11062.
A new client setting is now supported by the server,
`prioritizeFileConfiguration`. This is a boolean setting (default:
`false`) that, if set to `true`, will instruct the configuration
resolver to prioritize file configuration (aka discovered TOML files)
over configuration passed in by the editor.
A corresponding extension PR has been opened, which makes this setting
available for VS Code:
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/pull/457.
## Test Plan
To test this with VS Code, you'll need to check out [the VS Code
PR](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/pull/457) that adds this
setting.
The test process is similar to
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/11062, but in scenarios where the
editor configuration would take priority over file configuration, file
configuration should take priority.
## Summary
Resolves#11102
The error stems from these lines
f5c7a62aa6/crates/ruff_linter/src/noqa.rs (L697-L702)
I don't really understand the purpose of incrementing the last index,
but it makes the resulting range invalid for indexing into `contents`.
For now I just detect if the index is too high in `blanket_noqa` and
adjust it if necessary.
## Test Plan
Created fixture from issue example.
## Summary
This PR updates the playground to display the AST even if it contains a
syntax error. This could be useful for development and also to give a
quick preview of what error recovery looks like.
Note that not all recovery is correct but this allows us to iterate
quickly on what can be improved.
## Test Plan
Build the playground locally and test it.
<img width="1688" alt="Screenshot 2024-04-25 at 21 02 22"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/67177269/2b94934c-4f2c-4a9a-9693-3d8460ed9d0b">
## Summary
Fixes#11114.
As part of the `onClose` handler, we publish an empty array of
diagnostics for the document being closed, similar to
[`ruff-lsp`](187d7790be/ruff_lsp/server.py (L459-L464)).
This prevent phantom diagnostics from lingering after a document is
closed. We'll only do this if the client doesn't support pull
diagnostics, because otherwise clearing diagnostics is their
responsibility.
## Test Plan
Diagnostics should no longer appear for a document in the Problems tab
after the document is closed.
## Summary
This allows `raise from` in BLE001.
```python
try:
...
except Exception as e:
raise ValueError from e
```
Fixes#10806
## Test Plan
Test case added.
## Summary
Continuation of https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/9444.
> When the formatter is fully cached, it turns out we actually spend
meaningful time mapping from file to `Settings` (since we use a
hierarchical approach to settings). Using `matchit` rather than
`BTreeMap` improves fully-cached performance by anywhere from 2-5%
depending on the project, and since these are all implementation details
of `Resolver`, it's minimally invasive.
`matchit` supports escaping routing characters so this change should now
be fully compatible.
## Test Plan
On my machine I'm seeing a ~3% improvement with this change.
```
hyperfine --warmup 20 -i "./target/release/main format ../airflow" "./target/release/ruff format ../airflow"
Benchmark 1: ./target/release/main format ../airflow
Time (mean ± σ): 58.1 ms ± 1.4 ms [User: 63.1 ms, System: 66.5 ms]
Range (min … max): 56.1 ms … 62.9 ms 49 runs
Benchmark 2: ./target/release/ruff format ../airflow
Time (mean ± σ): 56.6 ms ± 1.5 ms [User: 57.8 ms, System: 67.7 ms]
Range (min … max): 54.1 ms … 63.0 ms 51 runs
Summary
./target/release/ruff format ../airflow ran
1.03 ± 0.04 times faster than ./target/release/main format ../airflow
```
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Add support for hover menu to ruff_server, as requested in
[10595](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10595).
Majority of new code is in hover.rs.
I reused the regex from ruff-lsp's implementation. Also reused the
format_rule_text function from ruff/src/commands/rule.rs
Added capability registration in server.rs, and added the handler to
api.rs.
## Test Plan
Tested in NVIM v0.10.0-dev-2582+g2a8cef6bd, configured with lspconfig
using the default options (other than cmd pointing to my test build,
with options "server" and "--preview"). OS: Ubuntu 24.04, kernel
6.8.0-22.
---------
Co-authored-by: Jane Lewis <me@jane.engineering>
## Summary
This is a follow-up to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10984 that
implements configuration resolution for editor configuration. By 'editor
configuration', I'm referring to the client settings that correspond to
Ruff configuration/options, like `preview`, `select`, and so on. These
will be combined with 'project configuration' (configuration taken from
project files such as `pyproject.toml`) to generate the final linter and
formatter settings used by `RuffSettings`. Editor configuration takes
priority over project configuration.
In a follow-up pull request, I'll implement a new client setting that
allows project configuration to override editor configuration, as per
[this issue](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/issues/425).
## Review guide
The first commit, e38966d8843becc7234fa7d46009c16af4ba41e9, is just
doing re-arrangement so that we can pass the right things to
`RuffSettings::resolve`. The actual resolution logic is in the second
commit, 0eec9ee75c10e5ec423bd9f5ce1764f4d7a5ad86. It might help to look
at these comments individually since the diff is rather messy.
## Test Plan
For the settings to show up in VS Code, you'll need to checkout this
branch: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/pull/456.
To test that the resolution for a specific setting works as expected,
run through the following scenarios, setting it in project and editor
configuration as needed:
| Set in project configuration? | Set in editor configuration? |
Expected Outcome |
|-------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| No | No | The editor should behave as if the setting was set to its
default value. |
| Yes | No | The editor should behave as if the setting was set to the
value in project configuration. |
| No | Yes | The editor should behave as if the setting was set to the
value in editor configuration. |
| Yes | Yes (but distinctive from project configuration) | The editor
should behave as if the setting was set to the value in editor
configuration. |
An exception to this is `extendSelect`, which does not have an analog in
TOML configuration. Instead, you should verify that `extendSelect`
amends the `select` setting. If `select` is set in both editor and
project configuration, `extendSelect` will only append to the `select`
value in editor configuration, so make sure to un-set it there if you're
testing `extendSelect` with `select` in project configuration.
## Summary
This PR refactors unary expression parsing with the following changes:
* Ability to get `OperatorPrecedence` from a unary operator (`UnaryOp`)
* Implement methods on `TokenKind`
* Add `as_unary_operator` which returns an `Option<UnaryOp>`
* Add `as_unary_arithmetic_operator` which returns an `Option<UnaryOp>`
(used for pattern parsing)
* Rename `is_unary` to `is_unary_arithmetic_operator` (used in the
linter)
resolves: #10752
## Test Plan
Verify that the existing test cases pass, no ecosystem changes, run the
Python based fuzzer on 3000 random inputs and run it on dozens of
open-source repositories.
## Summary
This PR refactors the binary expression parsing in a way to make it
readable and easy to understand. It draws inspiration from the suggested
edits in the linked messages in #10752.
### Changes
* Ability to get the precedence of an operator
* From a boolean operator (`BinOp`) to `OperatorPrecedence`
* From a binary operator (`Operator`) to `OperatorPrecedence`
* No comparison operator because all of them have the same precedence
* Implement methods on `TokenKind` to convert it to an appropriate
operator enum
* Add `as_boolean_operator` which returns an `Option<BoolOp>`
* Add `as_binary_operator` which returns an `Option<Operator>`
* No `as_comparison_operator` because it requires lookahead and I'm not
sure if `token.as_comparison_operator(peek)` is a good way to implement
it
* Introduce `BinaryLikeOperator`
* Constructed from two tokens using the methods from the second point
* Add `precedence` method using the conversion methods mentioned in the
first point
* Make most of the functions in `TokenKind` private to the module
* Use `self` instead of `&self` for `TokenKind`
fixes: #11072
## Test Plan
Refer #11088
## Summary
This PR does a few things but the main change is that is makes
associativity a property of operator precedence.
1. Rename `Precedence` -> `OperatorPrecedence`
2. Rename `parse_expression_with_precedence` ->
`parse_binary_expression_or_higher`
3. Move `current_binding_power` to `OperatorPrecedence::try_from_tokens`
[^1]
4. Add a `OperatorPrecedence::is_right_associative` method
5. Move from `increment_precedence` to using `<=` / `<` to check if the
parsing loop needs to stop [^2]
[^1]: Another alternative would be to have two separate methods to avoid
lookahead as it's required only for once case (`not in`). So,
`try_from_current_token(current).or_else(|| try_from_next_token(current,
peek))`
[^2]: This will allow us to easily make the refactors mentioned in
#10752
## Test Plan
Make sure the precedence parsing algorithm is still correct by running
the test suite, fuzz testing it and running it against a dozen or so
open-source repositories.
## Summary
This PR adds a new `ExpressionContext` struct which is used in
expression parsing.
This solves the following problem:
1. Allowing starred expression with different precedence
2. Allowing yield expression in certain context
3. Remove ambiguity with `in` keyword when parsing a `for ... in`
statement
For context, (1) was solved by adding `parse_star_expression_list` and
`parse_star_expression_or_higher` in #10623, (2) was solved by by adding
`parse_yield_expression_or_else` in #10809, and (3) was fixed in #11009.
All of the mentioned functions have been removed in favor of the context
flags.
As mentioned in #11009, an ideal solution would be to implement an
expression context which is what this PR implements. This is passed
around as function parameter and the call stack is used to automatically
reset the context.
### Recovery
How should the parser recover if the target expression is invalid when
an expression can consume the `in` keyword?
1. Should the `in` keyword be part of the target expression?
2. Or, should the expression parsing stop as soon as `in` keyword is
encountered, no matter the expression?
For example:
```python
for yield x in y: ...
# Here, should this be parsed as
for (yield x) in (y): ...
# Or
for (yield x in y): ...
# where the `in iter` part is missing
```
Or, for binary expression parsing:
```python
for x or y in z: ...
# Should this be parsed as
for (x or y) in z: ...
# Or
for (x or y in z): ...
# where the `in iter` part is missing
```
This need not be solved now, but is very easy to change. For context
this PR does the following:
* For binary, comparison, and unary expressions, stop at `in`
* For lambda, yield expressions, consume the `in`
## Test Plan
1. Add test cases for the `for ... in` statement and verify the
snapshots
2. Make sure the existing test suite pass
3. Run the fuzzer for around 3000 generated source code
4. Run the updated logic on a dozen or so open source repositories
(codename "parser-checkouts")
## Summary
Fixes#11059
Several major editors don't support [pull
diagnostics](https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/specifications/lsp/3.17/specification/#textDocument_pullDiagnostics),
a method of sending diagnostics to the client that was introduced in
version `0.3.17` of the specification. Until now, `ruff server` has only
used pull diagnostics, which resulted in diagnostics not being available
on Neovim and Helix, which don't support pull diagnostics yet (though
Neovim `10.0` will have support for this).
`ruff server` will now utilize the older method of sending diagnostics,
known as 'publish diagnostics', when pull diagnostics aren't supported
by the client. This involves re-linting a document every time it is
opened or modified, and then sending the diagnostics generated from that
lint to the client via the `textDocument/publishDiagnostics`
notification.
## Test Plan
The easiest way to test that this PR works is to check if diagnostics
show up on Neovim `<=0.9`.
## Summary
Fixes#10463
Add `FURB192` which detects violations like this:
```python
# Bad
a = sorted(l)[0]
# Good
a = min(l)
```
There is a caveat that @Skylion007 has pointed out, which is that
violations with `reverse=True` technically aren't compatible with this
change, in the edge case where the unstable behavior is intended. For
example:
```python
from operator import itemgetter
data = [('red', 1), ('blue', 1), ('red', 2), ('blue', 2)]
min(data, key=itemgetter(0)) # ('blue', 1)
sorted(data, key=itemgetter(0))[0] # ('blue', 1)
sorted(data, key=itemgetter(0), reverse=True)[-1] # ('blue, 2')
```
This seems like a rare edge case, but I can make the `reverse=True`
fixes unsafe if that's best.
## Test Plan
This is unit tested.
## References
https://github.com/dosisod/refurb/pull/333/files
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
The `operator.itemgetter` behavior changes where there's more than one
argument, such that `operator.itemgetter(0)` yields `r[0]`, rather than
`(r[0],)`.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/11075.
## Summary
There is no class `integer` in python, nor is there a type `integer`, so
I updated the docs to remove the backticks on these references, such
that it is the representation of an integer, and not a reference.
## Summary
Move `blanket-noqa` rule from the token checker to the noqa checker.
This allows us to make use of the line directives already computed in
the noqa checker.
## Test Plan
Verified test results are unchanged.
Resolves#10187
<details>
<summary>Old PR description; accurate through commit e86dd7d; probably
best to leave this fold closed</summary>
## Description of change
In the case of a printf-style format string with only one %-placeholder
and a variable at right (e.g. `"%s" % var`):
* The new behavior attempts to dereference the variable and then match
on the bound expression to distinguish between a 1-tuple (fix), n-tuple
(bug 🐛), or a non-tuple (fix). Dereferencing is via
`analyze::typing::find_binding_value`.
* If the variable cannot be dereferenced, then the type-analysis routine
is called to distinguish only tuple (no-fix) or non-tuple (fix). Type
analysis is via `analyze::typing::is_tuple`.
* If any of the above fails, the rule still fires, but no fix is
offered.
## Alternatives
* If the reviewers think that singling out the 1-tuple case is too
complicated, I will remove that.
* The ecosystem results show that no new fixes are detected. So I could
probably delete all the variable dereferencing code and code that tries
to generate fixes, tbh.
## Changes to existing behavior
**All the previous rule-firings and fixes are unchanged except for** the
"false negatives" in
`crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pyupgrade/UP031_1.py`. Those
previous "false negatives" are now true positives and so I moved them to
`crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pyupgrade/UP031_0.py`.
<details>
<summary>Existing false negatives that are now true positives</summary>
```
crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pyupgrade/UP031_0.py:134:1: UP031 Use format specifiers instead of percent format
|
133 | # UP031 (no longer false negatives)
134 | 'Hello %s' % bar
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ UP031
135 |
136 | 'Hello %s' % bar.baz
|
= help: Replace with format specifiers
crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pyupgrade/UP031_0.py:136:1: UP031 Use format specifiers instead of percent format
|
134 | 'Hello %s' % bar
135 |
136 | 'Hello %s' % bar.baz
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ UP031
137 |
138 | 'Hello %s' % bar['bop']
|
= help: Replace with format specifiers
crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pyupgrade/UP031_0.py:138:1: UP031 Use format specifiers instead of percent format
|
136 | 'Hello %s' % bar.baz
137 |
138 | 'Hello %s' % bar['bop']
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ UP031
|
= help: Replace with format specifiers
```
One of them newly offers a fix.
```
# UP031 (no longer false negatives)
-'Hello %s' % bar
+'Hello {}'.format(bar)
```
This fix occurs because the new code dereferences `bar` to where it was
defined earlier in the file as a non-tuple:
```python
bar = {"bar": y}
```
---
</details>
## Behavior requiring new tests
Additionally, we now handle a few cases that we didn't previously test.
These cases are when a string has a single %-placeholder and the
righthand operand to the modulo operator is a variable **which can be
dereferenced.** One of those was shown in the previous section (the
"dereference non-tuple" case).
<details>
<summary>New cases handled</summary>
```
crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pyupgrade/UP031_0.py:126:1: UP031 [*] Use format specifiers instead of percent format
|
125 | t1 = (x,)
126 | "%s" % t1
| ^^^^^^^^^ UP031
127 | # UP031: deref t1 to 1-tuple, offer fix
|
= help: Replace with format specifiers
crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pyupgrade/UP031_0.py:130:1: UP031 Use format specifiers instead of percent format
|
129 | t2 = (x,y)
130 | "%s" % t2
| ^^^^^^^^^ UP031
131 | # UP031: deref t2 to n-tuple, this is a bug
|
= help: Replace with format specifiers
```
One of these offers a fix.
```
t1 = (x,)
-"%s" % t1
+"{}".format(t1[0])
# UP031: deref t1 to 1-tuple, offer fix
```
The other doesn't offer a fix because it's a bug.
---
</details>
---
</details>
## Changes to existing behavior
In the case of a string with a single %-placeholder and a single
ambiguous righthand argument to the modulo operator, (e.g. `"%s" % var`)
the rule now fires and offers a fix. We explain about this in the "fix
safety" section of the updated documentation.
## Documentation changes
I swapped the order of the "known problems" and the "examples" sections
so that the examples which describe the rule are first, before the
exceptions to the rule are described. I also tweaked the language to be
more explicit, as I had trouble understanding the documentation at
first. The "known problems" section is now "fix safety" but the content
is largely similar.
The diff of the documentation changes looks a little difficult unless
you look at the individual commits.
## Summary
I happened to notice that we box `TypeParams` on `StmtClassDef` but not
on `StmtFunctionDef` and wondered why, since `StmtFunctionDef` is bigger
and sets the size of `Stmt`.
@charliermarsh found that at the time we started boxing type params on
classes, classes were the largest statement type (see #6275), but that's
no longer true.
So boxing type-params also on functions reduces the overall size of
`Stmt`.
## Test Plan
The `<=` size tests are a bit irritating (since their failure doesn't
tell you the actual size), but I manually confirmed that the size is
actually 120 now.
Occasionally you intentionally have iterables of differing lengths. The
rule permits this by explicitly adding `strict=False`, but this was not
documented.
## Summary
The rule does not currently document how to avoid it when having
differing length iterables is intentional. This PR adds that to the rule
documentation.
## Summary
This fixes a bug where the parser would panic when there is a "gap" in
the token source.
What's a gap?
The reason it's `<=` instead of just `==` is because there could be
whitespaces between
the two tokens. For example:
```python
# last token end
# | current token (newline) start
# v v
def foo \n
# ^
# assume there's trailing whitespace here
```
Or, there could tokens that are considered "trivia" and thus aren't
emitted by the token
source. These are comments and non-logical newlines. For example:
```python
# last token end
# v
def foo # comment\n
# ^ current token (newline) start
```
In either of the above cases, there's a "gap" between the end of the
last token and start
of the current token.
## Test Plan
Add test cases and update the snapshots.
## Summary
This PR adds a new `Clause::Case` and uses it to parse the body of a
`case` block. Earlier, it was using `Match` which would give an
incorrect error message like:
```
|
1 | match subject:
2 | case 1:
3 | case 2: ...
| ^^^^ Syntax Error: Expected an indented block after `match` statement
|
```
## Test Plan
Add test case and update the snapshot.
Add pylint rule invalid-hash-returned (PLE0309)
See https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/970 for rules
Test Plan: `cargo test`
TBD: from the description: "Strictly speaking `bool` is a subclass of
`int`, thus returning `True`/`False` is valid. To be consistent with
other rules (e.g.
[PLE0305](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10962)
invalid-index-returned), ruff will raise, compared to pylint which will
not raise."
## Summary
This PR fixes the bug in with items parsing where it would fail to
recognize that the parenthesized expression is part of a large binary
expression.
## Test Plan
Add test cases and verified the snapshots.
## Summary
This PR fixes the bug in parenthesized with items parsing where the `if`
expression would result into a syntax error.
The reason being that once we identify that the ambiguous left
parenthesis belongs to the context expression, the parser converts the
parsed with item into an equivalent expression. Then, the parser
continuous to parse any postfix expressions. Now, attribute, subscript,
and call are taken into account as they're grouped in
`parse_postfix_expression` but `if` expression has it's own parsing
function.
Use `parse_if_expression` once all postfix expressions have been parsed.
Ideally, I think that `if` could be included in postfix expression
parsing as they can be chained as well (`x if True else y if True else
z`).
## Test Plan
Add test cases and verified the snapshots.
## Summary
This PR fixes a bug in the new parser which involves the parser context
w.r.t. for statement. This is specifically around the `in` keyword which
can be present in the target expression and shouldn't be considered to
be part of the `for` statement header. Ideally it should use a context
which is passed between functions, thus using a call stack to set /
unset a specific variant which will be done in a follow-up PR as it
requires some amount of refactor.
## Test Plan
Add test cases and update the snapshots.
(Supersedes #9152, authored by @LaBatata101)
## Summary
This PR replaces the current parser generated from LALRPOP to a
hand-written recursive descent parser.
It also updates the grammar for [PEP
646](https://peps.python.org/pep-0646/) so that the parser outputs the
correct AST. For example, in `data[*x]`, the index expression is now a
tuple with a single starred expression instead of just a starred
expression.
Beyond the performance improvements, the parser is also error resilient
and can provide better error messages. The behavior as seen by any
downstream tools isn't changed. That is, the linter and formatter can
still assume that the parser will _stop_ at the first syntax error. This
will be updated in the following months.
For more details about the change here, refer to the PR corresponding to
the individual commits and the release blog post.
## Test Plan
Write _lots_ and _lots_ of tests for both valid and invalid syntax and
verify the output.
## Acknowledgements
- @MichaReiser for reviewing 100+ parser PRs and continuously providing
guidance throughout the project
- @LaBatata101 for initiating the transition to a hand-written parser in
#9152
- @addisoncrump for implementing the fuzzer which helped
[catch](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10903)
[a](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10910)
[lot](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10966)
[of](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10896)
[bugs](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10877)
---------
Co-authored-by: Victor Hugo Gomes <labatata101@linuxmail.org>
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
## Summary
The following client settings have been introduced to the language
server:
* `lint.preview`
* `format.preview`
* `lint.select`
* `lint.extendSelect`
* `lint.ignore`
* `exclude`
* `lineLength`
`exclude` and `lineLength` apply to both the linter and formatter.
This does not actually use the settings yet, but makes them available
for future use.
## Test Plan
Snapshot tests have been updated.
## Summary
A setup guide has been written for NeoVim under a new
`crates/ruff_server/docs/setup` folder, where future setup guides will
also go. This setup guide was adapted from the [`ruff-lsp`
guide](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp?tab=readme-ov-file#example-neovim).
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
Add pylint rule invalid-length-returned (PLE0303)
See https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/970 for rules
Test Plan: `cargo test`
TBD: from the description: "Strictly speaking `bool` is a subclass of
`int`, thus returning `True`/`False` is valid. To be consistent with
other rules (e.g.
[PLE0305](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10962)
invalid-index-returned), ruff will raise, compared to pylint which will
not raise."
## Summary
If the user is analyzing a script (i.e., we have no module path), it
seems reasonable to use the script name when trying to identify paths to
objects defined _within_ the script.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10960.
## Test Plan
Ran:
```shell
check --isolated --select=B008 \
--config 'lint.flake8-bugbear.extend-immutable-calls=["test.A"]' \
test.py
```
On:
```python
class A: pass
def f(a=A()):
pass
```
## Summary
The server now requests a [workspace diagnostic
refresh](https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/specifications/lsp/3.17/specification/#diagnostic_refresh)
when a configuration file gets changed. This means that diagnostics for
all open files will be automatically re-requested by the client on a
config change.
## Test Plan
You can test this by opening several files in VS Code, setting `select`
in your file configuration to `[]`, and observing that the diagnostics
go away once the file is saved (besides any `Pylance` diagnostics).
Restore it to what it was before, and you should see the diagnostics
automatically return once a save happens.
## Summary
I've added support for configuring the `ruff check` output file via the
environment variable `RUFF_OUTPUT_FILE` akin to #1731.
This is super useful when, e.g., generating a [GitLab code quality
report](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/testing/code_quality.html#implement-a-custom-tool)
while running Ruff as a pre-commit hook. Usually, `ruff check` should
print its human-readable output to `stdout`, but when run through
`pre-commit` _in a GitLab CI job_ it should write its output in `gitlab`
format to a file. So, to override these two settings only during CI,
environment variables come handy, and `RUFF_OUTPUT_FORMAT` already
exists but `RUFF_OUTPUT_FILE` has been missing.
A (simplified) GitLab CI job config for this scenario might look like
this:
```yaml
pre-commit:
stage: test
image: python
variables:
RUFF_OUTPUT_FILE: gl-code-quality-report.json
RUFF_OUTPUT_FORMAT: gitlab
before_script:
- pip install pre-commit
script:
- pre-commit run --all-files --show-diff-on-failure
artifacts:
reports:
codequality: gl-code-quality-report.json
```
## Test Plan
I tested it manually.
## Summary
This PR switches more callsites of `SemanticModel::is_builtin` to move
over to the new methods I introduced in #10919, which are more concise
and more accurate. I missed these calls in the first PR.
## Summary
Fixes#10866.
Introduces the `show_err_msg!` macro which will send a message to be
shown as a popup to the client via the `window/showMessage` LSP method.
## Test Plan
Insert various `show_err_msg!` calls in common code paths (for example,
at the beginning of `event_loop`) and confirm that these messages appear
in your editor.
To test that panicking works correctly, add this to the top of the `fn
run` definition in
`crates/ruff_server/src/server/api/requests/execute_command.rs`:
```rust
panic!("This should appear");
```
Then, try running a command like `Ruff: Format document` from the
command palette (`Ctrl/Cmd+Shift+P`). You should see the following
messages appear:

## Summary
Fixes#10780.
The server now send code actions to the client with a Ruff-specific
kind, `source.*.ruff`. The kind filtering logic has also been reworked
to support this.
## Test Plan
Add this to your `settings.json` in VS Code:
```json
{
"[python]": {
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.organizeImports.ruff": "explicit",
},
}
}
```
Imports should be automatically organized when you manually save with
`Ctrl/Cmd+S`.
## Summary
Configuration is no longer the property of a workspace but rather of
individual documents. Just like the Ruff CLI, each document is
configured based on the 'nearest' project configuration. See [the Ruff
documentation](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/configuration/#config-file-discovery)
for more details.
To reduce the amount of times we resolve configuration for a file, we
have an index for each workspace that stores a reference-counted pointer
to a configuration for a given folder. If another file in the same
folder is opened, the configuration is simply re-used rather than us
re-resolving it.
## Guide for reviewing
The first commit is just the restructuring work, which adds some noise
to the diff. If you want to quickly understand what's actually changed,
I recommend looking at the two commits that come after it.
f7c073d441 makes configuration a property
of `DocumentController`/`DocumentRef`, moving it out of `Workspace`, and
it also sets up the `ConfigurationIndex`, though it doesn't implement
its key function, `get_or_insert`. In the commit after it,
fc35618f17, we implement `get_or_insert`.
## Test Plan
The best way to test this would be to ensure that the behavior matches
the Ruff CLI. Open a project with multiple configuration files (or add
them yourself), and then introduce problems in certain files that won't
show due to their configuration. Add those same problems to a section of
the project where those rules are run. Confirm that the lint rules are
run as expected with `ruff check`. Then, open your editor and confirm
that the diagnostics shown match the CLI output.
As an example - I have a workspace with two separate folders, `pandas`
and `scipy`. I created a `pyproject.toml` file in `pandas/pandas/io` and
a `ruff.toml` file in `pandas/pandas/api`. I changed the `select` and
`preview` settings in the sub-folder configuration files and confirmed
that these were reflected in the diagnostics. I also confirmed that this
did not change the diagnostics for the `scipy` folder whatsoever.
## Summary
This change adds a rule to detect functions declared `async` but lacking
any of `await`, `async with`, or `async for`. This resolves#9951.
## Test Plan
This change was tested by following
https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/contributing/#rule-testing-fixtures-and-snapshots
and adding positive and negative cases for each of `await` vs nothing,
`async with` vs `with`, and `async for` vs `for`.
## Summary
This PR moves the `Q003` rule to AST checker.
This is the final rule that used the docstring detection state machine
and thus this PR removes it as well.
resolves: #7595resolves: #7808
## Test Plan
- [x] `cargo test`
- [x] Make sure there are no changes in the ecosystem
## Summary
Adds more aggressive logic to PLR1730, `if-stmt-min-max`
Closes#10907
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Hi! 👋
Thanks for sharing ruff as software libre — it helps me keep Python code
quality up with pre-commit, both locally and CI 🙏
While studying the examples at
https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/function-uses-loop-variable/#example I
noticed that the last of the examples had a bug: prior to this fix, `ì`
was passed to the lambda for `x` rather than for `i` — the two are
mixed-up. The reason it's easy to overlook is because addition is an
commutative operation and so `x + i` and `i + x` give the same result
(and least with integers), despite the mix-up. For proof, let me demo
the relevant part with before and after:
```python
In [1]: from functools import partial
In [2]: [partial(lambda x, i: (x, i), i)(123) for i in range(3)]
Out[2]: [(0, 123), (1, 123), (2, 123)]
In [3]: [partial(lambda x, i: (x, i), i=i)(123) for i in range(3)]
Out[3]: [(123, 0), (123, 1), (123, 2)]
```
Does that make sense?
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
Was manually tested using IPython.
CC @r4f @grandchild
## Summary
If `RUF100` was included in a per-file-ignore, we respected it on cases
like `# noqa: F401`, but not the blanket variant (`# noqa`).
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10906.
## Summary
Implement new rule: Prefer augmented assignment (#8877). It checks for
the assignment statement with the form of `<expr> = <expr>
<binary-operator> …` with a unsafe fix to use augmented assignment
instead.
## Test Plan
1. Snapshot test is included in the PR.
2. Manually test with playground.
Refs #3172
## Summary
Fix a typo in the docs example, and add a test for the case where a
negative pattern and a positive pattern overlap.
The behavior here is simple: patterns (positive or negative) are always
additive if they hit (i.e. match for a positive pattern, don't match for
a negated pattern). We never "un-ignore" previously-ignored rules based
on a pattern (positive or negative) failing to hit.
It's simple enough that I don't really see other cases we need to add
tests for (the tests we have cover all branches in the ignores_from_path
function that implements the core logic), but open to reviewer feedback.
I also didn't end up changing the docs to explain this more, because I
think they are accurate as written and don't wrongly imply any more
complex behavior. Open to reviewer feedback on this as well!
After some discussion, I think allowing negative patterns to un-ignore
rules is too confusing and easy to get wrong; if we need that, we should
add `per-file-selects` instead.
## Test Plan
Test/docs only change; tests pass, docs render and look right.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR adds the implementation for the current
[flake8-bugbear](https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8-bugbear)'s B038 rule.
The B038 rule checks for mutation of loop iterators in the body of a for
loop and alerts when found.
Rational:
Editing the loop iterator can lead to undesired behavior and is probably
a bug in most cases.
Closes#9511.
Note there will be a second iteration of B038 implemented in
`flake8-bugbear` soon, and this PR currently only implements the weakest
form of the rule.
I'd be happy to also implement the further improvements to B038 here in
ruff 🙂
See https://github.com/PyCQA/flake8-bugbear/issues/454 for more
information on the planned improvements.
## Test Plan
Re-using the same test file that I've used for `flake8-bugbear`, which
is included in this PR (look for the `B038.py` file).
Note: this is my first time using `rust` (beside `rustlings`) - I'd be
very happy about thorough feedback on what I could've done better
🙂 - Bring it on 😀
## Summary
Code cleanup for per-file ignores; use a struct instead of a tuple.
Named the structs for individual ignores and the list of ignores
`CompiledPerFileIgnore` and `CompiledPerFileIgnoreList`. Name choice is
because we already have a `PerFileIgnore` struct for a
pre-compiled-matchers form of the config. Name bikeshedding welcome.
## Test Plan
Refactor, should not change behavior; existing tests pass.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <alex.waygood@gmail.com>
## Summary
I believe this should close
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10880? The `.gitignore`
creation seems ok, since it truncates, but using `cachedir::is_tagged`
followed by `cachedir::add_tag` is not safe, as `cachedir::add_tag`
_fails_ if the file already exists.
This also matches the structure of the code in `uv`.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10880.
## Summary
Implement `write-whole-file` (`FURB103`), part of #1348. This is largely
a copy and paste of `read-whole-file` #7682.
## Test Plan
Text fixture added.
---------
Co-authored-by: Dhruv Manilawala <dhruvmanila@gmail.com>
## Summary
Improve `blanket-noqa` error message in cases where codes are provided
but not detected due to formatting issues. Namely `# noqa X100` (missing
colon) or `noqa : X100` (space before colon). The behavior is similar to
`NQA002` and `NQA003` from `flake8-noqa` mentioned in #850. The idea to
merge the rules into `PGH004` was suggested by @MichaReiser
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10325#issuecomment-2025535444.
## Test Plan
Test cases added to fixture.
Fixes#3172
## Summary
Allow prefixing [extend-]per-file-ignores patterns with `!` to negate
the pattern; listed rules / prefixes will be ignored in all files that
don't match the pattern.
## Test Plan
Added tests for the feature.
Rendered docs and checked rendered output.
Fixes#5499
## Summary
Add support for `FORCE_COLOR` env var, as specified at
https://force-color.org/
## Test Plan
I wrote an integration test for this, and then realized that can't work,
since we use a dev-dependency on `colored` with the `no-color` feature
to avoid ANSI color codes in test snapshots.
So this is just tested manually.
`cargo run --features test-rules -- check --no-cache --isolated -
--select RUF901 --diff < /dev/null` shows a colored diff.
`cargo run --features test-rules -- check --no-cache --isolated -
--select RUF901 --diff < /dev/null | less` does not have color, since we
pipe it to `less`.
`FORCE_COLOR=1 cargo run --features test-rules -- check --no-cache
--isolated - --select RUF901 --diff < /dev/null | less` does have color
(after this diff), even though we pipe it to `less`.
## Summary
Came across this code while digging into the semantic model with
@AlexWaygood, and found it confusing because of how it splits
`push_scope` from the paired `pop_scope` (took me a few minutes to even
figure out if/where we were popping the pushed scope). Since this
"cleanup" is already totally split by node type, there doesn't seem to
be any gain in having it as a separate "step" rather than just
incorporating it into the traversal clauses for those node types.
I left the equivalent cleanup step alone for the expression case,
because in that case it is actually generic across several different
node types, and due to the use of the common `visit_generators` utility
there isn't a clear way to keep the pushes and corresponding pops
localized.
Feel free to just reject this if I've missed a good reason for it to
stay this way!
## Test Plan
Tests and clippy.
## Summary
This is a follow-up to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10764.
Support for diagnostics, quick fixes, and source actions can now be
disabled via client settings.
## Test Plan
### Manual Testing
Set up your workspace as described in the test plan in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10764, up to step 2. You don't
need to add a debug statement.
The configuration for `folder_a` and `folder_b` should be as follows:
`folder_a`:
```json
{
"ruff.codeAction.fixViolation": {
"enable": true
}
}
```
`folder_b`
```json
{
"ruff.codeAction.fixViolation": {
"enable": false
}
}
```
Finally, open up your VS Code User Settings and un-check the `Ruff > Fix
All` setting.
1. Open a Python file in `folder_a` that has existing problems. The
problems should be highlighted, and quick fix should be available.
`source.fixAll` should not be available as a source action.
2. Open a Python file in `folder_b` that has existing problems. The
problems should be highlighted, but quick fixes should not be available
for any of them. `source.fixAll` should not be available as a source
action.
3. Open up your VS Code Workspace Settings (second tab under the search
bar) and un-check `Ruff > Lint: Enable`
4. Both files you tested in steps 1 and 2 should now lack any visible
diagnostics. `source.organizeImports` should still be available as a
source action.
## Summary
Fixes#3011.
Type checkers currently allow forward references in all contexts in stub
files, and stubs frequently make use of this capability (although it
doesn't actually seem to be specc'd anywhere --neither in PEP 484, nor
https://typing.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/stubs.html#id6, nor the
CPython typing docs). Implementing it so that Ruff allows forward
references in _all contexts_ in stub files seems non-trivial, however
(or at least, I couldn't figure out how to do it easily), so this PR
does not do that. Perhaps it _should_; if we think this apporach isn't
principled enough, I'm happy to close it and postpone changing anything
here.
However, this does reduce the number of F821 errors Ruff emits on
typeshed down from 76 to 2, which would mean that we could enable the
rule at typeshed. The remaining 2 F821 errors can be trivially fixed at
typeshed by moving definitions around; forward references in class bases
were really the only remaining places where there was a real _use case_
for forward references in stub files that Ruff wasn't yet allowing.
## Test plan
`cargo test`. I also ran this PR branch on typeshed to check to see if
there were any new false positives caused by the changes here; there
were none.
## Summary
`Path.read_bytes()` does not support any keyword arguments, so `FURB101`
should not be triggered if the file is opened in `rb` mode with any
keyword arguments.
## Test Plan
Move erroneous test to "Non-error" section of fixture.
## Summary
Historically, given:
```python
__all__ = [ # noqa: F822
"Bernoulli",
"Beta",
"Binomial",
]
```
The F822 violations would be attached to the `__all__`, so this `# noqa`
would be enforced for _all_ definitions in the list. This changed in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10525 for the better, in that we
now use the range of each string. But these `# noqa` directives stopped
working.
This PR sets the `__all__` as a parent range in the diagnostic, so that
these directives are respected once again.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10795.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Add new rule `pyupgrade - UP042` (I picked next available number).
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/discussions/3867
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9569
It should warn + provide a fix `class A(str, Enum)` -> `class
A(StrEnum)` for py311+.
## Test Plan
Added UP042.py test.
## Notes
I did not find a way to call `remove_argument` 2 times consecutively, so
the automatic fixing works only for classes that inherit exactly `str,
Enum` (regardless of the order).
I also plan to extend this rule to support IntEnum in next PR.
## Summary
This builds off of the work in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10652 to implement a command
executor, backwards compatible with the commands from the previous LSP
(`ruff.applyAutofix`, `ruff.applyFormat` and
`ruff.applyOrganizeImports`).
This involved a lot of refactoring and tweaks to the code action
resolution code - the most notable change is that workspace edits are
specified in a slightly different way, using the more general `changes`
field instead of the `document_changes` field (which isn't supported on
all LSP clients). Additionally, the API for synchronous request handlers
has been updated to include access to the `Requester`, which we use to
send a `workspace/applyEdit` request to the client.
## Test Plan
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/7932e30f-d944-4e35-b828-1d81aa56c087
## Summary
When a language server initializes, it is passed a serialized JSON
object, which is known as its "initialization options". Until now, `ruff
server` has ignored those initialization options, meaning that
user-provided settings haven't worked. This PR is the first step for
supporting settings from the LSP client. It implements procedures to
deserialize initialization options into a settings object, and then
resolve those settings objects into concrete settings for each
workspace.
One of the goals for user settings implementation in `ruff server` is
backwards compatibility with `ruff-lsp`'s settings. We won't support all
settings that `ruff-lsp` had, but the ones that we do support should
work the same and use the same schema as `ruff-lsp`.
These are the existing settings from `ruff-lsp` that we will continue to
support, and which are part of the settings schema in this PR:
| Setting | Default Value | Description |
|----------------------------------------|---------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| `codeAction.disableRuleComment.enable` | `true` | Whether to display
Quick Fix actions to disable rules via `noqa` suppression comments. |
| `codeAction.fixViolation.enable` | `true` | Whether to display Quick
Fix actions to autofix violations. |
| `fixAll` | `true` | Whether to register Ruff as capable of handling
`source.fixAll` actions. |
| `lint.enable` | `true` | Whether to enable linting. Set to `false` to
use Ruff exclusively as a formatter. |
| `organizeImports` | `true` | Whether to register Ruff as capable of
handling `source.organizeImports` actions. |
To be clear: this PR does not implement 'support' for these settings,
individually. Rather, it constructs a framework for these settings to be
used by the server in the future.
Notably, we are choosing *not* to support `lint.args` and `format.args`
as settings for `ruff server`. This is because we're now interfacing
with Ruff at a lower level than its CLI, and converting CLI arguments
back into configuration is too involved.
We will have support for linter and formatter specific settings in
follow-up PRs. We will also 'hook up' user settings to work with the
server in follow up PRs.
## Test Plan
### Snapshot Tests
Tests have been created in
`crates/ruff_server/src/session/settings/tests.rs` to ensure that
deserialization and settings resolution works as expected.
### Manual Testing
Since we aren't using the resolved settings anywhere yet, we'll have to
add a few printing statements.
We want to capture what the resolved settings look like when sent as
part of a snapshot, so modify `Session::take_snapshot` to be the
following:
```rust
pub(crate) fn take_snapshot(&self, url: &Url) -> Option<DocumentSnapshot> {
let resolved_settings = self.workspaces.client_settings(url, &self.global_settings);
tracing::info!("Resolved settings for document {url}: {resolved_settings:?}");
Some(DocumentSnapshot {
configuration: self.workspaces.configuration(url)?.clone(),
resolved_client_capabilities: self.resolved_client_capabilities.clone(),
client_settings: resolved_settings,
document_ref: self.workspaces.snapshot(url)?,
position_encoding: self.position_encoding,
url: url.clone(),
})
}
```
Once you've done that, build the server and start up your extension
testing environment.
1. Set up a workspace in VS Code with two workspace folders, each one
having some variant of Ruff file-based configuration (`pyproject.toml`,
`ruff.toml`, etc.). We'll call these folders `folder_a` and `folder_b`.
2. In each folder, open up `.vscode/settings.json`.
3. In folder A, use these settings:
```json
{
"ruff.codeAction.disableRuleComment": {
"enable": true
}
}
```
4. In folder B, use these settings:
```json
{
"ruff.codeAction.disableRuleComment": {
"enable": false
}
}
```
5. Finally, open up your VS Code User Settings and un-check the `Ruff >
Code Action: Disable Rule Comment` setting.
6. When opening files in `folder_a`, you should see logs that look like
this:
```
Resolved settings for document <file>: ResolvedClientSettings { fix_all: true, organize_imports: true, lint_enable: true, disable_rule_comment_enable: true, fix_violation_enable: true }
```
7. When opening files in `folder_b`, you should see logs that look like
this:
```
Resolved settings for document <file>: ResolvedClientSettings { fix_all: true, organize_imports: true, lint_enable: true, disable_rule_comment_enable: false, fix_violation_enable: true }
```
8. To test invalid configuration, change `.vscode/settings.json` in
either folder to be this:
```json
{
"ruff.codeAction.disableRuleComment": {
"enable": "invalid"
},
}
```
10. You should now see these error logs:
```
<time> [info] <duration> ERROR ruff_server::session::settings Failed to deserialize initialization options: data did not match any variant of untagged enum InitializationOptions. Falling back to default client settings...
<time> [info] <duration> WARN ruff_server::server No workspace settings found for file:///Users/jane/testbed/pandas
<duration> WARN ruff_server::server No workspace settings found for file:///Users/jane/foss/scipy
```
11. Opening files in either folder should now print the following
configuration:
```
Resolved settings for document <file>: ResolvedClientSettings { fix_all: true, organize_imports: true, lint_enable: true, disable_rule_comment_enable: true, fix_violation_enable: true }
```
## Summary
This PR adds a new semantic model flag to indicate that the checker is
inside an f-string replacement field. This will be used to ignore
certain checks if the target version doesn't support a specific feature
like PEP 701.
fixes: #10761
## Test Plan
Add a test case from the raised issue.
Fixes#3259
## Summary
Renames `UnnecessaryComprehensionAnyAll` to
`UnnecessaryComprehensionInCall` and extends the check to `sum`, `min`,
and `max`, in addition to `any` and `all`.
## Test Plan
Updated snapshot test.
Built docs locally and verified the docs for this rule still render
correctly.
## Summary
Needed for https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10686.
We no longer support `root_uri` as an initialization parameter, relying
solely on `workspace_folders` to find the working directories. This
means that the minimum supported LSP version is now `0.3.6`.
## Test Plan
When opening a folder in VS Code, you shouldn't see any errors in the
log which say `No workspace(s) were provided(...)`.
## Summary
We may not have had access to this in the past, but in short, if the
diagnostic is related to a specific section of a docstring, it seems
better to highlight the section (via the header) than the _entire_
docstring.
This should be completely compatible with existing `# noqa` since it's
always inside of a multi-line string anyway, and in such cases the `#
noqa` is always placed at the end of the multiline string.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10736.
## Summary
This PR adds the `as_str` implementation for all the operator methods.
It already exists for `CmpOp` which is being [used in the
linter](ffcd77860c/crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/flake8_simplify/rules/key_in_dict.rs (L117))
and it makes sense to implement it for the rest as well. This will also
be utilized in error messages for the new parser.
## Summary
This PR removes unused operator methods and impl traits. There is
already the `is_macro::Is` implementation for all the operators and this
seems unnecessary.
## Summary
We lost the per-rule ignores when these were migrated to the AST, so if
_any_ `Q` rule is enabled, they're now all enabled.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10724.
## Test Plan
Ran:
```shell
ruff check . --isolated --select Q --ignore Q000
ruff check . --isolated --select Q --ignore Q001
ruff check . --isolated --select Q --ignore Q002
ruff check . --isolated --select Q --ignore Q000,Q001
ruff check . --isolated --select Q --ignore Q000,Q002
ruff check . --isolated --select Q --ignore Q001,Q002
```
...against:
```python
'''
bad docsting
'''
a = 'single'
b = '''
bad multi line
'''
```
## Summary
An annotated lambda assignment within a class scope is often
intentional. For example, within a dataclass or Pydantic model, these
are treated as fields rather than methods (and so can be passed values
in constructors).
I originally wrote this to special-case dataclasses and Pydantic
models... But was left feeling like we'd see more false positives here
for little gain (an annotated lambda within a `class` is likely
intentional?). Open to opinions, though.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10718.
## Summary
Currently, [this
line](716688d44e/crates/ruff_linter/src/fix/edits.rs (L101))
assumes that the `noqa` comment begins with an octothorpe followed by a
space. (`# `) With anyone's random code, this of course is not always
true.
When there's a multi-byte character after the leading octothorpe, such
as
[`\u0085`](https://www.fileformat.info/info/unicode/char/85/index.htm),
we try slicing from within the character, causing a panic.
To fix this, the logic has been changed to remove unused `noqa`
directives and keep any trailing comments, or removing the whole comment
if the comment is just the unused `noqa`
Fixes#10097.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
Implement FURB164 in the issue #1348.
Relevant Refurb docs is here:
https://github.com/dosisod/refurb/blob/v2.0.0/docs/checks.md#furb164-no-from-float
I've changed the name from `no-from-float` to
`verbose-decimal-fraction-construction`.
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
I've written it in the `FURB164.py`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
When `relative-imports-order = "closest-to-furthest"` is set, we should
_still_ put non-relative imports after relative imports. It's rare for
them to be in the same section, but _possible_ if you use
`known-local-folder`.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10655.
## Test Plan
New tests.
Also sorted this file:
```python
from ..models import ABC
from .models import Question
from .utils import create_question
from django_polls.apps.polls.models import Choice
```
With both:
- `isort view.py`
- `ruff check view.py --select I --fix`
And the following `pyproject.toml`:
```toml
[tool.ruff.lint.isort]
order-by-type = false
relative-imports-order = "closest-to-furthest"
known-local-folder = ["django_polls"]
[tool.isort]
profile = "black"
reverse_relative = true
known_local_folder = ["django_polls"]
```
I verified that Ruff and isort gave the same result, and that they
_still_ gave the same result when removing the relevant setting:
```toml
[tool.ruff.lint.isort]
order-by-type = false
known-local-folder = ["django_polls"]
[tool.isort]
profile = "black"
known_local_folder = ["django_polls"]
```
## Summary
Add a setting `extend-allowed-calls` to allow users to define their own
list of calls which allow boolean traps.
Resolves#10485.
Resolves#10356.
## Test Plan
Extended text fixture and added setting test.
## Summary
This PR fixes the bug for `DTZ007` rule where it didn't consider to
check for the presence of `%z` in f-strings. It also considers the
string parts of an implicitly concatenated f-strings for which I want to
find a better solution (#10308).
fixes: #10601
## Test Plan
Add test cases and update the snapshots.
## Summary
Fixes#10589.
Code that violates `F401` or `F841` (in other words, unused variables or
imports) should now appear greyed out or 'unused' in an editor.
## Test Plan
Put the following test code in a new file within the extension
development host window:
```python
import math
def func():
if False:
unused = "<- this should be greyed out"
```
The following test code should have greyed out/unused import and
variable names, like so:
<img width="294" alt="Screenshot 2024-03-28 at 4 23 18 AM"
src="https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/assets/19577865/e84a6e7a-49e2-4fed-9624-f8f9559e0837">
## Summary
Fixes#10588.
Most diagnostics from `ruff server` now appear as a much less alarming
warning instead of an error. Three diagnostics still appear as errors:
`F821` (`undefined name <name>`), `E902` (`IOError`) and `E999`
(`SyntaxError`).
## Test Plan
With an extension using the path to a locally-built executable, open a
file with multiple highlighted problems. Toggle the `Experimental
Server` setting on and off. The highlights should stay as warnings.
Then, modify the file to have a syntactically incorrect element. The
start of the invalid syntax should now have a red highlight.
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
This PR updates the warning message for rule S305 to accurately reflect
the security concern over using ECB mode in block ciphers, which is
considered insecure compared to other modes like CBC or CTR. The
previous message incorrectly mentioned AES as a [block cipher
mode](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Block_cipher_mode_of_operation),
which has been corrected to avoid confusion.
Ref:
c85576d903/bandit/blacklists/calls.py (L99-L102)825fd7c990/crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/flake8_bandit/rules/suspicious_function_call.rs (L187-L216)
## Test Plan
No testing required as the change is limited to a minor change of
warning message update.
## Summary
The example for tab-after-comma (E242):
```python
a = 4,\t5
```
Use instead:
```python
a = 4, 3
```
is confusing since both the whitespace and the numbers are changed.
Change so the examples use the same numbers before/after.
## Test Plan
Untested.
- Clearly state in the documentation that passing `tz=None` is just as bad as not passing a `tz=` argument, from the perspective of these rules.
- Clearly state in the error messages exactly what the user is doing wrong, if the user is passing `tz=None` rather than failing to pass a `tz=` argument at all.
- Make error messages more concise, and separate out the suggested remedy from the thing that the user is identified as doing wrong.
Co-authored-by: Christian Clauss <cclauss@me.com>
## Summary
Fixes#10618.
This PR introduces a proper API for sending requests to the client and
handling any response sent back. Dynamic capability registration now
uses this new API, fixing an issue where a much more simplistic response
handler silently flushes a code action request that needed a response.
## Test Plan
#10618 can no longer be reproduced. No errors about unhandled responses
should appear in the extension output, and you should see this new log
when the server starts:
```
<DATE> <TIME> [info] <DURATION> INFO ruff_server::server Configuration file watcher successfully registered
```
## Summary
This PR adds an overview and roadmap to the `README.md` for the
`ruff_server` crate along with a rudimentary `CONTRIBUTING.md` that
explains some of the technical decisions behind the project and basic
information about local testing.
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
Similar to #10419, there was a case where there is a collision of C401
and C416 (as discussed in #10101).
Fixed this by implementing short-circuit for the comprehension of the
form `{x for x in foo}`.
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
Extended `C401.py` with the case where `set` is not builtin function,
and divided the case where the short-circuit should occur.
Removed the last testcase of `print(f"{ {set(a for a in 'abc')} }")`
test as this is invalid as a python code, but should I keep this?
## Summary
This is just a nitpicky improvement, but I thought it'd be a good
opportunity to look at the ruff source.
> The rules list in the documentation is generated using the registry
order. Currently, flake8-logging is separated from the rest of the
flake8 plugins. This patch puts it next to them.
https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/
If it makes sense, we could alternatively just sort the linters in
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/blob/main/crates/ruff_dev/src/generate_rules_table.rs.
Signed-off-by: Filipe Laíns <lains@riseup.net>
## Summary
This is not the holistic solution but just to fix that issue.
fixes: #10546
## Test Plan
Add a regression test for it and check the snapshots.
## Summary
Fixed false-positive on the rule `PLW1641`, where the explicit
assignment on the `__hash__` method is not counted as an definition of
`__hash__`. (Discussed in #10557).
Also, added one new testcase.
## Test Plan
Checked on `cargo test` in `eq_without_hash.py`.
Before the change, for the assignment into `__hash__`, only `__hash__ =
None` was counted as an explicit definition of `__hash__` method.
Probably any assignment into `__hash__` property could be counted as an
explicit definition of hash, so I removed `value.is_none_literal_expr()`
check.
## Summary
Closes#10228
The PR makes the blank lines rules keep track of the cell status when
running on a notebook, and makes the rules not trigger when the line is
the first of the cell.
## Test Plan
The example given in #10228 is added as a fixture, along with a few
tests from the main blank lines fixtures.
## Summary
Continuing with #7595, this PR moves the `Q004` rule to the AST checker.
## Test Plan
- [x] Existing test cases should pass
- [x] No ecosystem updates
## Summary
PEP 420 says [nested namespace
packages](https://peps.python.org/pep-0420/#nested-namespace-packages)
are allowed, i.e. marking a directory as a namespace package marks all
subdirectories in the subtree as namespace packages.
`is_package` is modified to use `Path::starts_with` and the order of
checks is reversed to do in-memory checks first before hitting the disk.
## Test Plan
Added unit tests. Previously all tests were run with `namespace_packages
== &[]`. Verified that one of the tests was failing before changing the
implementation.
## Future Improvements
The `is_package_with_cache` can probably be rewritten to avoid repeated
calls to `Path::starts_with`, by caching all directories up to the
`namespace_root`:
```ruff
let namespace_root = namespace_packages
.iter()
.filter(|namespace_package| path.starts_with(namespace_package))
.min();
```
## Summary
Closes#10337.
I've fixed the code to count usage of variable.
Usage count inside the block is reset when there is a following
statement.
- continue
- break
- return
## Test Plan
Add test case.
## Summary
The fix for PYI025 is currently marked as unsafe in non-global scopes
for both `.py` and `.pyi` files, on the grounds that all global-scope
symbols in Python are implicitly exported from the module, so changing
the name of something in the global scope could break other modules that
import the module we're fixing. Unlike in `.py` files, however, imported
symbols are never implicitly re-exported from stub files. Symbols are
only understood by static analysis tools as being re-exported from stubs
if they are marked as explicit re-exports, which take three forms:
```py
from foo import * # all symbols from foo are re-exported from the stub
# the "redundant" alias marks it as an explicit re-export
# (note that the alias needs to be identical to the symbol's "actual" name
# in order for it to be a re-export)
from bar import barrr as barrr
# inclusion in __all__ also marks it as an explicit re-export,
# just like in `.py` files
from baz import bazzz
__all__ = ["bazzz"]
```
This is [specc'd in PEP
484](https://peps.python.org/pep-0484/#stub-files), and means that we
can mark the fix for PYI025 as safe in more cases for `.pyi` files.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`. An existing test case goes from being an unsafe fix to a
safe fix in a `.pyi` fixture. I also added a new fixture so we have
coverage of global-scope imports that are marked as re-exports using
"redundant" `from collections.abc import Set as Set` aliases.
## Summary
Continuing with https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/7595, this PR
moves the `Q001`, `Q002`, `Q003` rules to the AST based checker.
## Test Plan
Make sure all of the existing test cases pass and verify there are no
ecosystem changes.
## Summary
This error was found browsing
https://github.com/qarmin/Automated-Fuzzer/actions/runs/8396966850.
Which failed when trying to autofix the PT014 violation in the following
code:
```python
@pytest.mark.parametrize('data, spec', [(1.0, 1.0), (1.0, 1.0)])
def test_numbers(data, spec):
...
```
Investigation revealed that the implementation was not properly tested,
when the duplicate value was also the last in the list. In particular
the following function, which is in charge of finding the comma
following an element to create the suggested fix,
0a99bd84ce/crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/flake8_pytest_style/rules/parametrize.rs (L647-L651)
would find the next comma even if it was outside the list itself leading
to a lot of code being deleted.
This PR fixes that.
## Test Plan
Added misbehaving code to the test fixture.
## Summary
Ensures that we use the raw identifier as provided in the source code,
rather than the normalized Unicode identifier.
This _does_ mean that we treat these as two separate identifiers, and
_don't_ merge them, even though Python will treat them as the same
symbol:
```python
import numpy as ℂℇℊℋℌℍℎℐℑℒℓℕℤΩℨKÅℬℭℯℰℱℹℴ
import numpy as CƐgHHHhIILlNZΩZKÅBCeEFio
```
I think that's fine, this is super rare anyway and would likely be
confusing for users.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10528.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Adds commas as an accepted separator between copyright years by default,
which is actually documented in one spot, but not currently accurate.
Fixes#9477.
## Summary
Fixes#10366.
`ruff server` now registers a file watcher on the client side using the
LSP protocol, and listen for events on configuration files. On such an
event, it reloads the configuration in the 'nearest' workspace to the
file that was changed.
## Test Plan
N/A
## Summary
Some contributors have referenced settings in their documentation
without adding the settings to an options section, this has lead to some
rendering issues (#10427). This PR addresses this looking for potential
inline links to settings, cross-checking them with the options sections,
and then linking them anyway if they are not found.
Resolves#10427.
## Test Plan
Manually verified that the correct modifications were made and no docs
were broken.
## Summary
In https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10341, we fixed some false
positives in `.pyi` files, but introduced others. This PR effectively
reverts the change in #10341 and fixes it in a slightly different way.
Instead of changing the _bindings_ we generate in the semantic model in
`.pyi` files, we instead change how we _resolve_ them.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10509.
- Improve clarity over the motivation for some rules
- Improve links to external references. In particular, reduce links to PEPs, as PEPs are generally historical documents rather than pieces of living documentation. Where possible, it's better to link to the official typing spec, the other docs at typing.readthedocs.io/en/latest, or the docs at docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html.
- Use more concise language in a few places
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Fix `E231` bug: Inconsistent catch compared to pycodestyle, such as when
dict nested in list. Resolves#10113.
## Test Plan
Example from #10113 added to test fixture.
## Summary
This is a follow up on https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10492
I incorrectly assumed that `subscript.value.end()` always points past
the value. However, this isn't the case for parenthesized values where
the end "ends" before the parentheses.
## Test Plan
I added new tests for the parenthesized case.
## Summary
This PR fixes an instability where formatting a subscribt
where the `slice` is not an `ExprSlice` and it has a trailing
end-of-line comment after its opening `[` required two formatting passes
to be stable.
The fix is to associate the trailing end-of-line comment as dangling
comment on `[` to preserve its position, similar to how Ruff does it for
other parenthesized expressions.
This also matches how trailing end-of-line subscript comments are
handled when the `slice` is an `ExprSlice`.
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10355
## Versioning
Shipping this as part of a patch release is fine because:
* It fixes a stability issue
* It doesn't impact already formatted code because Ruff would already
have moved to the comment to the end of the line (instead of preserving
it)
## Test Plan
Added tests
Fix a typos in the error message of rule C400
With the latest version of Ruff (0.3.3) if I have a `scratch.py` script
like that:
```python
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple
def generate_samples(test_cases: Dict) -> List[Tuple]:
return list(
(input, expected)
for input, expected in zip(test_cases["input_value"], test_cases["expected_value"])
)
```
and I run ruff
```shell
>>> ruff check scratch.py --select C400
>>> scratch.py:5:12: C400 Unnecessary generator (rewrite using `list()`
```
This PR fixes the error message from _"(rewrite using `list()`"_ to
_"(rewrite using `list()`)"_, and it fixes also the doc.
Related question: why I have this error message? The rule is not correct
in this case. Should I open an issue for that?
## Summary
This PR fixes a panic in the linter for `W605`.
Consider the following f-string:
```python
f"{{}}ab"
```
The `FStringMiddle` token would contain `{}ab`. Notice that the escaped
braces have _reduced_ the string. This means we cannot use the text
value from the token to determine the location of the escape sequence
but need to extract it from the source code.
fixes: #10434
## Test Plan
Add new test cases and update the snapshots.
## Summary
We're seeing failures in https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10470
because `resolve_qualified_import_name` isn't guaranteed to return a
specific import if a symbol is accessible in two ways (e.g., you have
both `import logging` and `from logging import error` in scope, and you
want `logging.error`). This PR breaks up the failing tests such that the
imports aren't in the same scope.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10470.
## Test Plan
I added a `bindings.reverse()` to `resolve_qualified_import_name` to
ensure that the tests pass regardless of the binding order.
## Summary
I used `cargo-shear` (see
[tweet](https://twitter.com/boshen_c/status/1770106165923586395)) to
remove some unused dependencies that `cargo udeps` wasn't reporting.
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Clarify `extend-select` documentation to avoid confusion regarding the
default `select`. Also match the `select` documentation. Resolves
#10389.
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
## Summary
This adds automatic fixes for the `PT007` rule.
I am currently reviewing and adding Ruff rules to Home Assistant. One
rule is PT007, which has multiple hundred occurrences in the codebase,
but no automatic fix, and this is not fun to do manually, especially
because using Regexes are not really possible with this.
My knowledge of the Ruff codebase and Rust in general is not good and
this is my first PR here, so I hope it is not too bad.
One thing where I need help is: How can I have the transformed code to
be formatted automatically, instead of it being minimized as it does it
now?
## Test Plan
Using the existing fixtures and updated snapshots.
## Summary
This PR removes the `Iterator::chain(...)` sequence in
`RuleCodePrefix::iter()` with `Vec::expand` to avoid an
overlong-recursive types.
The existing `RuleCodePrefix::iter` method chains all rule group
iterators together. This leads to very long recursive types
`Chain<Map<Chain<Map<Chain<Map.....>>>>` (proportional to the number of
rule groups).
This PR rewrites the macro to use `Vec::extend` instead, which removes
the long recursive type (at the cost of introducing a potential
allocation).
## Alternatives
An alternative would be to use a stack allocated array by unrolling the
`Linter::iter` methods (generated by `EnumIter`).
I don't think it's worth the extra complexity, considering that
`RuleCodePrefix::iter` isn't a hot function.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Fixes#10324
This removes an overeager failure case where we would exit early if no
root directory or workspace folders were provided on server
initialization. We now fall-back to the current working directory as a
workspace for that file.
## Test Plan
N/A
## Summary
#10151 documented the deviations between Ruff and Black with the new
2024 style guide in the `ruff-python-formatter/README.md`. However,
that's not the documentation shown
on the website when navigating to [intentional
deviations](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/formatter/black/).
This PR streamlines the `ruff-python-formatter/README.md` and links to
the documentation on the website instead of repeating the same content.
The PR also makes the 2024 style guide deviations available on the
website documentation.
## Test Plan
I built the documentation locally and verified that the 2024 style guide
known deviations are now shown on the website.
## Summary
In issue https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/6785 it is reported
that a docstring in the form of `''"assert" ' SAM macro definitions '''`
is autocorrected to `"""assert" ' SAM macro definitions '''` (note the
triple quotes one only one side), which breaks the python program due
`undetermined string lateral`.
* `Q002`: Not only would docstrings in the form of `''"assert" ' SAM
macro definitions '''` (single quotes) be autofixed wrongly, but also
e.g. `""'assert' ' SAM macro definitions '''` (double quotes). The bug
is present for docstrings in all scopes (e.g. module docstrings, class
docstrings, function docstrings)
* `Q000`: The autofix error is not only present for `Q002` (docstrings),
but also for inline strings (`Q000`). Therefore `s = ''"assert" ' SAM
macro definitions '''` will also be wrongly autofixed.
Note that situation in which the first string is non-empty can be fixed,
e.g. `'123'"assert" ' SAM macro definitions '''` -> `"123""assert" ' SAM
macro definitions '''` is valid.
## What
* Change FixAvailability of `Q000` `Q002` to `Sometimes`
* Changed both rules such that docstrings/inline strings that cannot be
fixed are still reported as bad quotes via diagnostics, but no fix is
provided
## Test Plan
* For `Q000`: Add docstrings in different scopes that (partially) would
have been autofixed wrongly
* For `Q002`: Add inline strings that (partially) would have been
autofixed wrongly
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/6785
## Summary
The upstream category check here
fd26b29986/crates/ruff_linter/src/upstream_categories.rs (L54-L65)
was not working because the code is actually "E0001" not "PLE0001", I
changed it so it will detect the upstream category correctly.
I also sorted the upstream categories alphabetically, so that the
document generation will be deterministic.
## Test Plan
I compared the diff before and after the change.
Fixes#10426
## Summary
Fix rule B030 giving a false positive with Tuple operations like `+`.
[Playground](https://play.ruff.rs/17b086bc-cc43-40a7-b5bf-76d7d5fce78a)
```python
try:
...
except (ValueError,TypeError) + (EOFError,ArithmeticError):
...
```
## Reviewer notes
This is a little more convoluted than I was expecting -- because we can
have valid nested Tuples with operations done on them, the flattening
logic has become a bit more complex.
Shall I guard this behind --preview?
## Test Plan
Unit tested.
## Summary
Implement `singledispatchmethod-function` from pylint, part of #970.
This is essentially a copy paste of #8934 for `@singledispatchmethod`
decorator.
## Test Plan
Text fixture added.
## Summary
Short-circuit implementation mentioned in #10403.
I implemented this by extending C400:
- Made `UnnecessaryGeneratorList` have information of whether the the
short-circuiting occurred (to put diagnostic)
- Add additional check for whether in `unnecessary_generator_list`
function.
Please give me suggestions if you think this isn't the best way to
handle this :)
## Test Plan
Extended `C400.py` a little, and written the cases where:
- Code could be converted to one single conversion to `list` e.g.
`list(x for x in range(3))` -> `list(range(3))`
- Code couldn't be converted to one single conversion to `list` e.g.
`list(2 * x for x in range(3))` -> `[2 * x for x in range(3)]`
- `list` function is not built-in, and should not modify the code in any
way.
## Summary
Trailing ellipses in objects defined in `typing.TYPE_CHECKING` might be
meaningful (it might be declaring a stub). Thus, we should skip the
`unnecessary-placeholder` (`PIE970`) rule in such contexts.
Closes#10358.
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run`
## Summary
Given `del X`, we'll typically add a `BindingKind::Deletion` to `X` to
shadow the current binding. However, if the deletion is inside of a
conditional operation, we _won't_, as in:
```python
def f():
global X
if X > 0:
del X
```
We will, however, track it as a reference to the binding. This PR adds
the expression context to those resolved references, so that we can
detect that the `X` in `global X` was "assigned to".
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10397.
## Summary
The previous documentation sounded as if typing a mutable default as a
`ClassVar` were optional. However, it is not, as not doing so causes a
`ValueError`. The snippet below was tested in Python's interactive
shell:
```
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass
>>> @dataclass
... class A:
... mutable_default: list[int] = []
...
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/lib/python3.11/dataclasses.py", line 1230, in dataclass
return wrap(cls)
^^^^^^^^^
File "/usr/lib/python3.11/dataclasses.py", line 1220, in wrap
return _process_class(cls, init, repr, eq, order, unsafe_hash,
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "/usr/lib/python3.11/dataclasses.py", line 958, in _process_class
cls_fields.append(_get_field(cls, name, type, kw_only))
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "/usr/lib/python3.11/dataclasses.py", line 815, in _get_field
raise ValueError(f'mutable default {type(f.default)} for field '
ValueError: mutable default <class 'list'> for field mutable_default is not allowed: use default_factory
>>>
```
This behavior is also documented in Python's docs, see
[here](https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html#mutable-default-values):
> [...] the
[dataclass()](https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html#dataclasses.dataclass)
decorator will raise a
[ValueError](https://docs.python.org/3/library/exceptions.html#ValueError)
if it detects an unhashable default parameter. The assumption is that if
a value is unhashable, it is mutable. This is a partial solution, but it
does protect against many common errors.
And
[here](https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html#class-variables)
it is documented why it works if it is typed as a `ClassVar`:
> One of the few places where
[dataclass()](https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html#dataclasses.dataclass)
actually inspects the type of a field is to determine if a field is a
class variable as defined in [PEP
526](https://peps.python.org/pep-0526/). It does this by checking if the
type of the field is typing.ClassVar. If a field is a ClassVar, it is
excluded from consideration as a field and is ignored by the dataclass
mechanisms. Such ClassVar pseudo-fields are not returned by the
module-level
[fields()](https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html#dataclasses.fields)
function.
In this PR I have changed the documentation to make it a little bit
clearer that not using `ClassVar` makes the code invalid.
## Summary
Ignoring all lines until the first logical line does not match the
behavior from pycodestyle. This PR therefore removes the `if
state.is_not_first_logical_line` skipping the line check before the
first logical line, and applies it only to `E302`.
For example, in the snippet below a rule violation should be detected on
the second comment and on the import.
```python
# first comment
# second comment
import foo
```
Fixes#10374
## Test Plan
Add test cases, update the snapshots and verify the ecosystem check output
## Summary
This PR updates the `StringLike::FString` variant to use `ExprFString`
instead of `FStringLiteralElement`.
For context, the reason it used `FStringLiteralElement` is that the node
is actually the string part of an f-string ("foo" in `f"foo{x}"`). But,
this is inconsistent with other variants where the captured value is the
_entire_ string.
This is also problematic w.r.t. implicitly concatenated strings. Any
rules which work with `StringLike::FString` doesn't account for the
string part in an implicitly concatenated f-strings. For example, we
don't flag confusable character in the first part of `"𝐁ad" f"𝐁ad
string"`, but only the second part
(https://play.ruff.rs/16071c4c-a1dd-4920-b56f-e2ce2f69c843).
### Update `PYI053`
_This is included in this PR because otherwise it requires a temporary
workaround to be compatible with the old logic._
This PR also updates the `PYI053` (`string-or-bytes-too-long`) rule for
f-string to consider _all_ the visible characters in a f-string,
including the ones which are implicitly concatenated. This is consistent
with implicitly concatenated strings and bytes.
For example,
```python
def foo(
# We count all the characters here
arg1: str = '51 character ' 'stringgggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggg',
# But not here because of the `{x}` replacement field which _breaks_ them up into two chunks
arg2: str = f'51 character {x} stringgggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggggg',
) -> None: ...
```
This PR fixes it to consider all _visible_ characters inside an f-string
which includes expressions as well.
fixes: #10310fixes: #10307
## Test Plan
Add new test cases and update the snapshots.
## Review
To facilitate the review process, the change have been split into two
commits: one which has the code change while the other has the test
cases and updated snapshots.
## Summary
Fixes#10367.
While the server is still in an unstable state, requiring a `--preview`
flag would be a good way to indicate this to end users.
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Adds a successful check message after no errors were found
Implements #8553
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
## Test Plan
Ran a check on a test file with `cargo run -p ruff_cli -- check test.py
--no-cache` and outputted as expected.
Ran the same check with `cargo run -p ruff_cli -- check test.py
--no-cache --silent` and the command was gone as expected.
<!-- How was it tested? -->
---------
Co-authored-by: Zanie Blue <contact@zanie.dev>
Re-implementation of https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/5845 but
instead of deprecating the option I toggle the default. Now users can
_opt-in_ via the setting which will give them an unsafe fix to remove
the import. Otherwise, we raise violations but do not offer a fix. The
setting is a bit of a misnomer in either case, maybe we'll want to
remove it still someday.
As discussed there, I think the safe fix should be to import it as an
alias. I'm not sure. We need support for offering multiple fixes for
ideal behavior though? I think we should remove the fix entirely and
consider it separately.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/5697
Supersedes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/5845
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR adds methods on `FString` to iterate over the two different kind
of elements it can have - literals and expressions. This is similar to
the methods we have on `ExprFString`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alex Waygood <Alex.Waygood@Gmail.com>
## Summary
Fix "TRIO115 false positive with with sleep(var) where var starts as 0"
#9935 based on the discussion in the issue.
## Test Plan
Issue code added to fixture
## Summary
I used `codespell` and `gramma` to identify mispellings and grammar
errors throughout the codebase and fixed them. I tried not to make any
controversial changes, but feel free to revert as you see fit.
## Summary
We had a report of a test failure on a specific architecture, and
looking into it, I think the test assumes that the hash keys are
iterated in a specific order. This PR thus adds a variant to our
settings display macro specifically for maps and sets. Like `CacheKey`,
it sorts the keys when printing.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10359.
## Summary
Fixes#10351
It seems the bug was caused by this section of code
b669306c87/crates/ruff_python_index/src/indexer.rs (L55-L58)
It's true that newline tokens cannot be immediately followed by line
continuations, but only outside parentheses. e.g. the exception
```
(
1
\
+ 2)
```
But why was this check put there in the first place? Is it guarding
against something else?
## Test Plan
New test was added to indexer
## Summary
When negating an expression like `a or b`, we need to wrap it in
parentheses, e.g., `not (a or b)` instead of `not a or b`, due to
operator precedence.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10335.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
This PR fixes the following false positive in a `.pyi` stub file:
```py
x: int
y = x # F821 currently emitted here, but shouldn't be in a stub file
```
In a `.py` file, this is invalid regardless of whether `from __future__ import annotations` is enabled or not. In a `.pyi` stub file, however, it's always valid, as an annotation counts as a binding in a stub file even if no value is assigned to the variable.
I also added more test coverage for `.pyi` stub files in various edge cases where ruff's behaviour is currently correct, but where `.pyi` stub files do slightly different things to `.py` files.
## Summary
Fixes#10295.
`E225` (`Missing whitespace around operator`) and `E275` (`Missing
whitespace after keyword`) try to add a white space even when the next
character is a `)` (which is a syntax error in most cases, the
exceptions already being handled). This causes `E202` (`Whitespace
before close bracket`) to try to remove the added whitespace, resulting
in an infinite loop when `E225`/`E275` re-add it.
This PR adds an exception in `E225` and `E275` to not trigger in case
the next token is a `)`. It is a bit simplistic, but it solves the
example given in the issue without introducing a change in behavior
(according to the fixtures).
## Test Plan
`cargo test` and the `ruff-ecosystem` check were used to check that the
PR's changes do not have side-effects.
A new fixture was added to check that running the 3 rules on the example
given in the issue does not cause ruff to fail to converge.
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
This PR introduces the `ruff_server` crate and a new `ruff server`
command. `ruff_server` is a re-implementation of
[`ruff-lsp`](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-lsp), written entirely in
Rust. It brings significant performance improvements, much tighter
integration with Ruff, a foundation for supporting entirely new language
server features, and more!
This PR is an early version of `ruff_lsp` that we're calling the
**pre-release** version. Anyone is more than welcome to use it and
submit bug reports for any issues they encounter - we'll have some
documentation on how to set it up with a few common editors, and we'll
also provide a pre-release VSCode extension for those interested.
This pre-release version supports:
- **Diagnostics for `.py` files**
- **Quick fixes**
- **Full-file formatting**
- **Range formatting**
- **Multiple workspace folders**
- **Automatic linter/formatter configuration** - taken from any
`pyproject.toml` files in the workspace.
Many thanks to @MichaReiser for his [proof-of-concept
work](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/7262), which was important
groundwork for making this PR possible.
## Architectural Decisions
I've made an executive choice to go with `lsp-server` as a base
framework for the LSP, in favor of `tower-lsp`. There were several
reasons for this:
1. I would like to avoid `async` in our implementation. LSPs are mostly
computationally bound rather than I/O bound, and `async` adds a lot of
complexity to the API, while also making harder to reason about
execution order. This leads into the second reason, which is...
2. Any handlers that mutate state should be blocking and run in the
event loop, and the state should be lock-free. This is the approach that
`rust-analyzer` uses (also with the `lsp-server`/`lsp-types` crates as a
framework), and it gives us assurances about data mutation and execution
order. `tower-lsp` doesn't support this, which has caused some
[issues](https://github.com/ebkalderon/tower-lsp/issues/284) around data
races and out-of-order handler execution.
3. In general, I think it makes sense to have tight control over
scheduling and the specifics of our implementation, in exchange for a
slightly higher up-front cost of writing it ourselves. We'll be able to
fine-tune it to our needs and support future LSP features without
depending on an upstream maintainer.
## Test Plan
The pre-release of `ruff_server` will have snapshot tests for common
document editing scenarios. An expanded test suite is on the roadmap for
future version of `ruff_server`.
## Summary
Fix#10282
This PR updates the Python grammar to include the `*` character in
`*args` `**kwargs` in the range of the `Parameter`
```
def f(*args, **kwargs): pass
# ~~~~ ~~~~~~ <-- range before the PR
# ^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^ <-- range after
```
The invalid syntax `def f(*, **kwargs): ...` is also now correctly
reported.
## Test Plan
Test cases were added to `function.rs`.
## Summary
This PR changes how we format `with` statements with a single with item
for Python 3.8 or older. This change is not compatible with Black.
This is how we format a single-item with statement today
```python
def run(data_path, model_uri):
with pyspark.sql.SparkSession.builder.config(
key="spark.python.worker.reuse", value=True
).config(key="spark.ui.enabled", value=False).master(
"local-cluster[2, 1, 1024]"
).getOrCreate():
# ignore spark log output
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("OFF")
print(score_model(spark, data_path, model_uri))
```
This is different than how we would format the same expression if it is
inside any other clause header (`while`, `if`, ...):
```python
def run(data_path, model_uri):
while (
pyspark.sql.SparkSession.builder.config(
key="spark.python.worker.reuse", value=True
)
.config(key="spark.ui.enabled", value=False)
.master("local-cluster[2, 1, 1024]")
.getOrCreate()
):
# ignore spark log output
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("OFF")
print(score_model(spark, data_path, model_uri))
```
Which seems inconsistent to me.
This PR changes the formatting of the single-item with Python 3.8 or
older to match that of other clause headers.
```python
def run(data_path, model_uri):
with (
pyspark.sql.SparkSession.builder.config(
key="spark.python.worker.reuse", value=True
)
.config(key="spark.ui.enabled", value=False)
.master("local-cluster[2, 1, 1024]")
.getOrCreate()
):
# ignore spark log output
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("OFF")
print(score_model(spark, data_path, model_uri))
```
According to our versioning policy, this style change is gated behind a
preview flag.
## Test Plan
See added tests.
Added
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10267
The issue with the current formatting is that the formatter flips
between the `SingleParenthesizedContextManager` and
`ParenthesizeIfExpands` or `SingleWithTarget` because the layouts use
incompatible formatting ( `SingleParenthesizedContextManager`:
`maybe_parenthesize_expression(context)` vs `ParenthesizeIfExpands`:
`parenthesize_if_expands(item)`, `SingleWithTarget`:
`optional_parentheses(item)`.
The fix is to ensure that the layouts between which the formatter flips
when adding or removing parentheses are the same. I do this by
introducing a new `SingleWithoutTarget` layout that uses the same
formatting as `SingleParenthesizedContextManager` if it has no target
and prefer `SingleWithoutTarget` over using `ParenthesizeIfExpands` or
`SingleWithTarget`.
## Formatting change
The downside is that we now use `maybe_parenthesize_expression` over
`parenthesize_if_expands` for expressions where
`can_omit_optional_parentheses` returns `false`. This can lead to stable
formatting changes. I only found one formatting change in our ecosystem
check and, unfortunately, this is necessary to fix the instability (and
instability fixes are okay to have as part of minor changes according to
our versioning policy)
The benefit of the change is that `with` items with a single context
manager and without a target are now formatted identically to how the
same expression would be formatted in other clause headers.
## Test Plan
I ran the ecosystem check locally
## Summary
This PR refactors the with item formatting to use more explicit layouts
to make it easier to understand the different formatting cases.
The benefit of the explicit layout is that it makes it easier to reasons
about layout transition between format runs. For example, today it's
possible that `SingleWithTarget` or `ParenthesizeIfExpands` add
parentheses around the with items for `with aaaaaaaaaa + bbbbbbbbbbbb:
pass`, resulting in `with (aaaaaaaaaa + bbbbbbbbbbbb): pass`. The
problem with this is that the next formatting pass uses the
`SingleParenthesizedContextExpression` layout that uses
`maybe_parenthesize_expression` which is different from
`parenthesize_if_expands(&expr)` or `optional_parentheses(&expr)`.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
I ran the ecosystem checks locally and there are no changes.
This PR modifies our AST so that nodes for string literals, bytes literals and f-strings all retain the following information:
- The quoting style used (double or single quotes)
- Whether the string is triple-quoted or not
- Whether the string is raw or not
This PR is a followup to #10256. Like with that PR, this PR does not, in itself, fix any bugs. However, it means that we will have the necessary information to preserve quoting style and rawness of strings in the `ExprGenerator` in a followup PR, which will allow us to provide a fix for https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/7799.
The information is recorded on the AST nodes using a bitflag field on each node, similarly to how we recorded the information on `Tok::String`, `Tok::FStringStart` and `Tok::FStringMiddle` tokens in #10298. Rather than reusing the bitflag I used for the tokens, however, I decided to create a custom bitflag for each AST node.
Using different bitflags for each node allows us to make invalid states unrepresentable: it is valid to set a `u` prefix on a string literal, but not on a bytes literal or an f-string. It also allows us to have better debug representations for each AST node modified in this PR.
## Summary
Fixes the handling end of line comments that belong to `**kwargs` when
the `**kwargs` come after a slash.
The issue was that we missed to include the `**kwargs` start position
when determining the start of the next node coming after the `/`.
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10281
## Test Plan
Added test
## Summary
Changes the generic recommendation to replace
```python
if foo == True: ...
```
with `if cond:` to `if foo:`.
Still uses a generic message for compound comparisons as a specific
message starts to become confusing. For example,
```python
if foo == True != False: ...
```
produces two recommendations, one of which would recommend `if True:`,
which is confusing.
Resolves [recommendation in a previous
PR](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/8613/files#r1514915070).
## Test Plan
`cargo nextest run`
## Summary
The code later in this file that checks for slices relies on the stack
of brackets to determine the position. I'm not sure why format strings
were being excluded from this, but the tests still pass with these match
guards removed.
Closes#10278
## Test Plan
~Still needs a test.~ Test case added for this example.
## Summary
This is a follow-up to https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/10238 to
offer fixes for the f-string rule regardless of the line length of the
resulting fix. To quote Alex in the linked PR:
> Yes, from the user's perspective I'd rather have a fix that may lead
to line length issues than have to fix them myself :-) Cleaning up line
lengths is easier than changing from `"".format()` to `f""`
I agree with this position, which is that if we're going to offer a
diagnostic, we should really be offering the user the ability to fix it
-- otherwise, we're just inconveniencing them.
## Summary
Given a format string like `"{x} {x}".format(x=foo())`, we should avoid
converting to an f-string, since doing so would require repeating the
function call (`f"{foo()} {foo()}"`), which could introduce side
effects.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10258.
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10235
This PR changes `UP032` to flag all `"".format` calls that can
technically be rewritten to an f-string, even if rewritting it to an
fstring, at least automatically, exceeds the line length (or increases
the amount by which it goes over the line length).
I looked at the Git history to understand whether the check prevents
some false positives (reported by an issue), but i haven't found a
compelling reason to limit the rule to only flag format calls that stay
in the line length limit:
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/7818 Changed the heuristic to
determine if the fix fits to address
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/discussions/7810
* https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/1905 first version of the rule
I did take a look at pyupgrade and couldn't find a similar check, at
least not in the rule code (maybe it's checked somewhere else?)
https://github.com/asottile/pyupgrade/blob/main/pyupgrade/_plugins/fstrings.py
## Breaking Change?
This could be seen as a breaking change according to ruff's [versioning
policy](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/versioning/):
> The behavior of a stable rule is changed
* The scope of a stable rule is significantly increased
* The intent of the rule changes
* Does not include bug fixes that follow the original intent of the rule
It does increase the scope of the rule, but it is in the original intent
of the rule (so it's not).
## Test Plan
See changed test output
## Summary
When you try to remove an internal representation leaking into another
type and end up rewriting a simple version of `smallvec`.
The goal of this PR is to replace the `Box<[&'a str]>` with
`Box<QualifiedName>` to avoid that the internal `QualifiedName`
representation leaks (and it gives us a nicer API too). However, doing
this when `QualifiedName` uses `SmallVec` internally gives us all sort
of funny lifetime errors. I was lost but @BurntSushi came to rescue me.
He figured out that `smallvec` has a variance problem which is already
tracked in https://github.com/servo/rust-smallvec/issues/146
To fix the variants problem, I could use the smallvec-2-alpha-4 or
implement our own smallvec. I went with implementing our own small vec
for this specific problem. It obviously isn't as sophisticated as
smallvec (only uses safe code), e.g. it doesn't perform any size
optimizations, but it does its job.
Other changes:
* Removed `Imported::qualified_name` (the version that returns a
`String`). This can be replaced by calling `ToString` on the qualified
name.
* Renamed `Imported::call_path` to `qualified_name` and changed its
return type to `&QualifiedName`.
* Renamed `QualifiedName::imported` to `user_defined` which is the more
common term when talking about builtins vs the rest/user defined
functions.
## Test plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10039
The [recommendation for typing stub
files](https://typing.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/stubs.html#blank-lines)
is to use **one** blank line to group related definitions and
otherwise omit blank lines.
The newly added blank line rules (`E3*`) didn't account for typing stub
files and enforced two empty lines at the top level and one empty line
otherwise, making it impossible to group related definitions.
This PR implements the `E3*` rules to:
* Not enforce blank lines. The use of blank lines in typing definitions
is entirely up to the user.
* Allow at most one empty line, including between top level statements.
## Test Plan
Added unit tests (It may look odd that many snapshots are empty but the
point is that the rule should no longer emit diagnostics)
## Summary
This PR changes the `E3*` rules to respect the `isort`
`lines-after-imports` and `lines-between-types` settings. Specifically,
the following rules required changing
* `TooManyBlannkLines` : Respects both settings.
* `BlankLinesTopLevel`: Respects `lines-after-imports`. Doesn't need to
respect `lines-between-types` because it only applies to classes and
functions
The downside of this approach is that `isort` and the blank line rules
emit a diagnostic when there are too many blank lines. The fixes aren't
identical, the blank line is less opinionated, but blank lines accepts
the fix of `isort`.
<details>
<summary>Outdated approach</summary>
Fixes
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10077#issuecomment-1961266981
This PR changes the blank line rules to not enforce the number of blank
lines after imports (top-level) if isort is enabled and leave it to
isort to enforce the right number of lines (depends on the
`isort.lines-after-imports` and `isort.lines-between-types` settings).
The reason to give `isort` precedence over the blank line rules is that
they are configurable. Users that always want to blank lines after
imports can use `isort.lines-after-imports=2` to enforce that
(specifically for imports).
This PR does not fix the incompatibility with the formatter in pyi files
that only uses 0 to 1 blank lines. I'll address this separately.
</details>
## Review
The first commit is a small refactor that simplified implementing the
fix (and makes it easier to reason about what's mutable and what's not).
## Test Plan
I added a new test and verified that it fails with an error that the fix
never converges. I verified the snapshot output after implementing the
fix.
---------
Co-authored-by: Hoël Bagard <34478245+hoel-bagard@users.noreply.github.com>
## Summary
When users provide configurations via `--config`, we use `shellexpand`
to ensure that we expand signifiers like `~` and environment variables.
In https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/9599, we modified `--config`
to accept either a path or an arbitrary setting. However, the detection
(to determine whether the value is a path or a setting) was lacking the
`shellexpand` behavior -- it was downstream. So we were always treating
paths like `~/ruff.toml` as values, not paths.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-vscode/issues/413.
The expression types in our AST are called `ExprYield`, `ExprAwait`,
`ExprStringLiteral` etc, except `ExprNamedExpr`, `ExprIfExpr` and
`ExprGenratorExpr`. This seems to align with [Python AST's
naming](https://docs.python.org/3/library/ast.html) but feels
inconsistent and excessive.
This PR removes the `Expr` postfix from `ExprNamedExpr`, `ExprIfExpr`,
and `ExprGeneratorExpr`.
## Summary
Charlie can probably explain this better than I but it turns out,
`CallPath` is used for two different things:
* To represent unqualified names like `version` where `version` can be a
local variable or imported (e.g. `from sys import version` where the
full qualified name is `sys.version`)
* To represent resolved, full qualified names
This PR splits `CallPath` into two types to make this destinction clear.
> Note: I haven't renamed all `call_path` variables to `qualified_name`
or `unqualified_name`. I can do that if that's welcomed but I first want
to get feedback on the approach and naming overall.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
This PR fixes for `invalid-first-argument` rules.
The fixes rename the first argument of methods and class methods to the
valid one. References to this argument are also renamed.
Fixes are skipped when another argument is named as the valid first
argument.
The fix is marked as unsafe due
The functions for the `N804` and `N805` rules are now merged, as they
only differ by the name of the valid first argument.
The rules were moved from the AST iteration to the deferred scopes to be
in the function scope while creating the fix.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
Allows `required-version` to be set with a version specifier, like
`>=0.3.1`.
If a single version is provided, falls back to assuming `==0.3.1`, for
backwards compatibility.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10192.
## Summary
This PR removes the unneeded lifetime `'b` from many of our `Visitor`
implementations.
The lifetime is unneeded because it is only constraint by `'a`, so we
can use `'a` directly.
## Test Plan
`cargo build`
## Summary
This PR changes the `CallPath` type alias to a newtype wrapper.
A newtype wrapper allows us to limit the API and to experiment with
alternative ways to implement matching on `CallPath`s.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Removes the unnecessary `exc` variable in `TRY300`'s docs example.
## Test Plan
```
python scripts/generate_mkdocs.py; mkdocs serve -f mkdocs.public.yml
```
## Summary
Fixes#10174 by allowing match cases to be enclosing nodes for
suppression comments. `else/elif` clauses are now also allowed to be
enclosing nodes.
## Test Plan
I've added the offending code from the original issue to the `RUF028`
snapshot test, and I've also expanded it to test the allowed `else/elif`
clause.
## Summary
This fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/7868.
Support isort's `default-section` feature which allows any imports that
match sections that are not in `section-order` to be mapped to a
specifically named section.
https://pycqa.github.io/isort/docs/configuration/options.html#default-section
This has a few implications:
- It is no longer required that all known sections are defined in
`section-order`.
- This is technically a bw-incompat change because currently if folks
define custom groups, and do not define a `section-order`, the code used
to add all known sections to `section-order` while emitting warnings.
**However, when this happened, users would be seeing warnings so I do
not think it should count as a bw-incompat change.**
## Test Plan
- Added a new test.
- Did not break any existing tests.
Finally, I ran the following config against Pyramid's complex codebase
that was previously using isort and this change worked there.
### pyramid's previous isort config
5f7e286b06/pyproject.toml (L22-L37)
```toml
[tool.isort]
profile = "black"
multi_line_output = 3
src_paths = ["src", "tests"]
skip_glob = ["docs/*"]
include_trailing_comma = true
force_grid_wrap = false
combine_as_imports = true
line_length = 79
force_sort_within_sections = true
no_lines_before = "THIRDPARTY"
sections = "FUTURE,THIRDPARTY,FIRSTPARTY,LOCALFOLDER"
default_section = "THIRDPARTY"
known_first_party = "pyramid"
```
### tested with ruff isort config
```toml
[tool.ruff.lint.isort]
case-sensitive = true
combine-as-imports = true
force-sort-within-sections = true
section-order = [
"future",
"third-party",
"first-party",
"local-folder",
]
default-section = "third-party"
known-first-party = [
"pyramid",
]
```
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
Fixes#6611
## Summary
This lint rule spots comments that are _intended_ to suppress or enable
the formatter, but will be ignored by the Ruff formatter.
We borrow some functions the formatter uses for determining comment
placement / putting them in context within an AST.
The analysis function uses an AST visitor to visit each comment and
attach it to the AST. It then uses that context to check:
1. Is this comment in an expression?
2. Does this comment have bad placement? (e.g. a `# fmt: skip` above a
function instead of at the end of a line)
3. Is this comment redundant?
4. Does this comment actually suppress any code?
5. Does this comment have ambiguous placement? (e.g. a `# fmt: off`
above an `else:` block)
If any of these are true, a violation is thrown. The reported reason
depends on the order of the above check-list: in other words, a `# fmt:
skip` comment on its own line within a list expression will be reported
as being in an expression, since that reason takes priority.
The lint suggests removing the comment as an unsafe fix, regardless of
the reason.
## Test Plan
A snapshot test has been created.
## Summary
Adapts the fix for rule B006 to no longer modify the body of function
stubs, while retaining the change in method signature.
## Test Plan
The existing tests for B006 were adapted to reflect this change in
behavior.
## Relevant issue
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10083
## Summary
The `lxml` library has been modified to address known vulnerabilities
and unsafe defaults. As such, the `defusedxml`
library is no longer necessary, `defusedxml` has deprecated its `lxml`
module.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10030.
## Summary
This is a not-unpopular directory name, and it's led to tons of issues
and user confusion (most recently:
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-pre-commit/issues/69). I've wanted to
remove it for a long time, but we need to do so as part of a minor
release.
## Summary
Currently, rule `RUF015` is not able to detect the usage of
`list(iterable).pop(0)` falling under the category of an _unnecessary
iterable allocation for accessing the first element_. This PR wants to
change that. See the underlying issue for more details.
* Provide extension to detect `list(iterable).pop(0)`, but not
`list(iterable).pop(i)` where i > 1
* Update corresponding doc
## Test Plan
* `RUF015.py` and the corresponding snap file were extended such that
their correspond to the new behaviour
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9190
---
PS: I've only been working on this ticket as I haven't seen any activity
from issue assignee @rmad17, neither in this repo nor in a fork. I hope
I interpreted his inactivity correctly. Didn't mean to steal his chance.
Since I stumbled across the underlying problem myself, I wanted to offer
a solution as soon as possible.
## Summary
It is a convention to use the `_()` alias for `gettext()`. We want to
avoid
statement expressions and assignments related to aliases of the gettext
API.
See https://docs.python.org/3/library/gettext.html for details. When one
uses `_() to mark a string for translation, the tools look for these
markers
and replace the original string with its translated counterpart. If the
string contains variable placeholders or formatting, it can complicate
the
translation process, lead to errors or incorrect translations.
## Test Plan
* Test file `RUF027_1.py` was extended such that the test reproduces the
false-positive
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10023.
---------
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
The original implementation of this applied the runtime-required context
to definitions _within_ the function, but not the signature itself. (We
had test coverage; the snapshot was just correctly showing the wrong
outcome.)
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10089.
## Summary
Update PLR1714 to ignore `sys.platform` and `sys.version` checks.
I'm not sure if these checks or if we need to add more. Please advise.
Fixes#10017
## Test Plan
Added a new test case and ran `cargo nextest run`
## Summary
Allows, e.g.:
```python
import os
os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"] = "1"
os.putenv("CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES", "4")
import torch
```
For now, this is only allowed in preview.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/10059
## Summary
Closes#10031
- Detect commented out `case` statements. Playground repro:
https://play.ruff.rs/5a305aa9-6e5c-4fa4-999a-8fc427ab9a23
- Add more support for one-line commented out code.
## Test Plan
Unit tested and tested with
```sh
cargo run -p ruff -- check crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/eradicate/ERA001.py --no-cache --preview --select ERA001
```
TODO:
- [x] `cargo insta test`
## Summary
Part of #7595
This PR moves the `RUF001` and `RUF002` rules to the AST checker. This
removes the use of docstring detection from these rules.
## Test Plan
As this is just a refactor, make sure existing test cases pass.
## Summary
Fixes#9895
The cause for this panic came from an offset error in the code. When
analyzing a hypothetical f-string, we attempt to re-parse it as an
f-string, and use the AST data to determine, among other things, whether
the format specifiers are correct. To determine the 'correctness' of a
format specifier, we actually have to re-parse the format specifier, and
this is where the issue lies. To get the source text for the specifier,
we were taking a slice from the original file source text... even though
the AST data for the specifier belongs to the standalone parsed f-string
expression, meaning that the ranges are going to be way off. In a file
with Unicode, this can cause panics if the slice is inside a char
boundary.
To fix this, we now slice from the temporary source we created earlier
to parse the literal as an f-string.
## Test Plan
The RUF027 snapshot test was amended to include a string with format
specifiers which we _should_ be calling out. This is to ensure we do
slice format specifiers from the source text correctly.
## Summary
_This is preview only feature and is available using the `--preview`
command-line flag._
With the implementation of [PEP 701] in Python 3.12, f-strings can now
be broken into multiple lines, can contain comments, and can re-use the
same quote character. Currently, no other Python formatter formats the
f-strings so there's some discussion which needs to happen in defining
the style used for f-string formatting. Relevant discussion:
https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/discussions/9785
The goal for this PR is to add minimal support for f-string formatting.
This would be to format expression within the replacement field without
introducing any major style changes.
### Newlines
The heuristics for adding newline is similar to that of
[Prettier](https://prettier.io/docs/en/next/rationale.html#template-literals)
where the formatter would only split an expression in the replacement
field across multiple lines if there was already a line break within the
replacement field.
In other words, the formatter would not add any newlines unless they
were already present i.e., they were added by the user. This makes
breaking any expression inside an f-string optional and in control of
the user. For example,
```python
# We wouldn't break this
aaaaaaaaaaa = f"asaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa { aaaaaaaaaaaa + bbbbbbbbbbbb + ccccccccccccccc } cccccccccc"
# But, we would break the following as there's already a newline
aaaaaaaaaaa = f"asaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa {
aaaaaaaaaaaa + bbbbbbbbbbbb + ccccccccccccccc } cccccccccc"
```
If there are comments in any of the replacement field of the f-string,
then it will always be a multi-line f-string in which case the formatter
would prefer to break expressions i.e., introduce newlines. For example,
```python
x = f"{ # comment
a }"
```
### Quotes
The logic for formatting quotes remains unchanged. The existing logic is
used to determine the necessary quote char and is used accordingly.
Now, if the expression inside an f-string is itself a string like, then
we need to make sure to preserve the existing quote and not change it to
the preferred quote unless it's 3.12. For example,
```python
f"outer {'inner'} outer"
# For pre 3.12, preserve the single quote
f"outer {'inner'} outer"
# While for 3.12 and later, the quotes can be changed
f"outer {"inner"} outer"
```
But, for triple-quoted strings, we can re-use the same quote char unless
the inner string is itself a triple-quoted string.
```python
f"""outer {"inner"} outer""" # valid
f"""outer {'''inner'''} outer""" # preserve the single quote char for the inner string
```
### Debug expressions
If debug expressions are present in the replacement field of a f-string,
then the whitespace needs to be preserved as they will be rendered as it
is (for example, `f"{ x = }"`. If there are any nested f-strings, then
the whitespace in them needs to be preserved as well which means that
we'll stop formatting the f-string as soon as we encounter a debug
expression.
```python
f"outer { x = !s :.3f}"
# ^^
# We can remove these whitespaces
```
Now, the whitespace doesn't need to be preserved around conversion spec
and format specifiers, so we'll format them as usual but we won't be
formatting any nested f-string within the format specifier.
### Miscellaneous
- The
[`hug_parens_with_braces_and_square_brackets`](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/8279)
preview style isn't implemented w.r.t. the f-string curly braces.
- The
[indentation](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/discussions/9785#discussioncomment-8470590)
is always relative to the f-string containing statement
## Test Plan
* Add new test cases
* Review existing snapshot changes
* Review the ecosystem changes
[PEP 701]: https://peps.python.org/pep-0701/
## Summary
Ignore `async for` loops when checking the SIM113 rule.
Closes#9995
## Test Plan
A new test case was added to SIM113.py with an async for loop.
## Summary
This PR is a small refactor to extract out the logic for normalizing
string in the formatter from the `StringPart` struct. It also separates
the quote selection into a separate method on the new
`StringNormalizer`. Both of these will help in the f-string formatting
to use `StringPart` and `choose_quotes` irrespective of normalization.
The reason for having separate quote selection and normalization step is
so that the f-string formatting can perform quote selection on its own.
Unlike string and byte literals, the f-string formatting would require
that the normalization happens only for the literal elements of it i.e.,
the "foo" and "bar" in `f"foo {x + y} bar"`. This will automatically be
handled by the already separate `normalize_string` function.
Another use-case in the f-string formatting is to extract out the
relevant information from the `StringPart` like quotes and prefix which
is to be passed as context while formatting each element of an f-string.
## Test Plan
Ensure that clippy is happy and all tests pass.
## Summary
This PR introduces a new semantic model flag `DOCSTRING` which suggests
that the model is currently in a module / class / function docstring.
This is the first step in eliminating the docstring detection state
machine which is prone to bugs as stated in #7595.
## Test Plan
~TODO: Is there a way to add a test case for this?~
I tested this using the following code snippet and adding a print
statement in the `string_like` analyzer to print if we're currently in a
docstring or not.
<details><summary>Test code snippet:</summary>
<p>
```python
"Docstring" ", still a docstring"
"Not a docstring"
def foo():
"Docstring"
"Not a docstring"
if foo:
"Not a docstring"
pass
class Foo:
"Docstring"
"Not a docstring"
foo: int
"Unofficial variable docstring"
def method():
"Docstring"
"Not a docstring"
pass
def bar():
"Not a docstring".strip()
def baz():
_something_else = 1
"""Not a docstring"""
```
</p>
</details>
## Summary
Implement [implicit readlines
(FURB129)](https://github.com/dosisod/refurb/blob/master/refurb/checks/iterable/implicit_readlines.py)
lint.
## Notes
I need a help/an opinion about suggested implementations.
This implementation differs from the original one from `refurb` in the
following way. This implementation checks syntactically the call of the
method with the name `readlines()` inside `for` {loop|generator
expression}. The implementation from refurb also
[checks](https://github.com/dosisod/refurb/blob/master/refurb/checks/iterable/implicit_readlines.py#L43)
that callee is a variable with a type `io.TextIOWrapper` or
`io.BufferedReader`.
- I do not see a simple way to implement the same logic.
- The best I can have is something like
```rust
checker.semantic().binding(checker.semantic().resolve_name(attr_expr.value.as_name_expr()?)?).statement(checker.semantic())
```
and analyze cases. But this will be not about types, but about guessing
the type by assignment (or with) expression.
- Also this logic has several false negatives, when the callee is not a
variable, but the result of function call (e.g. `open(...)`).
- On the other side, maybe it is good to lint this on other things,
where this suggestion is not safe, and push the developers to change
their interfaces to be less surprising, comparing with the standard
library.
- Anyway while the current implementation has false-positives (I
mentioned some of them in the test) I marked the fixes to be unsafe.
## Summary
Accept 0.0 and 1.0 as common magic values. This is in line with the
pylint behaviour, and I think makes sense conceptually.
## Test Plan
Test cases were added to
`crates/ruff_linter/resources/test/fixtures/pylint/magic_value_comparison.py`
## Summary
I was surprised to learn that we treat `x` in `[_ for x in y]` as an
"assignment" binding kind, rather than a dedicated comprehension
variable.
The docs previously mentioned an irrelevant config option, but were
missing a link to the relevant `ignore-init-module-imports` config
option which _is_ actually used.
Additionally, this commit adds a link to the documentation to explain
the conventions around a module interface which includes using a
redundant import alias to preserve an unused import.
(noticed this while filing #9962)
## Summary
This PR renames the semantic model flag `MODULE_DOCSTRING` to
`MODULE_DOCSTRING_BOUNDARY`. The main reason is for readability and for
the new semantic model flag `DOCSTRING` which tracks that the model is
in a module / class / function docstring.
I got confused earlier with the name until I looked at the use case and
it seems that the `_BOUNDARY` prefix is more appropriate for the
use-case and is consistent with other flags.
## Summary
This PR fixes the `DebugText` implementation to use the expression range
instead of the parenthesized range.
Taking the following code snippet as an example:
```python
x = 1
print(f"{ ( x ) = }")
```
The output of running it would be:
```
( x ) = 1
```
Notice that the whitespace between the parentheses and the expression is
preserved as is.
Currently, we don't preserve this information in the AST which defeats
the purpose of `DebugText` as the main purpose of the struct is to
preserve whitespaces _around_ the expression.
This is also problematic when generating the code from the AST node as
then the generator has no information about the parentheses the
whitespaces between them and the expression which would lead to the
removal of the parentheses in the generated code.
I noticed this while working on the f-string formatting where the debug
text would be used to preserve the text surrounding the expression in
the presence of debug expression. The parentheses were being dropped
then which made me realize that the problem is instead in the parser.
## Test Plan
1. Add a test case for the parser
2. Add a test case for the generator
## Summary
This PR ensures that if a list `x` is modified within a `for` loop, we
avoid flagging `list(x)` as unnecessary. Previously, we only detected
calls to exactly `.append`, and they couldn't be nested within other
statements.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9925.
## Summary
If these are defined within class scopes, they're actually attributes of
the class, and can be accessed through the class itself.
(We preserve our existing behavior for `.pyi` files.)
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9948.
Fixes#8368
Fixes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9186
## Summary
Arbitrary TOML strings can be provided via the command-line to override
configuration options in `pyproject.toml` or `ruff.toml`. As an example:
to run over typeshed and respect typeshed's `pyproject.toml`, but
override a specific isort setting and enable an additional pep8-naming
setting:
```
cargo run -- check ../typeshed --no-cache --config ../typeshed/pyproject.toml --config "lint.isort.combine-as-imports=false" --config "lint.extend-select=['N801']"
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Micha Reiser <micha@reiser.io>
Co-authored-by: Zanie Blue <contact@zanie.dev>
## Summary
Currently these rules apply the heuristic that if the original sequence
doesn't have a newline in between the final sequence item and the
closing parenthesis, the autofix won't add one for you. The feedback
from @ThiefMaster, however, was that this was producing slightly unusual
formatting -- things like this:
```py
__all__ = [
"b", "c",
"a", "d"]
```
were being autofixed to this:
```py
__all__ = [
"a",
"b",
"c",
"d"]
```
When, if it was _going_ to be exploded anyway, they'd prefer something
like this (with the closing parenthesis on its own line, and a trailing comma added):
```py
__all__ = [
"a",
"b",
"c",
"d",
]
```
I'm still pretty skeptical that we'll be able to please everybody here
with the formatting choices we make; _but_, on the other hand, this
_specific_ change is pretty easy to make.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`. I also ran the autofixes for RUF022 and RUF023 on CPython
to check how they looked; they looked fine to me.
## Summary
If a generic appears multiple times on the right-hand side, we should
only include it once on the left-hand side when rewriting.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9904.
## Summary
This review contains a fix for
[D405](https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/capitalize-section-name/)
(capitalize-section-name)
The problem is that Ruff considers the sub-section header as a normal
section if it has the same name as some section name. For instance, a
function/method has an argument named "parameters". This only applies if
you use Numpy style docstring.
See: [ISSUE](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9806)
The following will not raise D405 after the fix:
```python
def some_function(parameters: list[str]):
"""A function with a parameters parameter
Parameters
----------
parameters:
A list of string parameters
"""
...
```
## Test Plan
```bash
cargo test
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Mikko Leppänen <mikko.leppanen@vaisala.com>
Co-authored-by: Charlie Marsh <charlie.r.marsh@gmail.com>
## Summary
This PR reduces the size of `Expr` from 80 to 64 bytes, by reducing the
sizes of...
- `ExprCall` from 72 to 56 bytes, by using boxed slices for `Arguments`.
- `ExprCompare` from 64 to 48 bytes, by using boxed slices for its
various vectors.
In testing, the parser gets a bit faster, and the linter benchmarks
improve quite a bit.
## Summary
Corrects mentions of `Path.is_link` to `Path.is_symlink` (the former
doesn't exist).
## Test Plan
```sh
python scripts/generate_mkdocs.py && mkdocs serve -f mkdocs.public.yml
```
Fixes#9857.
## Summary
Statements like `logging.info("Today it is: {day}")` will no longer be
ignored by RUF027. As before, statements like `"Today it is:
{day}".format(day="Tuesday")` will continue to be ignored.
## Test Plan
The snapshot tests were expanded to include new cases. Additionally, the
snapshot tests have been split in two to separate positive cases from
negative cases.
## Summary
Django's `mark_safe` can also be used as a decorator, so we should
detect usages of `@mark_safe` for the purpose of the relevant Bandit
rule.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9780.
## Summary
Given:
```python
"""Make a summary line.
Note:
----
Per the code comment the next two lines are blank. "// The first blank line is the line containing the closing
triple quotes, so we need at least two."
"""
```
It turns out we excluded the line ending in `"""`, because it's empty
(unlike for functions, where it consists of the indent). This PR changes
the `following_lines` iterator to always include the trailing newline,
which gives us correct and consistent handling between function and
module-level docstrings.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9877.
#2977 added the `allow-dict-calls-with-keyword-arguments` configuration
option for the `unnecessary-collection-call (C408)` rule, but it did not
update the rule description.
## Summary
This PR adds the `AnyNode` and `AnyNodeRef` implementation for
`FStringFormatSpec` node which will be required in the f-string
formatting.
The main usage for this is so that we can pass in the node directly to
`suppressed_node` in case debug expression is used to format is as
verbatim text.
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
`max-positional-args` defaults to `max-args` if it's not specified and
the default to `max-args` is 5, so saying that the default is 3 is
definitely wrong. Ideally, we wouldn't specify a default at all for this
config option, but I don't think that's possible?
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
## Test Plan
<!-- How was it tested? -->
Not sure.
## Summary
When we fall through to parsing, the comment-detection rule is a
significant portion of lint time. This PR adds an additional fast
heuristic whereby we abort if a comment contains two consecutive name
tokens (via the zero-allocation lexer). For the `ctypeslib.py`, which
has a few cases that are now caught by this, it's a 2.5x speedup for the
rule (and a 20% speedup for token-based rules).
These are for descriptors which affects the behavior of the object _as a
property_; I do not think they should be called directly but there is no
alternative when working with the object directly.
Closes https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9789
## Summary
These run over nearly every identifier. It's rare to override them, so
when not provided, we can just use a match against the hardcoded default
set.
It turns out that for ASCII identifiers, this is nearly 2x faster:
```
Parser/before time: [15.388 ns 15.395 ns 15.406 ns]
Parser/after time: [8.3786 ns 8.5821 ns 8.7715 ns]
```
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
Fixes#8151
This PR implements a new rule, `RUF027`.
## What it does
Checks for strings that contain f-string syntax but are not f-strings.
### Why is this bad?
An f-string missing an `f` at the beginning won't format anything, and
instead treat the interpolation syntax as literal.
### Example
```python
name = "Sarah"
dayofweek = "Tuesday"
msg = "Hello {name}! It is {dayofweek} today!"
```
It should instead be:
```python
name = "Sarah"
dayofweek = "Tuesday"
msg = f"Hello {name}! It is {dayofweek} today!"
```
## Heuristics
Since there are many possible string literals which contain syntax
similar to f-strings yet are not intended to be,
this lint will disqualify any literal that satisfies any of the
following conditions:
1. The string literal is a standalone expression. For example, a
docstring.
2. The literal is part of a function call with keyword arguments that
match at least one variable (for example: `format("Message: {value}",
value = "Hello World")`)
3. The literal (or a parent expression of the literal) has a direct
method call on it (for example: `"{value}".format(...)`)
4. The string has no `{...}` expression sections, or uses invalid
f-string syntax.
5. The string references variables that are not in scope, or it doesn't
capture variables at all.
6. Any format specifiers in the potential f-string are invalid.
## Test Plan
I created a new test file, `RUF027.py`, which is both an example of what
the lint should catch and a way to test edge cases that may trigger
false positives.
## Summary
It turns out we saw a panic in cases when dedenting blocks like the `def
wrapper` here:
```python
def instrument_url(f: UrlFuncT) -> UrlFuncT:
# TODO: Type this with ParamSpec to preserve the function signature.
if not INSTRUMENTING: # nocoverage -- option is always enabled; should we remove?
return f
else:
def wrapper(
self: "ZulipTestCase", url: str, info: object = {}, **kwargs: Union[bool, str]
) -> HttpResponseBase:
```
Since we relied on the first line to determine the indentation, instead
of the first non-empty line.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
## Summary
This is a simple idea to avoid unnecessary work in the linter,
especially for rules that run on all name and/or all attribute nodes.
Imagine a rule like the NumPy deprecation check. If the user never
imported `numpy`, we should be able to skip that rule entirely --
whereas today, we do a `resolve_call_path` check on _every_ name in the
file. It turns out that there's basically a finite set of modules that
we care about, so we now track imports on those modules as explicit
flags on the semantic model. In rules that can _only_ ever trigger if
those modules were imported, we add a dedicated and extremely cheap
check to the top of the rule.
We could consider generalizing this to all modules, but I would expect
that not to be much faster than `resolve_call_path`, which is just a
hash map lookup on `TextSize` anyway.
It would also be nice to make this declarative, such that rules could
declare the modules they care about, the analyzers could call the rules
as appropriate. But, I don't think such a design should block merging
this.
## Summary
Often, when fixing, we need to dedent a block of code (e.g., if we
remove an `if` and dedent its body). Today, we use LibCST to parse and
adjust the indentation, which is really expensive -- but this is only
really necessary if the block contains a multiline string, since naively
adjusting the indentation for such a string can change the whitespace
_within_ the string.
This PR uses a simple dedent implementation for cases in which the block
doesn't intersect with a multi-line string (or an f-string, since we
don't support tracking multi-line strings for f-strings right now).
We could improve this even further by using the ranges to guide the
dedent function, such that we don't apply the dedent if the line starts
within a multiline string. But that would also need to take f-strings
into account, which is a little tricky.
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
<!--
Thank you for contributing to Ruff! To help us out with reviewing,
please consider the following:
- Does this pull request include a summary of the change? (See below.)
- Does this pull request include a descriptive title?
- Does this pull request include references to any relevant issues?
-->
## Summary
When I was looking at the v0.2.0 release, this method showed up in a
CodSpeed regression (we were calling it more), so I decided to quickly
look at speeding it up. @BurntSushi suggested using Aho-Corasick, and it
looks like it's about 7 or 8x faster:
```text
Parser/AhoCorasick time: [8.5646 ns 8.5914 ns 8.6191 ns]
Parser/Iterator time: [64.992 ns 65.124 ns 65.271 ns]
```
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
I noticed that the comment doesn't match the behavior:
- zip function is not used anymore
- parameters are not scanned in reverse
## Summary
<!-- What's the purpose of the change? What does it do, and why? -->
## Test Plan
No need
Signed-off-by: Mikael Arguedas <mikael.arguedas@gmail.com>
## Summary
Adds an additional warning macro (we should consolidate these later)
that shows a warning once based on the content of the warning itself.
This is less efficient than `warn_user_once!` and `warn_user_by_id!`,
but this is so expensive that it doesn't matter at all.
Applies this macro to the various warnings for the v0.2.0 release, and
also includes the filename in said warnings, so the FastAPI case is now:
```text
warning: The top-level linter settings are deprecated in favour of their counterparts in the `lint` section. Please update the following options in /Users/crmarsh/workspace/fastapi/pyproject.toml:
- 'ignore' -> 'lint.ignore'
- 'select' -> 'lint.select'
- 'isort' -> 'lint.isort'
- 'pyupgrade' -> 'lint.pyupgrade'
- 'per-file-ignores' -> 'lint.per-file-ignores'
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Zanie <contact@zanie.dev>
## Summary
This was causing build failures for #9599. We were referencing the
command line overrides instead of the merged configuration data, hence
the issue.
## Test Plan
A snapshot test was added.
Follow-up to #9754 and #9689. Alternative to #9714.
Marks `TRY200` as removed and redirects to `B904` instead of marking as
deprecated and suggesting `B904` instead.
Extends https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/9752 adding internal test
rules for redirection
Fixes a bug where we did not see warnings for exact codes that are
redirected (just prefixes)
Cherry-picked from https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/pull/9714 which is
being abandoned for now because we need to invest more into our
redirection infrastructure before it is feasible.
Fixes a bug in the implementation where we improperly included
deprecated rules in `RuleSelector.rules()` when preview is on. Includes
some clean-up of error messages and the implementation.
# Conflicts:
# crates/ruff/tests/integration_test.rs
## Summary
This rule was added to `flake8-type-checking` as `TC010`. We're about to
stabilize it, so we might as well use the correct code.
See: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff/issues/9573.
## Summary
This PR stabilizes the preview rules from:
- `flake8-trio` (6 rules)
- `flake8-quotes` (1 rule)
- `pyupgrade` (1 rule)
- `flake8-pyi` (1 rule)
- `flake8-simplify` (2 rules)
- `flake8-bandit` (9 rules; 14 remain in preview)
- `flake8-type-checking` (1 rule)
- `numpy` (1 rule)
- `ruff` (4 rules, one elevated from nursery; 6 remain in preview as
they were added within the last 30 days)
- `flake8-logging` (4 rules)
I see these are largely uncontroversial.
Adds a new `Deprecated` rule group in addition to `Stable` and
`Preview`.
Deprecated rules:
- Warn on explicit selection without preview
- Error on explicit selection with preview
- Are excluded when selected by prefix with preview
Deprecates `TRY200`, `ANN101`, and `ANN102` as a proof of concept. We
can consider deprecating them separately.
Extends #9682 to error if the nursery selector is used or nursery rules
are selected without preview.
Part of #7992 — we will remove this in 0.3.0 instead so we can provide
nice errors in 0.2.0.
# Conflicts:
# crates/ruff/tests/integration_test.rs
# crates/ruff_workspace/src/configuration.rs
Fixes#7350
## Summary
* `--show-source` and `--no-show-source` are now deprecated.
* `output-format` supports two new variants, `full` and `concise`.
`text` is now a deprecated variant, and any use of it is treated as the
default serialization format.
* `--output-format` now default to `concise`
* In preview mode, `--output-format` defaults to `full`
* `--show-source` will still set `--output-format` to `full` if the
output format is not otherwise specified.
* likewise, `--no-show-source` can override an output format that was
set in a file-based configuration, though it will also be overridden by
`--output-format`
## Test Plan
A lot of tests were updated to use `--output-format=full`. Additional
tests were added to ensure the correct deprecation warnings appeared,
and that deprecated options behaved as intended.
# Conflicts:
# crates/ruff/tests/integration_test.rs
## Summary
Un-gates the behavior to allow `sys.path` modifications between imports,
which removed a bunch of false positives in the ecosystem CI at the
time.
## Summary
At present, our versioning policy forbids the addition of safe fixes to
stable rules outside of a minor release, so we've accumulated a bunch of
new fixes that are behind `--preview`, and can be ungated in v0.2.0.
To find these, I just grepped for `preview.is_enabled()` and identified
all such cases. I then audited the `preview_rules` test fixtures and
removed any tests that existed only to test this autofix behavior.
# Conflicts:
# crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/flake8_simplify/snapshots/ruff_linter__rules__flake8_simplify__tests__SIM114_SIM114.py.snap
# crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/flake8_simplify/snapshots/ruff_linter__rules__flake8_simplify__tests__preview__SIM114_SIM114.py.snap
## Summary
This rule was added to flake8-bugbear. In general, we tend to prefer
redirecting to prominent plugins when our own rules are reimplemented
(since more projects have `B` activated than `RUF`).
## Test Plan
`cargo test`
# Conflicts:
# crates/ruff_linter/src/rules/ruff/rules/mod.rs